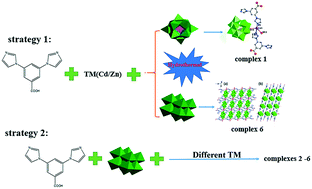
By changing the transition metals (TMs) and polyanions, six polyoxometalate (POM)-based complexes 1–6 were synthesized by the hydrothermal method, namely [CdII(L1)2(HPMo12O40)]·2H2O (1), {MII2(H2O)4(L1)2[H2(β-Mo8O26)]}n·xH2O (n = 1, x = 1, M = Co (2), Cu (3), Fe (4); n = 0.5, x = 0, M = Ni (5), Zn (6)). The organic component 3,5-bis-(2,5-dihydro-imidazole-1-yl)benzoic acid (L1) is a tripodal ligand containing two imidazole and one carboxylic acid group. The N donors in the imidazole groups and the O donors in the carboxylic acid group of L1 can coordinate with different transition metal atoms to construct POM-based complexes. In complex 1, the Keggin anions are linked by [Cd(L1)2]2+ subunits to construct a chain. Complexes 2–6 are isostructural with [β-Mo8O26]4− anions linked by double metal–organic chains to build a 2D layer. The electrochemical behaviour and photocatalytic properties of these complexes were studied. These complexes can be used as amperometric sensors for the amperometric detection of Cr(VI), Fe(III) and H2O2. Moreover, these complexes can be used for fluorescence selective sensing of Cr3+.