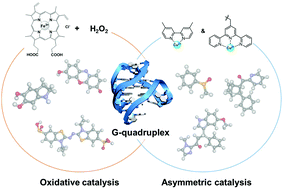
DNA is receiving attention as a useful biomaterial in a broad range of research fields beyond its classical role as a biopolymer for storage and delivery of genetic information. Based on its chemical and thermal stability and easy accessibility, a series of DNA-based hybrid catalysts have been developed and successfully applied to various asymmetric reactions in water. Besides the canonical Watson–Crick duplex, the G-quadruplex structure has been actively exploited as horseradish-peroxidase (HRP)-mimicking DNAzymes via specific complexation with hemin. G-quadruplexes also provide a fascinating scaffold to develop a switchable catalytic system. This review summarizes the beginning, progress, and prospects of the noncanonical DNA-based hybrid catalysts, focusing on the G-quadruplexes as versatile scaffolds for catalysis.