In situ monitoring of mechanochemical MOF formation by NMR relaxation time correlation†
Abstract
In this paper, we present a new approach to monitoring mechanochemical transformations, based on a magnetic resonance (MR) method in which relaxation time correlation maps are used to track the formation of the popular metal–organic framework (MOF) materials Zn-MOF-74 and ZIF-8. The two-dimensional (2D) relaxation correlation measurement employed yields a 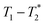 spectrum which visually and analytically identifies different 1H environments in the sample of interest. The measurement is well-suited to analyzing solid mixtures, and liquids, in complex systems. Application in this work to monitoring MOF formation shows changes in signal amplitudes, and their MR lifetime coordinates, within the 2D plots as the reaction progresses, confirming reaction completion. This new measurement provides a simple way to analyse solid-state reactions without dissolution, and there is a logical pathway to benchtop measurement with a new generation of permanent magnet-based MR instruments. The methodology described permits measurement in an MR compatible milling container, which may be directly transferred from the shaker assembly to the MR magnet for in situ measurement of the entire reaction mixture.
spectrum which visually and analytically identifies different 1H environments in the sample of interest. The measurement is well-suited to analyzing solid mixtures, and liquids, in complex systems. Application in this work to monitoring MOF formation shows changes in signal amplitudes, and their MR lifetime coordinates, within the 2D plots as the reaction progresses, confirming reaction completion. This new measurement provides a simple way to analyse solid-state reactions without dissolution, and there is a logical pathway to benchtop measurement with a new generation of permanent magnet-based MR instruments. The methodology described permits measurement in an MR compatible milling container, which may be directly transferred from the shaker assembly to the MR magnet for in situ measurement of the entire reaction mixture.

- This article is part of the themed collection: Fundamental Basis of Mechanochemical Reactivity


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...