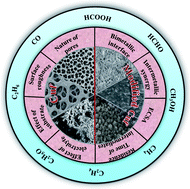
For the attenuation of CO2, a prominent greenhouse gas, nanostructured copper has been proven to be a paragon in electrochemical CO2 reduction (ECR), and is an attractive and green approach to obtain value-added products. In this review, firstly, the fundamentals of ECR, its challenges and advantages are summarised, which may help newcomers in this field to understand the reduction process. Cu has gained much attention in ECR due to its unique advantages for the production of hydrocarbon compared to other pure metallic electrocatalysts. Therefore, focusing on Cu, a comprehensive overview of the recent research specifically related to copper foam (Cuf) and Cuf-based bimetallic nanocatalysts is summarised. Together with challenges, different research directions for the enhancement of the activity and selectivity of Cuf-based electrocatalysts and efficient conversion of CO2 to reusable forms of carbon for practical applications are proposed.