Jian-Ling Ni, Yu Liang, Juan-Juan Shao, Jun-Feng Li, Guang-Jun Li, Li-Zhuang Chen and Fang-Ming Wang
CrystEngComm, 2021,23, 5516-5521
DOI:
10.1039/D1CE00499A,
Paper
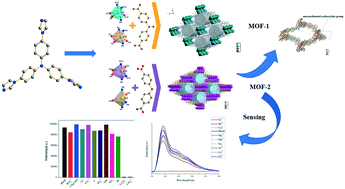
Two new title MOFs, namely [Cd2(TIPA)2(bpodc)2]n (1 or MOF-1), [Cd2(TIPA)2(oba)2]n (2 or MOF-2) (TIPA = tris(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)amine, bpodc = benzophenone-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid, oba = 4,4′-oxydibenzoic acid), have been synthesized via a solvothermal method. MOF-1 and MOF-2 both have a 2-fold interpenetrating 3D framework, and the calculation of PLATON display that porosity are 18.6% and 19.5%, respectively. Attributing to MOF-2's uncoordinated carboxylate groups, it exhibits a high sensitivity in detecting Fe3+ with a very large quenching coefficient Ksv up to 27 027 M−1. Moreover, MOF-2 also has potential applications in chemical sensing of CrO42− and Cr2O72−.