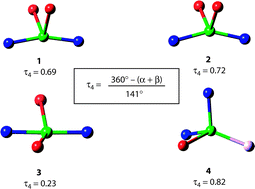
Four Cu(I) complexes were synthesized with a family of pyridylmethylamide ligands, HLR [HLR = N-(2-pyridylmethyl)acetamide, R = null; 2,2-dimethyl-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)propionamide, R = Me3; 2,2,2-triphenyl-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)acetamide, R = Ph3)]. Complexes 1–3 were synthesized from the respective ligand and [Cu(CH3CN)4]PF6 in a 2 : 1 molar ratio: [Cu(HL)2]PF6 (1), [Cu2(HLMe3)4](PF6)2 (2), [Cu(HLPh3)2]PF6 (3). Complex 4, [Cu(HL)(CH3CN)(PPh3)]PF6, was synthesized from the reaction of HL with [Cu(CH3CN)4]PF6 and PPh3 in a 1 : 1 : 1 molar ratio. X-Ray crystal structures reveal that complexes 1, 3 and 4 are mononuclear Cu(I) species, while complex 2 is a Cu(I) dimer. The copper ions are four-coordinate with geometries ranging from distorted tetrahedral to seesaw in 1, 2, and 4. Complexes 1 and 2 are very air sensitive and they display similar electrochemical properties. The coordination geometry of complex 3 is nearly linear, two-coordinate. Complex 3 is exceptionally stable with respect to oxidation in the air, and its cyclic voltammetry shows no oxidation wave in the range of 0–1.5 V. The unusual inertness of complex 3 towards oxidation is attributed to the protection from bulky triphenyl substituent of the HLPh3 ligand. A new geometric parameter for four-coordinate compounds, τ4, is proposed as an improved, simple metric for quantitatively evaluating the geometry of four-coordinate complexes and compounds.