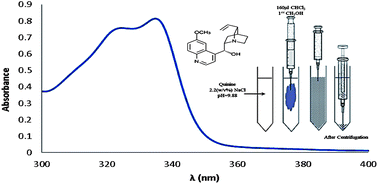
Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) followed by UV-Vis spectrophotometry was applied for extraction/preconcentration and determination of trace levels of quinine (QN). Chloroform and methanol were chosen as the extraction solvent and the disperser solvent, respectively. A central composite design (CCD) was applied to optimize the effective parameters of DLLME including volume of extraction solvent, pH, and salt concentration. The optimal conditions were obtained as 160 μL for the volume of extraction solvent, 9.88 for pH, and 2.2% (w/v) for salt concentration. The linear dynamic range (LDR) was 25–700 μg L−1 with a correlation coefficient of 0.994. The limit of detection (LOD) and relative standard deviation (RSD) were 14.71 μg L−1 and 1.13%, respectively. The method was successfully applied for the determination of QN in real samples and satisfactory relative recoveries (101.51–108.02%) were obtained.