Step-change in high temperature steam electrolysis performance of perovskite oxide cathodes with exsolution of B-site dopants
Abstract
B-site doped, A-site deficient perovskite 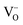 ) and fixed A-site (
) and fixed A-site (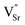 ) and inherent (γ) oxygen vacancies) beyond a certain limit. The presence of electrocatalytically active Fe0 or Ni0
) and inherent (γ) oxygen vacancies) beyond a certain limit. The presence of electrocatalytically active Fe0 or Ni0 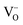 concentrations dramatically lowered the activation barrier to steam electrolysis compared to the parent material (x = 0). The use of defect chemistry to drive the exsolution of less reducible dopant
concentrations dramatically lowered the activation barrier to steam electrolysis compared to the parent material (x = 0). The use of defect chemistry to drive the exsolution of less reducible dopant


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...