Nucleation mechanism and kinetics from the analysis of polythermal crystallisation data: methyl stearate from kerosene solutions†
Abstract
A polythermal methodology to assess the mechanisms and the kinetics of solution crystallisation is described and used in connection with a recently proposed model for the dependence of the critical undercooling for crystallisation on the cooling rate (D. Kashchiev, A. Borissova, R. B. Hammond, K. J. Roberts, J. Cryst. Growth, 312 (2010) 698–704; J. Phys. Chem. B, 114 (2010) 5441–5446). This first principles model allows determination of crystallisation parameters that could otherwise only be obtained by combined application of both the isothermal and the polythermal methods. The methodology is validated through analysis of experimental data measured for methyl stearate crystallising from kerosene solutions with concentrations from 200 to 350 g l−1. The analysis reveals a progressive heterogeneous nucleation mechanism and crystallite interfacial tension values between 1.64 and 1.79 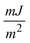 with no obvious dependence on the solution concentration, in good agreement with values derived by isothermal methods. Sensitivity analysis leads to the conclusion that a minimum of four different cooling rates spanning at least one order of magnitude together with at least five repeats for crystallisation temperature values at each cooling rate are appropriate. Extensive supplementary material provides a mathematical description of the above authors' model, insight into the relationship between this model and the empirical Nyvlt model, and further detail concerning the results of the sensitivity analysis carried out on the experimental methodology used.
with no obvious dependence on the solution concentration, in good agreement with values derived by isothermal methods. Sensitivity analysis leads to the conclusion that a minimum of four different cooling rates spanning at least one order of magnitude together with at least five repeats for crystallisation temperature values at each cooling rate are appropriate. Extensive supplementary material provides a mathematical description of the above authors' model, insight into the relationship between this model and the empirical Nyvlt model, and further detail concerning the results of the sensitivity analysis carried out on the experimental methodology used.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...