The optical properties of low infrared transmittance WO3−x nanocrystal thin films prepared by DC magnetron sputtering under different oxygen ratios†
Abstract
Low infrared transmittance WO3−x (0 < x < 1) ratios, as transparent conductors with high transmittance in the visible range and UV blocking. The infrared shielding properties could be adjusted by tuning the oxygen ratio during the sputtering process. The intrinsic defects, such as oxygen vacancy (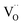 ) and special atom (W5+), determine the main optical properties by localized states originated from the electron caused by interband transition and the surface dipole of the plasmon oscillation of the nanoparticle with optical scattering. The structures, morphology, defects and chemical states were investigated. With respect to oxygen ratio, it has little effect on the structure and morphology, yet the optical shielding performance, defects and chemical states can be controlled linearly by considering the oxygen ratio during the sputtering process. The WO3−x thin films have great potential for application in infrared shielding and energy conservation.
) and special atom (W5+), determine the main optical properties by localized states originated from the electron caused by interband transition and the surface dipole of the plasmon oscillation of the nanoparticle with optical scattering. The structures, morphology, defects and chemical states were investigated. With respect to oxygen ratio, it has little effect on the structure and morphology, yet the optical shielding performance, defects and chemical states can be controlled linearly by considering the oxygen ratio during the sputtering process. The WO3−x thin films have great potential for application in infrared shielding and energy conservation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...