Micelle formation of a non-ionic surfactant in non-aqueous molecular solvents and protic ionic liquids (PILs)†
Abstract
Many ionic liquids and low molecular weight polar solvents have been reported to support amphiphile self-assembly, with most of these reported for the first time in the last decade. This phenomenon is attributed to the solvophobic effect (analogous to the hydrophobic effect in water). However, to date there has been no systematic study which evaluates micelle formation in a large library of non-aqueous solvents. Here we investigate micelle formation of a non-ionic amphiphile, hexa-ethyleneglycol mono n-dodecyl ether, C12E6, in a diverse range of molecular solvents and protic ionic liquids (PILs). Nine of the 19 non-aqueous molecular solvents investigated, and all four of the PILs, were found to support micelle formation. A link was investigated between the solvent cohesive energy density (as estimated using the Gordon parameter) and both the critical micelle concentration and the related free energy of micellization 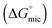 . In addition, the chemical structure and liquid mesostructure of the solvent were found to be important factors in the ability of the solvents to support micelle formation.
. In addition, the chemical structure and liquid mesostructure of the solvent were found to be important factors in the ability of the solvents to support micelle formation.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...