Enhanced molecular adsorption of ethylene on reduced anatase TiO2 (001): role of surface O-vacancies†
Abstract
A density functional theory (DFT)-based study of ethylene (C2H4) adsorption on a reduced anatase titanium dioxide (TiO2) (001) surface, i.e., with a surface oxygen vacancy (Ovac), is presented. It was found that C2H4 preferably adsorbs on the Ovac-site. The excess electrons originating from the removed oxygen weaken the C2H4 C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C double bond by filling the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) or
C double bond by filling the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) or 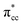 of C2H4, and simultaneously enhance the binding of C2H4 to the reduced anatase TiO2 (001). The bonding between the two C2H4 C atoms and the two Ti atoms nearest to the Ovac-site produces two σ-type bonds, leading to the emergence of a new localized mid-gap state. This hybrid
of C2H4, and simultaneously enhance the binding of C2H4 to the reduced anatase TiO2 (001). The bonding between the two C2H4 C atoms and the two Ti atoms nearest to the Ovac-site produces two σ-type bonds, leading to the emergence of a new localized mid-gap state. This hybrid 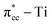 3d defect state can account for the ∼0.7 eV decrease in the band-gap observed in previous optical measurements of carbon-coated TiO2, formed after TiO2 exposure to C2H4 gas (Mater. Lett. 108, 2013, 134). Subsequent calculations on two initial decomposition pathways of C2H4 adsorbed on the Ovac-site show that the C–H bond and C–C bond cleaving require high activation barriers where the C–H bond cleaving is slightly easier compared to the C–C bond cleaving, 2.94 eV and 3.01 eV, respectively, (as calculated using DFT-D2+Ud = 3 eV) and the final states of the two initial decomposition pathways show similar endothermic characteristics. This finding indicates that the surface Ovac-sites tend to favor the formation of molecularly adsorbed Ti-bound sp3-C2H4 (–Ti–CH2CH2–Ti–) as compared to the dissociative adsorption case.
3d defect state can account for the ∼0.7 eV decrease in the band-gap observed in previous optical measurements of carbon-coated TiO2, formed after TiO2 exposure to C2H4 gas (Mater. Lett. 108, 2013, 134). Subsequent calculations on two initial decomposition pathways of C2H4 adsorbed on the Ovac-site show that the C–H bond and C–C bond cleaving require high activation barriers where the C–H bond cleaving is slightly easier compared to the C–C bond cleaving, 2.94 eV and 3.01 eV, respectively, (as calculated using DFT-D2+Ud = 3 eV) and the final states of the two initial decomposition pathways show similar endothermic characteristics. This finding indicates that the surface Ovac-sites tend to favor the formation of molecularly adsorbed Ti-bound sp3-C2H4 (–Ti–CH2CH2–Ti–) as compared to the dissociative adsorption case.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...