Electromechanical properties of Nb doped 0.76Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–0.24SrTiO3 ceramic
Abstract
In this report, the piezoelectric, dielectric and ferroelectric characteristics of 0.76Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3 (BNT)–0.24SrTiO3 (ST) with niobium (Nb) (Nb-added BNT–24ST) ceramics synthesized by using a solid-state reaction are described. The X-ray diffraction analysis and field effect scanning electron microscopy of Nb-added BNT–24ST ceramics reveal the influence of Nb on the perovskite structure and suppression of grain growth within the composition range studied. The electromechanical properties of BNT–24ST ceramics were significantly increased up to 0.5 wt% Nb, and decreased with a further increased Nb content. Around the critical composition (0.5 wt% Nb) with an electric field of 5 kV mm−1, a maximum strain (Smax) of 0.28% 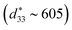 at room temperature was obtained. Saturated polarization reached a maximum value of 27 μC cm−2 at a level of 0.5% Nb. The depolarization temperature moved to lower temperatures with Nb content and the peaks became more diffuse with an increasing content of Nb. Using a study of kinetic dynamics, the activation energy drop with 24ST and Nb-added 24ST is well explained by Vogel–Fulcher (VF) behavior and the Kolmogorov–Avrami–Ishibashi (KAI) model, which suggest that the B site vacancy generation in the perovskite structure has a reduction in energy barrier (Ea) with Nb addition. Increase of the phase transition region also occurred in Nb-added 24ST (>50 °C). This work indicated that this material can be considered as a suitable candidate material for high temperature, stable, lead free actuators.
at room temperature was obtained. Saturated polarization reached a maximum value of 27 μC cm−2 at a level of 0.5% Nb. The depolarization temperature moved to lower temperatures with Nb content and the peaks became more diffuse with an increasing content of Nb. Using a study of kinetic dynamics, the activation energy drop with 24ST and Nb-added 24ST is well explained by Vogel–Fulcher (VF) behavior and the Kolmogorov–Avrami–Ishibashi (KAI) model, which suggest that the B site vacancy generation in the perovskite structure has a reduction in energy barrier (Ea) with Nb addition. Increase of the phase transition region also occurred in Nb-added 24ST (>50 °C). This work indicated that this material can be considered as a suitable candidate material for high temperature, stable, lead free actuators.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...