Co-encapsulation of tamoxifen citrate and quercetin using 2HP-β-cyclodextrin: a response surface experimental design†
Abstract
The aim of this study is to prepare a nanosphere containing the insoluble anti-cancer drug called tamoxifen citrate. The synthesized nanosphere is composed of tamoxifen citrate (TMC), 2-hydroxy propyl-β-cyclodextrin (2HP-β-CD), quercetin (QT) and polycaprolactone (PCL), which was prepared using water in oil in water emulsion solvent extraction method. 2HP-β-CD and QT were applied to enhance the solubility and bioavailability of the drug, respectively. The response surface method was used to optimize the operating variables such as PCL polymer mass, stabilizer percentage, continuous water volume and 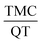 ratio based on the central composite design. Quadratic models were developed for two responses: the drug encapsulation efficiency and the nanosphere size. According to the results, the optimum conditions to achieve a nanosphere of a small size and high drug entrapment efficiency included 30 mg PCL, 2% (w/v) PVA stabilizer, 80 ml water and
ratio based on the central composite design. Quadratic models were developed for two responses: the drug encapsulation efficiency and the nanosphere size. According to the results, the optimum conditions to achieve a nanosphere of a small size and high drug entrapment efficiency included 30 mg PCL, 2% (w/v) PVA stabilizer, 80 ml water and 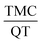 equivalent ratio of 0.5. According to the UV analysis based on the second derivative spectrophotometric technique, the estimated encapsulation efficiency of TMC was 53% ± 2. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that the mean particle size of the synthesized nanospheres was 205 nm, which is appropriate for oral usage. In addition, the in vitro release of TMC and QT in the simulated body environment (SGF and SIF) was performed at 37 °C. The in vitro release of TMC at pH = 7.4 showed that TMC and QT had a slow and simultaneous release behaviour. This confirms the controllable release of TMC in the new synthesized nanoparticle form.
equivalent ratio of 0.5. According to the UV analysis based on the second derivative spectrophotometric technique, the estimated encapsulation efficiency of TMC was 53% ± 2. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that the mean particle size of the synthesized nanospheres was 205 nm, which is appropriate for oral usage. In addition, the in vitro release of TMC and QT in the simulated body environment (SGF and SIF) was performed at 37 °C. The in vitro release of TMC at pH = 7.4 showed that TMC and QT had a slow and simultaneous release behaviour. This confirms the controllable release of TMC in the new synthesized nanoparticle form.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...