Isotopic and quantum-rovibrational-state effects for the ion–molecule reaction
 in the collision energy range of 0.03–10.00 eV
in the collision energy range of 0.03–10.00 eV
Abstract
We report detailed quantum-rovibrational-state-selected integral cross sections for the formation of H3O+via H-transfer (σHT) and H2DO+via D-transfer (σDT) from the 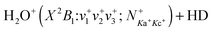 reaction in the center-of-mass collision energy (Ecm) range of 0.03–10.00 eV, where (v+1v+2v+3) = (000), (100), and (020) and
reaction in the center-of-mass collision energy (Ecm) range of 0.03–10.00 eV, where (v+1v+2v+3) = (000), (100), and (020) and 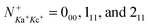 . The Ecm inhibition and rotational enhancement observed for these reactions at Ecm < 0.5 eV are generally consistent with those reported previously for H2O+ + H2(D2) reactions. However, in contrast to the vibrational inhibition observed for the latter reactions at low Ecm < 0.5 eV, both the σHT and σDT for the H2O+ + HD reaction are found to be enhanced by (100) vibrational excitation, which is not predicted by the current state-of-the-art theoretical dynamics calculations. Furthermore, the (100) vibrational enhancement for the H2O+ + HD reaction is observed in the full Ecm range of 0.03–10.00 eV. The fact that vibrational enhancement is only observed for the reaction of H2O+ + HD, and not for H2O+ + H2(D2) reactions suggests that the asymmetry of HD may play a role in the reaction dynamics. In addition to the strong isotopic effect favoring the σHT channel of the H2O+ + HD reaction at low Ecm < 0.5 eV, competition between the σHT and σDT of the H2O+ + HD reaction is also observed at Ecm = 0.3–10.0 eV. The present state-selected study of the H2O+ + HD reaction, along with the previous studies of the H2O+ + H2(D2) reactions, clearly shows that the chemical reactivity of H2O+ toward H2 (HD, D2) depends not only on Ecm, but also on the rotational and vibrational states of H2O+(X2B1). The detailed σHT and σDT values obtained here with single rovibrational-state selections of the reactant H2O+ are expected to be valuable benchmarks for state-of-the-art theoretical calculations on the chemical dynamics of the title reaction.
. The Ecm inhibition and rotational enhancement observed for these reactions at Ecm < 0.5 eV are generally consistent with those reported previously for H2O+ + H2(D2) reactions. However, in contrast to the vibrational inhibition observed for the latter reactions at low Ecm < 0.5 eV, both the σHT and σDT for the H2O+ + HD reaction are found to be enhanced by (100) vibrational excitation, which is not predicted by the current state-of-the-art theoretical dynamics calculations. Furthermore, the (100) vibrational enhancement for the H2O+ + HD reaction is observed in the full Ecm range of 0.03–10.00 eV. The fact that vibrational enhancement is only observed for the reaction of H2O+ + HD, and not for H2O+ + H2(D2) reactions suggests that the asymmetry of HD may play a role in the reaction dynamics. In addition to the strong isotopic effect favoring the σHT channel of the H2O+ + HD reaction at low Ecm < 0.5 eV, competition between the σHT and σDT of the H2O+ + HD reaction is also observed at Ecm = 0.3–10.0 eV. The present state-selected study of the H2O+ + HD reaction, along with the previous studies of the H2O+ + H2(D2) reactions, clearly shows that the chemical reactivity of H2O+ toward H2 (HD, D2) depends not only on Ecm, but also on the rotational and vibrational states of H2O+(X2B1). The detailed σHT and σDT values obtained here with single rovibrational-state selections of the reactant H2O+ are expected to be valuable benchmarks for state-of-the-art theoretical calculations on the chemical dynamics of the title reaction.

- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 PCCP HOT Articles



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
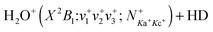 in the collision energy range of 0.03–10.00 eV
in the collision energy range of 0.03–10.00 eV