A quantum-rovibrational-state-selected study of the
 reaction in the collision energy range of 0.05–10.00 eV: translational, rotational, and vibrational energy effects
reaction in the collision energy range of 0.05–10.00 eV: translational, rotational, and vibrational energy effects
Abstract
We report detailed absolute integral cross sections (σ's) for the quantum-rovibrational-state-selected ion–molecule reaction 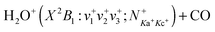 in the center-of-mass collision energy (Ecm) range of 0.05–10.00 eV, where (v+1v+2v+3) = (000), (100), and (020), and
in the center-of-mass collision energy (Ecm) range of 0.05–10.00 eV, where (v+1v+2v+3) = (000), (100), and (020), and 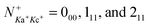 . Three product channels, HCO+ + OH, HOCO+ + H, and CO+ + H2O, are identified. The measured σ(HCO+) curve [σ(HCO+) versus Ecm plot] supports the hypothesis that the formation of the HCO+ + OH channel follows an exothermic pathway with no potential energy barriers. Although the HOCO+ + H channel is the most exothermic, the σ(HOCO+) is found to be significantly lower than the σ(HCO+). The σ(HOCO+) curve is bimodal, indicating two distinct mechanisms for the formation of HOCO+. The σ(HOCO+) is strongly inhibited at Ecm < 0.4 eV, but is enhanced at Ecm > 0.4 eV by (100) vibrational excitation. The Ecm onsets of σ(CO+) determined for the (000) and (100) vibrational states are in excellent agreement with the known thermochemical thresholds. This observation, along with the comparison of the σ(CO+) curves for the (100) and (000) states, shows that kinetic and vibrational energies are equally effective in promoting the CO+ channel. We have also performed high-level ab initio quantum calculations on the potential energy surface, intermediates, and transition state structures for the titled reaction. The calculations reveal potential barriers of ≈0.5–0.6 eV for the formation of HOCO+, and thus account for the low σ(HOCO+) and its bimodal profile observed. The Ecm enhancement for σ(HOCO+) at Ecm ≈ 0.5–5.0 eV can be attributed to the direct collision mechanism, whereas the formation of HOCO+ at low Ecm < 0.4 eV may involve a complex mechanism, which is mediated by the formation of a loosely sticking complex between HCO+ and OH. The direct collision and complex mechanisms proposed also allow the rationalization of the vibrational inhibition at low Ecm and the vibrational enhancement at high Ecm observed for the σ(HOCO+).
. Three product channels, HCO+ + OH, HOCO+ + H, and CO+ + H2O, are identified. The measured σ(HCO+) curve [σ(HCO+) versus Ecm plot] supports the hypothesis that the formation of the HCO+ + OH channel follows an exothermic pathway with no potential energy barriers. Although the HOCO+ + H channel is the most exothermic, the σ(HOCO+) is found to be significantly lower than the σ(HCO+). The σ(HOCO+) curve is bimodal, indicating two distinct mechanisms for the formation of HOCO+. The σ(HOCO+) is strongly inhibited at Ecm < 0.4 eV, but is enhanced at Ecm > 0.4 eV by (100) vibrational excitation. The Ecm onsets of σ(CO+) determined for the (000) and (100) vibrational states are in excellent agreement with the known thermochemical thresholds. This observation, along with the comparison of the σ(CO+) curves for the (100) and (000) states, shows that kinetic and vibrational energies are equally effective in promoting the CO+ channel. We have also performed high-level ab initio quantum calculations on the potential energy surface, intermediates, and transition state structures for the titled reaction. The calculations reveal potential barriers of ≈0.5–0.6 eV for the formation of HOCO+, and thus account for the low σ(HOCO+) and its bimodal profile observed. The Ecm enhancement for σ(HOCO+) at Ecm ≈ 0.5–5.0 eV can be attributed to the direct collision mechanism, whereas the formation of HOCO+ at low Ecm < 0.4 eV may involve a complex mechanism, which is mediated by the formation of a loosely sticking complex between HCO+ and OH. The direct collision and complex mechanisms proposed also allow the rationalization of the vibrational inhibition at low Ecm and the vibrational enhancement at high Ecm observed for the σ(HOCO+).

- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 PCCP HOT Articles



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
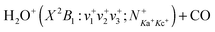 reaction in the collision energy range of 0.05–10.00 eV: translational, rotational, and vibrational energy effects
reaction in the collision energy range of 0.05–10.00 eV: translational, rotational, and vibrational energy effects