Multilayered intercalation of 1-octanol into Brodie graphite oxide†
Abstract
Multilayered intercalation of 1-octanol into the structure of Brodie graphite oxide (B-GO) was studied as a function of temperature and pressure. Reversible phase transition with the addition/removal of one layer of 1-octanol was found at 265 K by means of X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC). The same transition was observed at ambient temperature upon a pressure increase above 0.6 GPa. This transition was interpreted as an incongruent melting of the low temperature/high pressure B-GO intercalated structure with five layers of 1-octanol parallel to GO sheets (L-solvate), resulting in the formation of a four-layered structure that is stable under ambient conditions (A-solvate). Vacuum heating allows the removal of 1-octanol from the A-solvate layer by layer, while distinct sets of (00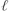 ) reflections are observed for three-, two-, and one-layered solvate phases. Step by step removal of the 1-octanol layers results in changes of distance between graphene oxide planes by ∼4.5 Å. This experiment proved that both L- and A-solvates are structures with layers of 1-octanol parallel to GO planes. Unusual intercalation with up to five distinct layers of 1-octanol is remarkably different from the behaviour of small alcohol molecules (methanol and ethanol), which intercalate B-GO structure with only one layer under ambient conditions and a maximum of two layers at lower temperatures or higher pressures. The data presented in this study make it possible to rule out a change in the orientation of alcohol molecules from parallel to perpendicular to the GO planes, as suggested in the 1960s to explain larger expansion of the GO lattice due to swelling with larger alcohols.
) reflections are observed for three-, two-, and one-layered solvate phases. Step by step removal of the 1-octanol layers results in changes of distance between graphene oxide planes by ∼4.5 Å. This experiment proved that both L- and A-solvates are structures with layers of 1-octanol parallel to GO planes. Unusual intercalation with up to five distinct layers of 1-octanol is remarkably different from the behaviour of small alcohol molecules (methanol and ethanol), which intercalate B-GO structure with only one layer under ambient conditions and a maximum of two layers at lower temperatures or higher pressures. The data presented in this study make it possible to rule out a change in the orientation of alcohol molecules from parallel to perpendicular to the GO planes, as suggested in the 1960s to explain larger expansion of the GO lattice due to swelling with larger alcohols.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...