The reactions of α-amino acids and α-amino acid esters with high valent transition metal halides: synthesis of coordination complexes, activation processes and stabilization of α-ammonium acylchloride cations†
Abstract
Titanium tetrachloride smoothly reacted with a selection of α-amino acids (aaH) in CH2Cl2 affording yellow to orange solid coordination compounds, 1a–d, in 70–78% yields. The salts [NHEt3][TiCl4(aa)], 2a–b, were obtained from TiCl4/aaH/NEt3 (aa = L-phenylalanine, N,N-dimethylphenylalanine), in 60–65% yields. The complex 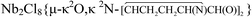 , 3, was isolated from the reaction of L-proline with NbCl5/NHiPr2, performed in CH2Cl2 at room temperature. The X-ray structure of 3 features a bridging (E)-1,2-bis(3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-5-yl)ethene-1,2-diolate ligand, resulting from the unprecedented C–C coupling between two proline units. Unusually stable α-ammonium acyl chlorides were prepared by the reactions of PCl5/MCln (MCln = NbCl5, WCl6) with L-proline, N,N-dimethylphenylalanine, sarcosine and L-methionine. MX5 (M = Nb, Ta; X = F, Cl) reacted with L-leucine methylester and L-proline ethylester to give ionic coordination compounds, [MX4L2][MX6] (M = Nb, L = Me2CHCH2CH(NH2)CO2Me, X = F, 9; Cl, 11a; M = Nb, X = Cl,
, 3, was isolated from the reaction of L-proline with NbCl5/NHiPr2, performed in CH2Cl2 at room temperature. The X-ray structure of 3 features a bridging (E)-1,2-bis(3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-5-yl)ethene-1,2-diolate ligand, resulting from the unprecedented C–C coupling between two proline units. Unusually stable α-ammonium acyl chlorides were prepared by the reactions of PCl5/MCln (MCln = NbCl5, WCl6) with L-proline, N,N-dimethylphenylalanine, sarcosine and L-methionine. MX5 (M = Nb, Ta; X = F, Cl) reacted with L-leucine methylester and L-proline ethylester to give ionic coordination compounds, [MX4L2][MX6] (M = Nb, L = Me2CHCH2CH(NH2)CO2Me, X = F, 9; Cl, 11a; M = Nb, X = Cl, 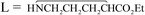 , 11c; Ta, 11d), in moderate to good yields. [NbCl5(Me2CHCH2CHNH3CO2Me)][NbCl6], 12, was isolated as a co-product of the reaction of NbCl5 with L-leucine isopropylester, and crystallographically characterized. The reaction of NbCl5 with L-serine isopropylester afforded NbCl3(OCH2CHNHCO2iPr), 13, in 66% yield. The activation of the ester O–R bond was observed in the reactions of L-leucine methyl ester with NbF5 and L-proline ethyl ester with MBr5 (M = Nb, Ta), these reactions proceeding with the release of EtF and EtBr, respectively. All the metal products were characterized by analytical and spectroscopic methods, while DFT calculations were carried out in order to provide insight into the structural and mechanistic aspects.
, 11c; Ta, 11d), in moderate to good yields. [NbCl5(Me2CHCH2CHNH3CO2Me)][NbCl6], 12, was isolated as a co-product of the reaction of NbCl5 with L-leucine isopropylester, and crystallographically characterized. The reaction of NbCl5 with L-serine isopropylester afforded NbCl3(OCH2CHNHCO2iPr), 13, in 66% yield. The activation of the ester O–R bond was observed in the reactions of L-leucine methyl ester with NbF5 and L-proline ethyl ester with MBr5 (M = Nb, Ta), these reactions proceeding with the release of EtF and EtBr, respectively. All the metal products were characterized by analytical and spectroscopic methods, while DFT calculations were carried out in order to provide insight into the structural and mechanistic aspects.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...