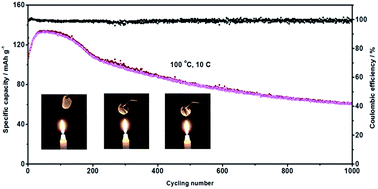
Solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs) have significant potential to improve the energy density of lithium batteries and exhibit good flexibility, electrochemical stability and increased safety. In this study, a biocompatible and biodegradable SPE is prepared by using the natural product, wheat flour. The SPE is found to have an ionic conductivity of 2.62 × 10−5 S cm−1 at 25 °C with a Li+ ionic transference number of 0.51. FTIR and SEM are used to characterize the chemical and physical structures of the SPE. The results show that the enhanced ionic conductivity is mainly due to good compatibility of wheat flour with PEO and the decreased crystallinity of the electrolyte. Using the SPE, both NCM-811 and LiFePO4 batteries can be used in the temperature range of 25–100 °C. The experimental results demonstrate the potential of nature-derived solid materials for high energy and high safety green energy storage systems.