Thickness- and temperature-dependent structural and electromechanical properties of (100)-oriented Sc-doped (Na0.85K0.15)0.5Bi0.5TiO3 ferroelectric films
Abstract
(100)-oriented Sc-doped (Na0.85K0.15)0.5Bi0.5TiO3 (NKBT-Sc) films with different thicknesses of about 100–620 nm were grown on Pt(111)/Ti/SiO2/Si substrates by a sol–gel method. A LaNiO3 (LNO) layer of about 20 nm thickness was introduced at the film–substrate interface or alternatively with NKBT-Sc layers to form a sandwich multilayer structured film. The film thickness- and temperature-dependent structural and electromechanical properties of the films were investigated. A rhombohedral–tetragonal phase transition phase occurred with the variation of NKBT-Sc film thickness, and during this process a two-phase coexistence existed in an appropriate film thickness region, inducing an increased remnant polarization (Pr) value at an intermediate thickness (∼460 nm) of about 23.7 μC cm−2. The effective piezoelectric coefficient 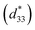 initially increased from about 32 pm V−1 for the thinnest film (∼100 nm) to a peak value of about 73 pm V−1 (∼460 nm), but then decreased as the film thickness further increased. With the insertion of the LNO layers alternatively inside the NKBT-Sc film, the sandwich multilayer structure further enhanced the degree of the (001)-orientation and was beneficial for the crystallization process, leading to better electromechanical properties than the NKBT-Sc/LNO/substrate structure composite film. A high piezoelectric coefficient
initially increased from about 32 pm V−1 for the thinnest film (∼100 nm) to a peak value of about 73 pm V−1 (∼460 nm), but then decreased as the film thickness further increased. With the insertion of the LNO layers alternatively inside the NKBT-Sc film, the sandwich multilayer structure further enhanced the degree of the (001)-orientation and was beneficial for the crystallization process, leading to better electromechanical properties than the NKBT-Sc/LNO/substrate structure composite film. A high piezoelectric coefficient 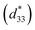 of about 82 pm V−1, dielectric constant εr of about 523 and remnant polarization (Pr) of about 26.2 μC cm−2, which gradually increased with the decrease of the testing temperature from 20 °C to −120 °C, together with a with a low dielectric loss (tan δ) of about 0.055 were simultaneously obtained in the sandwich multilayer structured film with NKBT-Sc film thickness of about 460 nm.
of about 82 pm V−1, dielectric constant εr of about 523 and remnant polarization (Pr) of about 26.2 μC cm−2, which gradually increased with the decrease of the testing temperature from 20 °C to −120 °C, together with a with a low dielectric loss (tan δ) of about 0.055 were simultaneously obtained in the sandwich multilayer structured film with NKBT-Sc film thickness of about 460 nm.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...