The halogen effect on the 13C NMR chemical shift in substituted benzenes†
Abstract
Recent research [Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 6570–6576] showed for R-substituted benzenes with R = NH2, NO2 that the substitution effects on the 13C NMR chemical shifts are correlated with changes in the σ-bonding framework and do not follow directly the electron-donating or -withdrawing effects on the π orbitals. In the present work we extend the study to halogen (X = F, Cl, Br or I) substituted R-benzenes. The effect of X and R groups on 13C NMR chemical shifts in X–R-benzenes are investigated by density functional calculations and localized molecular orbital analyses. Deshielding effects caused by the X atom on the directly bonded carbon nucleus are observed for F and Cl derivatives due to a paramagnetic coupling between occupied π orbitals and unoccupied 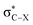 antibonding orbitals. The SO coupling plays an important role in the carbon magnetic shielding of Br and I derivatives, as is well known, and the nature of X also modulates the 13C paramagnetic shielding contributions. Overall, the X and R substituent effects are approximately additive.
antibonding orbitals. The SO coupling plays an important role in the carbon magnetic shielding of Br and I derivatives, as is well known, and the nature of X also modulates the 13C paramagnetic shielding contributions. Overall, the X and R substituent effects are approximately additive.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
