First acid ionization constant of the drinking water relevant chemical cyanuric acid from 5 to 35 °C†
Abstract
Cyanuric acid is present in drinking water when chemicals commonly referred to as dichlor (anhydrous sodium dichloroisocyanurate or sodium dichloroisocyanurate dihydrate) or trichlor (trichloroisocyanuric acid) are used as alternative free chlorine sources. Cyanuric acid and its ionization products combine with hypochlorous acid, forming various chlorinated cyanurates through a series of equilibrium reactions. Methods to measure the free chlorine (hypochlorous acid plus hypochlorite ion) concentration in systems adding cyanuric acid exhibit measurement bias. To overcome this limitation, one option is use of the established water chemistry of the free chlorine and cyanuric acid system to estimate free chlorine concentrations. Unfortunately, the equilibrium water chemistry has only been determined for 25 °C, limiting the usefulness of the water chemistry estimate in actual drinking water systems where temperatures may vary over a wide range (e.g., 5 to 35 °C). As a first step in extending the water chemistry model to relevant drinking water temperatures, the first acid ionization constant (K6) for cyanuric acid (H3Cy) and its first ionization product (H2Cy−) was determined using spectrophotometric techniques from 5 to 35 °C where 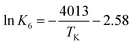 or
or 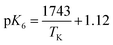 and ΔH° = 33.4 ± 1.7 kJ mol−1. As an example of temperature's impact (pH 7), the H2Cy− fraction of total cyanurate (sum of H3Cy and H2Cy−) effectively doubles from 5 to 35 °C. With K6's temperature dependence established, studies can be conducted to update the existing water chemistry model with temperature dependence, allowing free chlorine concentration simulation in drinking water systems with cyanuric acid present.
and ΔH° = 33.4 ± 1.7 kJ mol−1. As an example of temperature's impact (pH 7), the H2Cy− fraction of total cyanurate (sum of H3Cy and H2Cy−) effectively doubles from 5 to 35 °C. With K6's temperature dependence established, studies can be conducted to update the existing water chemistry model with temperature dependence, allowing free chlorine concentration simulation in drinking water systems with cyanuric acid present.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...