A novel nanofiltration membrane inspired by an asymmetric porous membrane for selective fractionation of monovalent anions in electrodialysis†
Abstract
The present study describes the synthesis of new nanofiltration membranes inspired by asymmetric porous membranes used as monovalent anion selective membranes for electro-membrane separation. The membrane surface was firstly modified, by deposition of a mussel-inspired “bio-glue” polydopamine (PDA) layer, and subsequently a compact polyamide layer was polymerized on the surface of the membrane's active layer. The chemical constitution and structure of these modified porous membranes were explored by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The surface roughness and hydrophilicity of the membranes were explored by atomic force microscopy (AFM) and water contact angle measurements, respectively. In addition, the electrochemical properties of the surface of the modified membranes were analyzed in terms of membrane surface resistance and zeta potential values. As for the performance of these modified porous membranes, this was investigated by measuring the permselectivity of a Cl−/SO42− system. The obtained results show that the new membranes exhibit an enhanced monovalent anion permselectivity, which is in agreement with the improved membrane surface properties. Furthermore, membranes modified by the addition of a PDA layer and a dense polyamide active layer lead to a significant improvement in selectivity 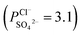 , compared with a conventional interfacial polymerization modified membrane
, compared with a conventional interfacial polymerization modified membrane 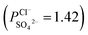 . The excellent performance can be ascribed to the synergistic effect of the compact PDA layer and negatively charged interfacial polymerization layer, dependent on the sieving and electrostatic repulsion, respectively. Thus, this process is promising for the further development of porous monovalent selective anion exchange membranes.
. The excellent performance can be ascribed to the synergistic effect of the compact PDA layer and negatively charged interfacial polymerization layer, dependent on the sieving and electrostatic repulsion, respectively. Thus, this process is promising for the further development of porous monovalent selective anion exchange membranes.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...