Ru@UiO-66(Ce) catalyzed acceptorless dehydrogenation of primary amines to nitriles: the roles of Lewis acid–base pairs in the reaction†
Abstract
UiO-66(Ce)-encapsulated ruthenium nanoparticles (Ru@UiO-66(Ce)) was designed and used for dehydrogenation of primary amines to nitriles in water without any hydrogen acceptors and additives. Introduction of metal Ru to UiO-66(Ce) contributes to the formation of Lewis acid–base pairs 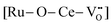 on the catalyst owing to the metal–support interaction, acting as active sites for activation of amines and transfer of hydrogen. Ab initio calculation results further confirm the roles of Lewis acid–base pairs in the reaction.
on the catalyst owing to the metal–support interaction, acting as active sites for activation of amines and transfer of hydrogen. Ab initio calculation results further confirm the roles of Lewis acid–base pairs in the reaction.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...