Unraveling the role of Ti in the stability of positive layered oxide electrodes for rechargeable Na-ion batteries†
Abstract
The many advantages of Na-ion batteries (NIBs) in terms of availability and cost of raw materials compared with Li-ion batteries (LIBs) are hindered by the stability of Na-based electrodes. The most promising NIB positive electrodes are Co- and Ni-free sodium manganese rich layered oxides with the general formula 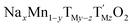 (y < 0.33, TM = transition metal/s). Although their stability is greatly improved when doped with electrochemically inactive species such as Mg or Ti, the rationale behind this has not been understood to date. Here, we demonstrate how a given degree of TiIV doping (z = 0.1) helps to stabilize the crystal structure of sodium manganese rich layered oxides by absorbing electrochemically induced strain; a remarkable step forward on the quest of finding the best NIB positive electrode. In this case, any Mn–Ti substitution below z = 0.1 will not be enough to absorb the strain and substitutions above this value will increase the amount of Jahn–Teller active MnIII leading to destabilization of the crystal structure with poor electrochemical performance. The possibility of controlling structural and electrochemical properties by TM substitution is the starting point towards the design of electrode materials that will ultimately lead towards competitive Na-ion batteries.
(y < 0.33, TM = transition metal/s). Although their stability is greatly improved when doped with electrochemically inactive species such as Mg or Ti, the rationale behind this has not been understood to date. Here, we demonstrate how a given degree of TiIV doping (z = 0.1) helps to stabilize the crystal structure of sodium manganese rich layered oxides by absorbing electrochemically induced strain; a remarkable step forward on the quest of finding the best NIB positive electrode. In this case, any Mn–Ti substitution below z = 0.1 will not be enough to absorb the strain and substitutions above this value will increase the amount of Jahn–Teller active MnIII leading to destabilization of the crystal structure with poor electrochemical performance. The possibility of controlling structural and electrochemical properties by TM substitution is the starting point towards the design of electrode materials that will ultimately lead towards competitive Na-ion batteries.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...