Heterogeneous activation of persulfate for the degradation of bisphenol A with Ni2SnO4–RGO†
Abstract
Spherical Ni2SnO4 nanoparticles were uniformly loaded on reduced graphene oxide (RGO) sheets via a hydrothermal process. The obtained nickel stannate–reduced graphene oxide (Ni2SnO4–RGO) composite was used as a catalyst for activating persulfate (PS). The heterostructure composed of Ni2SnO4 and RGO prevents both the agglomeration of Ni2SnO4 nanoparticles and the restacking of RGO sheets. The synergy between the two components affords enhanced Ni2SnO4–RGO catalytic activity. Using Ni2SnO4–RGO to activate PS can degrade bisphenol A (BPA) at a faster rate with less PS, in comparison with the most recently reported catalysts. BPA solution (50 mL, 0.10 mM) can be 100% degraded by PS (0.02 g) within 30 min at pH 8 using Ni2SnO4–RGO (0.02 g) as the catalyst. Moreover, the preparation of Ni2SnO4–RGO is simple, inexpensive and environment-friendly. The radical scavenging study indicates that sulfate radicals (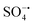 ) and hydroxyl radicals (˙OH) are involved in the oxidation, in which
) and hydroxyl radicals (˙OH) are involved in the oxidation, in which 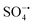 plays a leading role. In addition, Ni2SnO4–RGO retains high catalytic activity after four consecutive cycles, exhibiting greatly enhanced stability in comparison with Ni2SnO4. Besides, the effect of different inorganic anions on the degradation was also explored.
plays a leading role. In addition, Ni2SnO4–RGO retains high catalytic activity after four consecutive cycles, exhibiting greatly enhanced stability in comparison with Ni2SnO4. Besides, the effect of different inorganic anions on the degradation was also explored.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...