Supramolecular synthon hierarchy in cyclopropyl-containing peptide-derived compounds†
Abstract
Considering the increasing importance of cyclopropyl-containing peptide-derived compounds in the pharmaceutical industry, herein, we report the crystal engineering of a series of novel derivatives, i.e., diethyl 2-acetamido-2-(cyclopropylmethyl)malonate (1), 2-(cyclopropylmethyl)-2-acetamidopropanedioic acid (2) [Ac-b-cyclopropyl-(R,S)-Ala-OH], 2-(cyclopropylmethyl)-2-acetamidopropanedioic acid hydrate (3), 2-acetamido-3-cyclopropylpropanoic acid (4), and (2S)-2-[cyclopropyl(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbonyl)amino]propanoic acid (5) [Fmoc-b-cyclopropyl-(S)-Ala-OH]. Although several cyclopropyl-based peptide-derived structures have been reported in the literature, to the best of our knowledge, studies on the synthon hierarchy in this class of structures are limited. Thus, to address this gap, herein, we report a multidisciplinary study to shed light on the role of cyclopropyl synthons in (bio)supramolecular assemblies, opening a new vista for the further applications of this unique scaffold. The synthesis was achieved via a multi-step protocol in good yield and the structures were determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The diverse supramolecular synthons responsible for the arrangement of molecules in the crystal lattice of either new compounds or all cyclopropyl-containing peptide-derived solids deposited in the CSD thus far were specified and summarized, building a library. The self-assembly is directed by the cooperative interplay of H-bonds and π-stacking interactions. Quantum-chemical computational studies revealed that the cyclopropyl ring is capable of 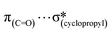 ,
, 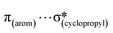 ,
, 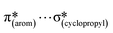 and
and 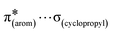 interactions. The molecular docking study delineated the C–H⋯C(cyclopropyl) and C–H(cyclopropyl)⋯π interactions of the cyclopropyl moiety with the essential amino acid residues inside the active pocket of the human androgen receptor, highlighting the vital role of cyclopropyl in the supramolecular landscape of the bio-complex. Indeed, 2 shows a significant docking score with effective binding affinity, and thus is a promising candidate for prostate cancer prevention or management.
interactions. The molecular docking study delineated the C–H⋯C(cyclopropyl) and C–H(cyclopropyl)⋯π interactions of the cyclopropyl moiety with the essential amino acid residues inside the active pocket of the human androgen receptor, highlighting the vital role of cyclopropyl in the supramolecular landscape of the bio-complex. Indeed, 2 shows a significant docking score with effective binding affinity, and thus is a promising candidate for prostate cancer prevention or management.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...