Unraveling the interactions of reductants and reaction path over Cu-ZSM-5 for model coal-gas-SCR via a transient reaction study†
Abstract
Selective catalytic reduction with coal gas can be a solution for NOx emission control in the iron and steel industry; nevertheless coal-gas-SCR is not clearly understood and hard to study due to the multiple reductants in coal gas (H2, CO, and CH4). In this work, Cu-ZSM-5 was selected as a candidate catalyst after being compared with other Cu-zeolite catalysts. The activity evaluations of various SCR reaction with different reductant combinations revealed that there are interactions and synergistic effects between components of coal gas. Subsequently, with the help of TPD, TPSR, and transient reaction studies, the interactions between these reductants over Cu-ZSM-5 were clarified and the reaction mechanism network of coal-gas-SCR was also well established. We found that H2 can enhance the CO-SCR performance by promoting the NCO route. However, CO would restrain H2-SCR through covering the active sites by bicarbonate species. Moreover, NCO and 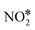 efficiently activate CH4, consequently improving the CH4-SCR performance following the CH3NO route at low temperature.
efficiently activate CH4, consequently improving the CH4-SCR performance following the CH3NO route at low temperature.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...