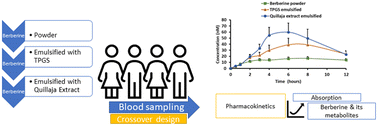
Berberine is widely used for the prevention of cancers and diabetes. However, the absorption rate of berberine is less than 1% in humans. The objective of this research was to determine whether emulsification improves the absorption and affects the metabolism of orally ingested berberine. Twelve healthy subjects, both men and women, received 800 mg berberine in a powder or emulsified form by vitamin E TPGS or Quillaja extract using a randomized crossover design. Blood samples were collected 12 hours after a dose. Berberine and its metabolites in plasma were analyzed with and without hydrolysis by glucuronidase and sulfatase on UHPLC-MS/MS. The area under the curve (AUC0–12 h) and peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of berberine was 6.7 nM h and 0.9 nM in participants who received berberine powder. They were increased to 12.6 nM h and 2.0 nM by TPGS emulsification and 28.0 nM h and 5.1 nM by Quillaja extract emulsification, respectively. Berberrubine and demethyleneberberine were detected as major phase-1 metabolites of berberine. The AUC0–12 of both free and total berberrubine was significantly increased by TPGS and Quillaja extract. Emulsification by Quillaja extract was more effective than TPGS to increase the plasma concentrations of free and total demethyleneberberine. However, the ratios of phase-1 metabolites and ratios of phase-2 conjugates were not affected by emulsification. Absorption increases of berberine by TPGS or Quillaja extract emulsification may lead to enhanced bioactivity in humans.