Bio-based copolyesters involving 1,4:3,6-dianhydrohexitols and sebacic acid: 2,6-pyridinedicarboxylic acid as platforms for high gas barrier food packaging†
Abstract
Proposing renewable structures for food packaging applications is necessary for contributing to a low-carbon and sustainable world. Thus, bio-based copolyesters, involving isosorbide (or isomannide), sebacoyl dichloride, and a second rigid acid structure (succinyl dichloride, isophthaloyl chloride or 2,6-pyridinedicarbonyl dichloride), were synthesized via polycondensation reactions. The 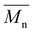 values ranged from 10 600 to 18 000 g mol−1. 1H NMR spectroscopy established the random copolymerization and enabled the calculation of the respective monomer ratios in the copolymers. All copolyesters were thermally stable with Td5% higher than 328 °C and Tg ranging from 30 to 64 °C. The tensile test revealed plastic fractures for aliphatic copolyesters and brittle fractures for aromatic ones. The highest Young's modulus and tensile strength were obtained for aromatic copolyesters, whereas the largest elongation at break was observed for aliphatic ones. All copolyesters showed good gas barrier properties, and the best result was comparable to the widely used semi-crystalline PET.
values ranged from 10 600 to 18 000 g mol−1. 1H NMR spectroscopy established the random copolymerization and enabled the calculation of the respective monomer ratios in the copolymers. All copolyesters were thermally stable with Td5% higher than 328 °C and Tg ranging from 30 to 64 °C. The tensile test revealed plastic fractures for aliphatic copolyesters and brittle fractures for aromatic ones. The highest Young's modulus and tensile strength were obtained for aromatic copolyesters, whereas the largest elongation at break was observed for aliphatic ones. All copolyesters showed good gas barrier properties, and the best result was comparable to the widely used semi-crystalline PET.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...