In vivo MRI tracking and therapeutic efficacy of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells labeled with ferrimagnetic vortex iron oxide nanorings for liver fibrosis repair†
Abstract
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have showed promising effects in the treatment of liver fibrosis. Long-term and noninvasive in vivo tracking of transplanted MSCs is essential for understanding the therapeutic mechanism of MSCs during the therapy of liver fibrosis. In this study, we report the development of a ferrimagnetic vortex iron oxide nanoring (FVIO)-based nanotracer for the long-term visualization of transplanted human MSCs (hMSCs) by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The FVIOs were prepared by a hydrothermal reaction followed by hydrogen reduction. To endow the FVIOs with biocompatibility, polyethylene glycol amine (mPEG-NH2) was covalently coupled on the surface of FVIOs, forming FVIO@PEG nanotracers with high 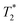 contrast enhancement and intracellular uptake. The hMSCs labeled with FVIO@PEG nanotracers exhibited enhanced MRI contrast than those labeled with a commercial contrast agent, and could be continuously monitored by MRI in liver fibrosis mice for 28 days after transplantation, clearly clarifying the migration behavior of hMSCs in vivo. Moreover, we explored the therapeutic mechanism of the FVIO@PEG labeled hMSCs in the amelioration of liver fibrosis, including the reduction in inflammation and oxidative stress, the inhibition of hepatic fibrosis-caused histopathological damage, as well as the down-regulation of the expression of relevant cytokines. The results obtained in this work may deepen our understanding of the behavior and role of hMSCs in the treatment of liver fibrosis, which is key to the clinical application of stem cells in the therapy of liver diseases.
contrast enhancement and intracellular uptake. The hMSCs labeled with FVIO@PEG nanotracers exhibited enhanced MRI contrast than those labeled with a commercial contrast agent, and could be continuously monitored by MRI in liver fibrosis mice for 28 days after transplantation, clearly clarifying the migration behavior of hMSCs in vivo. Moreover, we explored the therapeutic mechanism of the FVIO@PEG labeled hMSCs in the amelioration of liver fibrosis, including the reduction in inflammation and oxidative stress, the inhibition of hepatic fibrosis-caused histopathological damage, as well as the down-regulation of the expression of relevant cytokines. The results obtained in this work may deepen our understanding of the behavior and role of hMSCs in the treatment of liver fibrosis, which is key to the clinical application of stem cells in the therapy of liver diseases.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...