Structural, morphological, and electrical properties of silver-substituted ZnAl2O4 nanoparticles
Abstract
In this paper, nanoparticles of 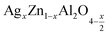 (x = 0.05 and x = 0.1) were synthesized by the sol–gel auto-combustion method and characterized by various techniques. X-ray diffraction (XRD) for structural characterization confirms the successful formation of a cubic spinel structure with the space group Fd
(x = 0.05 and x = 0.1) were synthesized by the sol–gel auto-combustion method and characterized by various techniques. X-ray diffraction (XRD) for structural characterization confirms the successful formation of a cubic spinel structure with the space group Fd![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m. Their morphology was evaluated with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) which shows an agglomeration of nanoparticles. To characterize the electrical behavior of our compounds, we used impedance spectroscopy at temperatures ranging from 313 K to 653 K and frequencies ranging from 0.1 Hz to 1 MHz. The experimental data for the real and imaginary impedance parts were mounted on the equivalent grain resistance (Rg)//fractal capacitance (CPE) circuit. Indeed, the activation energies extracted from the electrical conductivity and the resistance of the grain resistance (Rg) closed and confirmed a transformation of the electrical behavior confirmed by a decrease in the resistance of the materials. The study of the alternating conductivity shows a Jonscher curve behavior and a thermally activated conduction process. The variation of the exponent “s” as a function of temperature shows, on the one hand, the presence of two models of conduction correlated barrier jump (CBH) and non-overlapping small polaron tunneling (NSPT) for x = 0.05 and, on the other hand, a CBH model for x = 0.1.
m. Their morphology was evaluated with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) which shows an agglomeration of nanoparticles. To characterize the electrical behavior of our compounds, we used impedance spectroscopy at temperatures ranging from 313 K to 653 K and frequencies ranging from 0.1 Hz to 1 MHz. The experimental data for the real and imaginary impedance parts were mounted on the equivalent grain resistance (Rg)//fractal capacitance (CPE) circuit. Indeed, the activation energies extracted from the electrical conductivity and the resistance of the grain resistance (Rg) closed and confirmed a transformation of the electrical behavior confirmed by a decrease in the resistance of the materials. The study of the alternating conductivity shows a Jonscher curve behavior and a thermally activated conduction process. The variation of the exponent “s” as a function of temperature shows, on the one hand, the presence of two models of conduction correlated barrier jump (CBH) and non-overlapping small polaron tunneling (NSPT) for x = 0.05 and, on the other hand, a CBH model for x = 0.1.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...