Preparation and electrical properties of inorganic electride [Y2Ti2O6]2+(2e−)
Abstract
Oxygen-depleted samples [Y2Ti2O7−x]2x+(2xe−) (0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) were prepared by reducing Y2TiO7 powders at 500 °C to 650 °C using CaH2 as a reductive agent, where x represents the content of 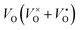 , which was determined by thermogravimetric analysis. Powder X-ray diffraction patterns illustrate that the pure pyrochlore phase is kept for the samples with x ≤ 1.0, whereas the apparent x values surpass 1.0, and the impurity phase Y2O3 appears. The electride [Y2Ti2O7−x]2x+(2xe−) (x ≈ 1.0) can be obtained under a reductive condition, in which the concentration of VO is 7.75 × 1021 cm−3. The electron paramagnetic resonance measurements gave the concentration of unpaired electrons in the electride as 1.30 × 1021 cm−3, indicating that the degree of the ionization of
, which was determined by thermogravimetric analysis. Powder X-ray diffraction patterns illustrate that the pure pyrochlore phase is kept for the samples with x ≤ 1.0, whereas the apparent x values surpass 1.0, and the impurity phase Y2O3 appears. The electride [Y2Ti2O7−x]2x+(2xe−) (x ≈ 1.0) can be obtained under a reductive condition, in which the concentration of VO is 7.75 × 1021 cm−3. The electron paramagnetic resonance measurements gave the concentration of unpaired electrons in the electride as 1.30 × 1021 cm−3, indicating that the degree of the ionization of 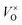 is less than 10%. Conductivity measurements for a sintered pellet sample (relative density ∼ 70%) indicate that the electride has quite high conductivity (∼1.09 S cm−1 at 300 K). The conduction was interpreted by using the variable range hopping mechanisms.
is less than 10%. Conductivity measurements for a sintered pellet sample (relative density ∼ 70%) indicate that the electride has quite high conductivity (∼1.09 S cm−1 at 300 K). The conduction was interpreted by using the variable range hopping mechanisms.
![Graphical abstract: Preparation and electrical properties of inorganic electride [Y2Ti2O6]2+(2e−)](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=D2RA05847B&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2022)


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...