Effect of rare-earth (RE) ionic radius on the dielectric properties of Sr99%RE1%TiO3 (RE = La, Nd, Yb) single crystals†
Abstract
High-performance dielectric materials are essential components of electronic devices. In this work, RE-doped SrTiO3 (RE = La, Nd, Yb) single crystals with excellent dielectric properties were prepared by the Verneuil method. For La-STO and Nd-STO, the RE ions are substituted for Sr2+ only, and the excellent dielectric properties are mainly caused by defect dipoles associated with oxygen vacancies including 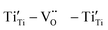 and
and 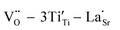 defect dipole clusters. For Yb-STO, Yb3+ partially replaces Ti4+, forming an additional defect dipole
defect dipole clusters. For Yb-STO, Yb3+ partially replaces Ti4+, forming an additional defect dipole 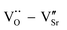 , resulting in the best dielectric properties (ε′ = 3.6 × 104, tan δ = 0.0036 under 1 kHz). In addition, N2 atmosphere treatment promotes the production of oxygen vacancies and Ti3+ and the formation of more defect dipoles, thus further optimizing the dielectric properties of Yb-STO (ε′ = 4.9 × 104, tan δ = 0.004 under 1 kHz). This work suggests that the dielectric properties of RE-doped SrTiO3 materials are closely related to oxygen vacancies, and the simultaneous substitution of Sr2+ and Ti4+ should enable obtaining dielectric properties superior to those of the substitution of Sr2+ only. The present work provides a clearer understanding of the origin of SrTiO3 dielectric properties, which is of great significance to the development of SrTiO3-based dielectric materials.
, resulting in the best dielectric properties (ε′ = 3.6 × 104, tan δ = 0.0036 under 1 kHz). In addition, N2 atmosphere treatment promotes the production of oxygen vacancies and Ti3+ and the formation of more defect dipoles, thus further optimizing the dielectric properties of Yb-STO (ε′ = 4.9 × 104, tan δ = 0.004 under 1 kHz). This work suggests that the dielectric properties of RE-doped SrTiO3 materials are closely related to oxygen vacancies, and the simultaneous substitution of Sr2+ and Ti4+ should enable obtaining dielectric properties superior to those of the substitution of Sr2+ only. The present work provides a clearer understanding of the origin of SrTiO3 dielectric properties, which is of great significance to the development of SrTiO3-based dielectric materials.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...