Computational prediction of the critical micelle concentration (CMC) of surfactants using the non-Bornian solvation model†
Abstract
The non-Bornian solvation model was used to predict the Gibbs energy change for the adsorption–desorption processes of ionic (14 anionic and 9 cationic) surfactants and 19 non-ionic surfactants at the interface between oil (O) (=nitrobenzene) and water (W). Except for 10 non-ionic surfactants (polyoxyethylenes) having semi-hydrophobic –OC2H4– groups, both ionic and non-ionic surfactants showed a clear energy minimum in their adsorption–desorption processes, providing reliable values of Gibbs energies, 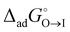 and
and 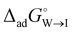 , for the two adsorption processes from their respective bulk phases to the interface (I). It was then found that the critical micelle concentration (CMC) for surfactants (especially for the ionic ones) is linearly related to the two independent variables, i.e.,
, for the two adsorption processes from their respective bulk phases to the interface (I). It was then found that the critical micelle concentration (CMC) for surfactants (especially for the ionic ones) is linearly related to the two independent variables, i.e., 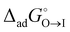 and
and 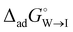 .
.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...