Self-assembly of choline-based surface-active ionic liquids and concentration-dependent enhancement in the enzymatic activity of cellulase in aqueous medium†
Abstract
The micellization of choline-based anionic surface-active ionic liquids (SAILs) having lauroyl sarcosinate [Sar]−, dodecylsulfate [DS]−, and deoxycholate [Doc]− as counter-ions was investigated in an aqueous medium. Density functional theory (DFT) was employed to investigate the net interactional energy (Enet), extent of non-covalent interactions, and band gap of the choline-based SAILs. The critical micelle concentration (cmc) along with various parameters related to the surface adsorption, counter-ion binding (β), and polarity of the cores of the micelles were deduced employing surface tension measurements, conductometric titrations and fluorescence spectroscopy, respectively. A dynamic light scattering (DLS) system equipped with zeta-potential measurement set-up and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) were used to predict the size, zeta-potential, and morphology, respectively, of the formed micelles. Thermodynamic parameters such as standard Gibb's free energy 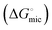 and standard enthalpy
and standard enthalpy 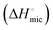 change of micellization were calculated using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC). Upon comparing with sodium salt analogues, it was established that the micellization was predominantly governed by the extent of hydration of [Cho]+, the head groups of the respective anions, and the degree of counter-ion binding (β). Considering the concentration dependence of the enzyme–SAIL interactions, aqueous solutions of the synthesized SAILs at two different concentrations (below and above the cmc) were utilized as the medium for testing the enzymatic activity of cellulase. The activity of cellulase was found to be ∼7- to ∼13-fold higher compared to that observed in buffers in monomeric solutions of the SAILs and followed the order: [Cho][Sar] > [Cho][DS] > [Cho][Doc]. In the micellar solution, a ∼4- to 5-fold increase in enzymatic activity was observed.
change of micellization were calculated using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC). Upon comparing with sodium salt analogues, it was established that the micellization was predominantly governed by the extent of hydration of [Cho]+, the head groups of the respective anions, and the degree of counter-ion binding (β). Considering the concentration dependence of the enzyme–SAIL interactions, aqueous solutions of the synthesized SAILs at two different concentrations (below and above the cmc) were utilized as the medium for testing the enzymatic activity of cellulase. The activity of cellulase was found to be ∼7- to ∼13-fold higher compared to that observed in buffers in monomeric solutions of the SAILs and followed the order: [Cho][Sar] > [Cho][DS] > [Cho][Doc]. In the micellar solution, a ∼4- to 5-fold increase in enzymatic activity was observed.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...