Thermodynamics of the Eu(iii)–Mg–SO4–H2O and Eu(iii)–Na–SO4–H2O systems. Part II: spectroscopy experiments, complexation and Pitzer/SIT models†
Abstract
A time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS) study was carried out to investigate the Eu(III)–SO4 complexation at room temperature over a wide range of Na2SO4 concentrations (0–2 mol kg−1). Spectroscopic observations confirm the step-wise formation of the aqueous complexes Eu(SO4)+, Eu(SO4)2− and Eu(SO4)33− over the investigated Na2SO4 concentrations. Combining TRLFS data obtained in this study and solubility data reported in Part I of this work for the Eu2(SO4)3–Na2SO4–H2O and Eu2(SO4)3–MgSO4–H2O systems, thermodynamic and activity models were derived based on the SIT and Pitzer formalisms. A combination of the geochemical calculation codes PhreeqC (SIT), PhreeSCALE (Pitzer) and the parameter estimation code PEST was used to determine the solubility products 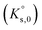 of Eu2(SO4)3·8H2O(cr) and Na2Eu2(SO4)4·2H2O(cr), stability constants of the Eu(III)–SO4 complexes (β0i), and the specific binary and ternary interaction parameters (εij, β(0)ij, β(1)ij, Cϕij, θik, Ψijk) for both activity models. The thermodynamic constants determined in this work are discussed with reference to values available in the literature.
of Eu2(SO4)3·8H2O(cr) and Na2Eu2(SO4)4·2H2O(cr), stability constants of the Eu(III)–SO4 complexes (β0i), and the specific binary and ternary interaction parameters (εij, β(0)ij, β(1)ij, Cϕij, θik, Ψijk) for both activity models. The thermodynamic constants determined in this work are discussed with reference to values available in the literature.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...