UV-Vis spectrophotometric determination of rare earth elements (REE) speciation at near-neutral to alkaline pH. Part I: m-cresol purple properties from 25–75 °C and Er hydrolysis†
Abstract
The speciation and mobility of rare earth elements (REE) strongly depends on pH, which controls the formation of charged aqueous hydroxyl species. The latter potentially play an important role in controlling heavy REE adsorption on clay minerals in near-neutral to alkaline waters such as in regolith-hosted REE mineral deposits. However, accurate REE hydrolysis constants are needed for developing geochemical models that can predict the role of these charged species in natural systems. Here, we develop a robust experimental UV-Vis spectrophotometric method using m-cresol purple to determine in situ pH from 25 to 75 °C. This method is used to derive the average ligand number and hydrolysis constants of erbium (Er) at 25 °C in aqueous solutions with low ionic strength (≤0.001 mol L−1) at pH from ∼7 to 9.5 and in the presence of Er concentrations from 0 to 0.057 mM. The average ligand number ranges between 1 and 3 indicating that Er(OH)2+, Er(OH)2+ and Er(OH)03 control speciation in the experiments. The logarithm of the Er hydrolysis constants (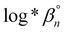 , n = 1 to 3) derived at infinite dilution for the reaction Er3+ + nH2O = Er(OH)n3−n + nH+ are:
, n = 1 to 3) derived at infinite dilution for the reaction Er3+ + nH2O = Er(OH)n3−n + nH+ are: 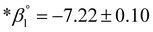 ,
, 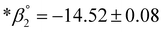 ,
, 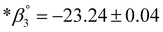 . Implementation of these experimental data into a geochemical model indicates that the Er(OH)2+ and Er(OH)03 species are both stable in a much wider pH range than previously predicted. Consequently, the positively charged REE hydroxyl complexes can potentially control the fractionation of light vs. heavy REE via adsorption as observed in the formation of certain regolith-hosted REE deposits.
. Implementation of these experimental data into a geochemical model indicates that the Er(OH)2+ and Er(OH)03 species are both stable in a much wider pH range than previously predicted. Consequently, the positively charged REE hydroxyl complexes can potentially control the fractionation of light vs. heavy REE via adsorption as observed in the formation of certain regolith-hosted REE deposits.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...