Designing antiperovskite derivatives via atomic-position splitting for photovoltaic applications†
Abstract
Due to the success of halide perovskites in the photovoltaic field, halide perovskite-derived semiconductors have also been widely studied for optoelectronic applications. However, the photovoltaic performance of these perovskite derivatives still lags significantly behind their perovskite counterparts, mainly due to deficiencies at the B-site or X-site of the derivatives, which disrupt the connectivity of the key [BX6] octahedra units. Herein, we developed a class of antiperovskite-derived materials with the formula 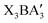 , achieved by splitting the A anion, originally at the corner site of the cubic antiperovskite structure, into three edge-centered sites. This structural transformation maintains the three-dimensional octahedral framework. The thermodynamic stability, dynamical stability, and band gaps of 80
, achieved by splitting the A anion, originally at the corner site of the cubic antiperovskite structure, into three edge-centered sites. This structural transformation maintains the three-dimensional octahedral framework. The thermodynamic stability, dynamical stability, and band gaps of 80 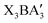 compounds were calculated using first-principles calculations. Based on criteria including stability and electronic properties, we identified 9 promising antiperovskite derivatives for further evaluation of their photovoltaic performance. Notably, the calculated theoretical maximum efficiencies of Ba3BiI3, Ba3SbI3, and Ba3BiBr3 all exceed 24.5%, which is comparable to that of CH3NH3PbI3 solar cells. Interpretable machine learning analysis was further carried out to identify critical physical descriptors influencing thermodynamic stability and band gap. Our work provides a novel approach for designing high performance perovskite-type structure-inspired semiconductors with potential for optoelectronic applications.
compounds were calculated using first-principles calculations. Based on criteria including stability and electronic properties, we identified 9 promising antiperovskite derivatives for further evaluation of their photovoltaic performance. Notably, the calculated theoretical maximum efficiencies of Ba3BiI3, Ba3SbI3, and Ba3BiBr3 all exceed 24.5%, which is comparable to that of CH3NH3PbI3 solar cells. Interpretable machine learning analysis was further carried out to identify critical physical descriptors influencing thermodynamic stability and band gap. Our work provides a novel approach for designing high performance perovskite-type structure-inspired semiconductors with potential for optoelectronic applications.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...