Temperature response of defect photoluminescence in locally functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes†
Abstract
In vivo temperature monitoring has garnered significant attention for studying biological processes such as cellular differentiation and enzymatic activity. However, current nanoscale thermometers utilizing photoluminescence (PL) in the visible to first near-infrared (NIR-I) region based on organic dyes, quantum dots, and lanthanide-doped nanoparticles face challenges in terms of tissue penetration and sensitivity. In this study, we investigated the temperature dependence of 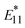 PL (1140 nm) and
PL (1140 nm) and 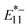 PL (1260 nm) of locally functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes (lf-SWCNTs) that emit in the second near-infrared region (NIR-II). The effects of interfacial dielectric environments (hydrophobic surfactant dispersion vs. hydrophilic gel coating), defect density, and nanotube length on the temperature responsiveness were systematically examined. The results demonstrated that
PL (1260 nm) of locally functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes (lf-SWCNTs) that emit in the second near-infrared region (NIR-II). The effects of interfacial dielectric environments (hydrophobic surfactant dispersion vs. hydrophilic gel coating), defect density, and nanotube length on the temperature responsiveness were systematically examined. The results demonstrated that 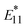 PL was more sensitive to temperature changes than
PL was more sensitive to temperature changes than 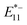 PL and lf sites having a lower dielectric environment further enhanced temperature responsiveness. Additionally, longer lf-SWCNTs exhibited greater temperature responsiveness than the shorter ones. These findings provide valuable insights into optimizing gel-coated lf-SWCNTs to achieve higher temperature responsiveness and develop biocompatible temperature sensors capable of monitoring deep tissues within complex biological environments.
PL and lf sites having a lower dielectric environment further enhanced temperature responsiveness. Additionally, longer lf-SWCNTs exhibited greater temperature responsiveness than the shorter ones. These findings provide valuable insights into optimizing gel-coated lf-SWCNTs to achieve higher temperature responsiveness and develop biocompatible temperature sensors capable of monitoring deep tissues within complex biological environments.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...