Dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles: New synthetic and characterization methods and catalytic applications
V. Sue
Myers
,
Michael G.
Weir
,
Emily V.
Carino
,
David F.
Yancey
,
Surojit
Pande
and
Richard M.
Crooks
*
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Texas Materials Institute, Center for Nano- and Molecular Science and Technology, The University of Texas at Austin, 1 University Station, A5300, Austin, TX 78712-0165. E-mail: crooks@cm.utexas.edu; Tel: +512-475-8674
First published on 27th June 2011
Abstract
In this article we describe the synthesis, characterization, and applications of dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles (DENs). These materials are synthesized using a template approach in which metal ions are extracted into the interior of dendrimers and then subsequently reduced chemically to yield nearly size-monodisperse particles having diameters in the 1–2 nm range. Monometallic, bimetallic (alloy and core@shell), and semiconductor nanoparticles have been prepared by this route. The dendrimer component of these composites serves not only as a template for preparing the nanoparticle replica, but also as a stabilizer for the nanoparticle. In this perspective, we report on progress in the synthesis, characterization, and applications of these materials since our last review in 2005. Significant advances in the synthesis of core@shell DENs, characterization, and applications to homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis (including electrocatalysis) are emphasized.
V. Sue Myers was born in New Orleans, Louisiana (USA) in 1981. She received a double B.A. degree in chemistry and biochemistry from the University of Colorado at Boulder in 2003. She spent several years as a chemist at Boundless Corporation doing research on lithium ion battery technologies. She is currently a Ph.D. candidate in the Crooks research group at The University of Texas at Austin. Her research focuses on electrocatalysis using dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles. |
Michael G. Weir received a B.S. in chemical engineering in 1999 and a M.S. in chemistry in 2005 from Lamar University. His Ph.D. studies, which he completed at The University of Texas at Austin in December, 2010, focused on the synthesis, characterization, and catalytic properties of dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles. He is presently pursuing postdoctoral studies at the University of Nevada in Las Vegas. |
Emily V. Carino was born in Cambridge, MA (USA) in 1981. She received a B.S. degree in kinesiology from the University of Massachusetts in Amherst in 2006 and an M.A in chemistry from The University of Texas at Austin in 2008. She is presently a Ph.D. student in the Crooks research group, and her studies focus on the electrochemical synthesis of dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles. |
David F. Yancey was born in Bloomington, Indiana (USA) in 1986 and grew up in Richland, Michigan. He received his B.S. in chemistry from the University of Michigan. At present he is a Ph.D. candidate in the Crooks research group at The University of Texas at Austin. His studies focus on synthesizing and characterizing core@shell dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles as model electrocatalysts for comparison to theoretical studies. |
Surojit Pande received his Ph.D. in 2009 from IIT- Kharagpur, India. His dissertation studies focused on the synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles for applications to catalysis and surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. He is currently a postdoctoral fellow in the Crooks research group at The University of Texas at Austin with research interests in homogeneous catalysis using dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles. |
Richard M. Crooks was born near Chicago, Illinois (USA) in 1954. He received his B.S. degree in chemistry from the University of Illinois (Urbana) and Ph.D. in electrochemistry from The University of Texas at Austin in 1987. Following a two-year postdoctoral position at MIT, he began his independent career at the University of New Mexico. In 1993 he took a position at Texas A&M University and in 2005 moved to The University of Texas at Austin where he is presently the Robert A. Welch Chair in Materials Chemistry. The Crooks research group has interests in electrochemistry, micro- and nanoelectrochemical systems, nanomaterials, and catalysis. |
Introduction and scope
Since it was first introduced by our group in 1998,1 the technique of dendrimer templating has proven to be a versatile method for synthesizing nanoparticles having well-defined sizes, compositions, and structures. The basic approach for synthesizing dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles (DENs) is comprised of two steps (Scheme 1). First, appropriate metal ions are mixed with a dendrimer solution. This results in encapsulation of the metal ions within the dendrimer. The means by which metal ions complex to the dendrimer interior depends on the identity of the metal, and this effect has been investigated in several theoretical2–5 and empirical6–9 studies. Second, a chemical reducing agent is added to this solution resulting in the formation of DENs.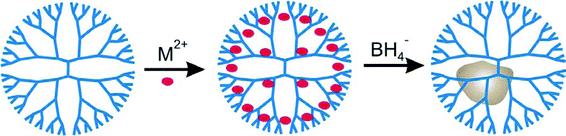 | ||
| Scheme 1 | ||
The DEN synthesis offers some significant advantages over other methods for preparing nanoparticles in the 1–2 nm size range. Most of these advantages arise from the presence of the dendrimer, which both templates and stabilizes the encapsulated nanoparticles. For example, the composition of DENs can be selected by choosing the identity and ratio of metal ions complexed to the dendrimer in the first step of the synthesis. Likewise, the structure of DENs can also be controlled via slight variations to the synthetic procedure: simultaneous complexation and reduction of Pt2+ and Pd2+ ions within a sixth-generation, hydroxyl-terminated poly(amido amine) (PAMAM) dendrimer (G6–OH) results in bimetallic PtPd alloy nanoparticles.10,11 In contrast, when the component metal ions are complexed and reduced sequentially, core@shell DENs may result.12 The size of DENs is controlled by selecting the metal ion: dendrimer ratio. DENs as large as 4 nm in diameter have been reported,13 but the more typical size range is 1 to 2 nm.14–17 The very small size of DENs is one of their main virtues, because the physical and chemical properties of metals change quickly in this size regime.18,19
In addition to their templating function, which largely controls the size, composition, and structure of DENs, the dendrimer also stabilizes the encapsulated nanoparticles against agglomeration. The nature of the dendrimer as a stabilizing agent is fundamentally different from other stabilizers, such as capping agents, because the dendrimer does not passivate or specifically coordinate to the nanoparticle surface. In the case of DENs, the nanoparticles are sterically confined to the interior region of the dendrimer,13 and the degree of chemical interaction of the dendrimer with the surface of the nanoparticle is minimal.20,21 Accordingly, the surface of DENs is free to engage in catalytic reactions, as long as the substrate is small enough to penetrate the branched periphery of the dendrimer. Most other approaches for stabilizing nanoparticles rely on a specific chemical interaction between a ligand and the nanoparticle surface. Typically, this results in reduced access of reactants to surface atoms and, hence, lower reaction rates.22–24
Another advantage of the dendrimer is that its periphery consists of many tens, or even thousands, of individual functional groups. As discussed later, these functional groups can be easily modified to tune the solubility of the dendrimer. Functional groups on the dendrimer surface are also convenient handles for immobilizing DENs on solid supports, thereby enabling the use of DENs for applications in electrocatalysis and heterogeneous catalysis.
In 2001 we published an early review of DENs-related research.25 This article focused on the direct synthesis of several monometallic DENs, including a detailed discussion of Cu DENs. One particularly interesting aspect of Cu DENs described in that report, is that they can undergo galvanic exchange for a more noble metal.26 In addition to synthesis, this review also spotlighted our early homogeneous catalysis studies. These involved the use of Pd DENs for hydrogenation and Heck carbon-coupling reactions in aqueous,27 organic,28 biphasic fluorous/organic systems,29 and supercritical CO2 solvents.30 In 2003 we updated just the catalysis aspects of our DENs studies.31
By 2005, we and others had made substantial additional progress in understanding and applying DENs to interesting chemical problems. Accordingly, we published a second comprehensive review paper that provided a good snapshot of the field as it stood at that time.14 The emphasis in this second review was also on synthesis and catalysis. Key advances discussed included the following: (1) size-selective hydrogenation using Pd DENs wherein the encapsulating dendrimer was used as a nanofilter to control access of reactants to the particle surface;32 (2) the use of Pd DENs for Suzuki carbon-coupling reactions;33 (3) the synthesis of bimetallic DENs and the synergistic effect of PtPd DENs for homogeneous hydrogenation of allyl alcohol;10 (4) heterogeneous catalysis and electrocatalysis using immobilized DENs;34 (5) extraction of DENs from within the dendrimer interior and into an organic phase using alkyl thiols as the extractant.35 The field of DENs has evolved sufficiently during the past six years to merit an updated summary of progress.
In addition to the aforementioned reviews, a few other important review articles have appeared. Chandler and Gilbertson discussed the synthesis of bimetallic DENs and their applications to catalysis in 2006.17 Rempel and co-workers published a similar review on bimetallic materials two years later.16 Finally, in 2008, Vohs and Fahlman published a review that included the synthesis and application of DENs with particular emphasis on formation of thin films, DEN-catalyzed carbon nanotube growth, and biomedical applications.15
The scope of the present review is limited to new synthesis and characterization techniques, and catalytic applications of DENs developed since our 2005 review. We have excluded several other important avenues of research. For example, there have been several recent studies of heterogeneous catalysts prepared by deposition of DENs onto a support followed by removal of the dendrimer, typically by thermal decomposition.36–38 Although this method is an effective way to produce small, supported particles and has practical applications in the field of catalysis, the loss of the dendrimer results in some agglomeration of the nanoparticles. The use of DENs for biomedical applications, which is a key emerging field, has also been excluded from this review.39,40
Nomenclature
Dendrimers are a class of regular, highly branched, and highly symmetrical polymers. For further details on the broad field of dendrimer chemistry the reader is referred to a recently published book.41 Additional specialized reviews are also available.42–46 Here, we briefly summarize some of the jargon that has evolved within the dendrimer community, and also provide some background information that is essential for understanding DENs.The generation of a dendrimer is the number of repeating branch points as traced from the dendrimer center to the periphery. PAMAM dendrimers range in generation from 0 to 10. The number of peripheral functional groups on the dendrimer increases exponentially with increasing generation whereas its diameter increases approximately linearly. As a result, higher generation dendrimers exhibit structures with increasingly crowded peripheries and open cores containing voids.47–50
A dendrimer of generation n with terminal functional groups R is notated Gn–R. Most studies of DENs have been carried out using Gn–OH or Gn–NH2 (n = 4 or 6) PAMAM dendrimers, because these intermediate generation materials have a well-developed three-dimensional structure (which is essential for stabilizing the encapsulated nanoparticle) but are not so large as to have an overly crowded periphery. The metal ion-dendrimer precursor complexes are denoted Gn–R(Am+)x, where A is the metal ion used, m is its oxidation state, and x represents the stoichiometric amount of A used in the synthesis. Monometallic and alloy bimetallic DENs are denoted as Gn–R(Ax) and Gn–R(AxBy), respectively, where A and B are the metals comprising the DENs, and x and y represent the stoichiometry used in the synthesis. Core@shell bimetallic DENs are denoted as Gn–R(Ax@By), where A and B are the metals comprising the core and shell materials, respectively. Typically, “magic number” values of x and y are chosen to yield nanoparticles having stable, closed shell structures. For instance, fcc cuboctahedral particles with one, two, and three complete shells contain 13, 55, and 147 atoms, respectively.
As mentioned previously, the PAMAM family of dendrimers is most frequently used for synthesizing DENs, and, unless otherwise indicated, the studies discussed in this review refer to them. Note, however, that other types of dendrimers, such as the poly(propylene imine) (PPI),51,52phenylazomethine (DPA),53,54 and triazole55–57 families have also been used for this purpose. An important distinction can be made between dendrimer-stabilized nanoparticles (DSNs) and DENs. DSNs differ from DENs in that DSNs are not located within the voids of a single dendrimer, but rather are stabilized by the peripheral groups of the dendrimer. Therefore, DSNs are stabilized by multiple dendrimers and are usually quite a bit larger than DENs. DSNs are not included within the scope of this review.
New synthetic routes and novel DEN materials
Synthetic methods for preparing DENs having interesting compositions and structures continue to emerge. Recent advances include the synthesis of DENs in organic solvents, the use of galvanic exchange to yield both monometallic and bimetallic structures, and the synthesis of core@shell DENs via underpotential deposition (UPD).Hydrophobic DENs
In the last review we discussed the extraction of DENs into organic solvents by use of appropriate ligands, usually alkanethiols. This extraction process removes the nanoparticle from the dendrimer in the form of a monolayer-protected cluster (MPC, Scheme 2) composed of a metal center surrounded by a protective layer of strongly adsorbed ligands.35,58 Similar materials prepared by direct reduction of the metal salt in the presence of alkanethiols have been studied extensively by Murray and others.59 However, it is possible to prepare DENs directly in organic solvents using PAMAM dendrimers functionalized on their periphery with hydrophobic groups. This provides a means for synthesizing DENs comprised of air- and water-sensitive metals.60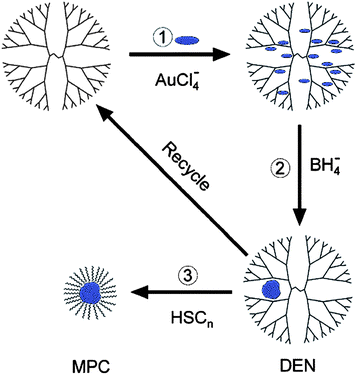 | ||
| Scheme 2 | ||
An example of this approach involved the synthesis of Au DENs in toluenevia direct dendrimer templating using G4 PAMAM dendrimers functionalized on their periphery with dodecyl groups (G4–C12).60UV-vis spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) indicated that Au DENs synthesized in toluene are nearly indistinguishable from those synthesized in water.13,21,61 The Au DENs prepared in toluene could then be extracted into water (the inverse of the process shown in Scheme 2) as MPCs using the hydrophilic ligands tiopronin and glutathione. This synthesis established the general synthetic method used for more reactive, oxophilic metals.
Ni and Fe DENs62,63 cannot be prepared in water, but we showed they could be synthesized and were stable in G6–C12 dendrimers dissolved in N2-saturated toluene. The characterization of these materials was accomplished using UV-vis spectroscopy, TEM, and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). Time-resolved UV-vis studies of Ni and Fe DENs showed that the DENs are stable indefinitely in the absence of air and water, but that they degrade within minutes upon exposure to air. TEM sizing of G6–C12(Ni55) and G6–C12(Ni147) indicated diameters of 0.8 ± 0.2 nm and 1.2 ± 0.3 nm, respectively. These values can be compared to the calculated diameters of 1.0 and 1.2 nm, respectively. G6–C12(Fe55) and G6–C12(Fe147) have diameters of 0.9 ± 0.2 nm and 1.1 ± 0.2 nm, respectively, close to the predicted values of 0.8 and 1.2 nm, respectively. Magnetic characterization, using a superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID), revealed that both sizes of Ni DENs are ferromagnetic and exhibit low hysteresis and suppressed magnetic saturation. The Fe particles vary from superparamagnetic (55-atom DENs) to ferromagnetic (147-atom DENs) depending on the particle size (Fig. 1). These studies provide a good example of how quickly physical properties change as a function of nanoparticle size.
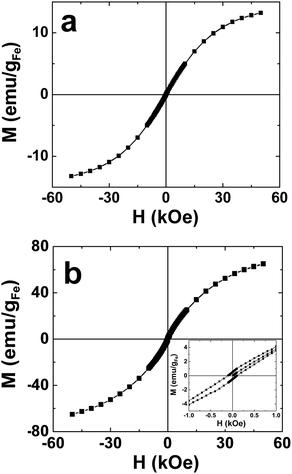 | ||
| Fig. 1 Magnetization (M) of (a) G6–C12(Fe55) and (b) G6–C12(Fe147) DENs as a function of the applied magnetic field (H) (M–H loops). The inset in frame (b) shows the hysteresis associated with the G6–C12(Fe147) DENs. | ||
NiSn bimetallic DENs containing ∼147 atoms, which are being investigated for Li battery applications,64,65 were synthesized under a N2 atmosphere in toluene at five different Ni:Sn ratios.66 In this case, we believe that sequestration of Ni2+ and Sn2+ ions within G6–C12 dendrimers is not due to specific interactions with interior functional groups, but rather to increased solubility of the ions within the dendrimer core relative to the much more hydrophobic solvent. TEM, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), EDS, and UV-vis spectroscopy indicated that co-reduction of the two metals yields bimetallic DENs having diameters comparable to the expected values.
Chandler et al. synthesized supported Au and NiAu bimetallic DENs by anchoring G5–NH2 PAMAM dendrimers onto silica supports prior to complexation.36 The anchored dendrimers were alkylated and suspended in toluene. Au2+ and Ni2+ ions were co-complexed to the dendrimers followed by purification and chemical reduction with BH4− in MeOH. The total metal ion:dendrimer ratio was maintained at 147![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. After reduction, the particles were extracted as MPCs from within the supported dendrimers using decanethiol. TEM micrographs obtained after extraction indicated particle sizes of 2.2 ± 0.5 nm. Single-particle EDS was used to prove the bimetallic composition of the particles. The MPCs were then deposited onto a metal oxide support and the capping agents were thermally removed for further catalytic studies.
1. After reduction, the particles were extracted as MPCs from within the supported dendrimers using decanethiol. TEM micrographs obtained after extraction indicated particle sizes of 2.2 ± 0.5 nm. Single-particle EDS was used to prove the bimetallic composition of the particles. The MPCs were then deposited onto a metal oxide support and the capping agents were thermally removed for further catalytic studies.
Galvanic exchange
Galvanic exchange refers to an electrochemical process in which electrons transfer between two metals in different oxidation states and having different redox potentials (eqn (1)).| A(0) + Bm+ → Am+ + B(0) | (1) |
Recently, we used this approach to synthesize G6–OH(Pt55) and G6–OH(Pd55) DENs from G6–OH(Cu55) precursor nanoparticles.26 The standard potentials for the relevant half reactions are given in eqn (2)–(4).68
| Cu2+ + 2e− = Cu(s) E0 = 0.340 V | (2) |
| PtCl42− + 2e− = Pt(s) + 4Cl− E0 = 0.579 V | (3) |
| PdCl42− + 2e− = Pd(s) + 4Cl− E0 = 0.620 V | (4) |
| G6–OH(Cu55) + 55 PtCl42− → 55 Cu2+ + G6–OH(Pt55) + 220 Cl− | (5) |
| G6–OH(Cu55) + 55 PdCl42− → 55 Cu2+ + G6–OH(Pd55) + 220 Cl− | (6) |
Fig. 2 shows the UV-vis spectra for G6–OH(Cu2+)55, G6–OH(Cu55), and G6–OH(Pt55). The spectrum of the Cu precursor complex is dominated by a strong absorbance at λmax = 300 nm, which arises from a ligand-to-metal charge transfer (LMCT) between the tertiary amines of the dendrimer and Cu2+.25,26 After addition of a reducing agent, BH4−, the strong absorbance at 300 nm is replaced with a spectrum exhibiting monotonically increasing absorbance toward higher energy, which is characteristic of Cu DENs.25,26 The absence of a plasmon band at ∼570 nm confirms that the Cu particles are in the correct size range.69,70
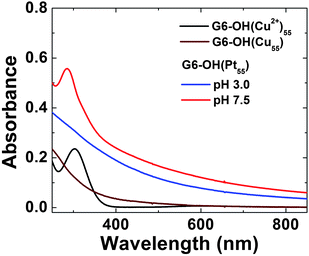 | ||
| Fig. 2 Absorption spectra of 10.0 μM G6–OH(Cu2+)55 (pH 7.5), G6–OH(Cu55) (pH 8.0), and G6–OH(Pt55) DENs (pH 7.5 and 3.0). All the spectra were collected in a 1.0 mm cuvette using a 10.0 μM G6–OH blank. | ||
At pH 7.5, the Pt DENs formed by galvanic exchange exhibit two spectral features (Fig. 2): a sloping baseline and a prominent band at λmax = 290 nm. These features arise from the Pt nanoparticles and the amine/Cu2+ LMCT band, respectively. The presence of the LMCT band indicates that after galvanic exchange Cu2+ recomplexes to the dendrimer. However, at pH 3.0 protons compete for the tertiary amine binding sites, Cu2+ is expelled from the dendrimer, and the LMCT band is lost. Dialysis at pH 3 makes it possible to remove Cu2+ from the DEN solution. UV-vis spectra of G6–OH(Pd55) prepared by galvanic exchange at pH 3.0 and 7.5 exhibit similar characteristics to those shown in Fig. 2.
A number of different techniques have been used to characterize Pt and Pd DENs prepared by galvanic exchange. For example, TEM indicates that 55-atom Pt and Pd DENs have the expected sizes (1.5 ± 0.2 and 1.4 ± 0.2 nm, respectively), and XPS was used to show that the Pt2+ and Pd2+ are fully reduced, zerovalent metals after galvanic exchange. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis indicates the Pt–Pt coordination number (CN) for G6–OH(Pt55) DENs is 7.4 ± 0.8, close to the calculated CN of 7.86 for a perfect 55-atom cuboctahedron.71 Taken together, these results indicate that a one-to-one exchange occurs between the reduced metal and the oxidized Cu during intradendrimer galvanic exchange.
The galvanic exchange method allows Pt DENs to be prepared in ∼3 h, as compared to 96 h for the usual BH4−-based Pt DENs synthesis (Scheme 1). Moreover, Pt DENs prepared by galvanic exchange are fully reduced, unlike those prepared by the conventional chemical reduction method (vide infra).72
Partial galvanic exchange of a metal nanoparticle has been proposed as a method to produce bimetallic DENs.26 Specifically, addition of a substoichiometric amount of the more noble metal ions would result in exchange of just a fraction of the original DEN. This approach has been reported to yield bimetallic Pt@Au particles from Cu DEN precursors.73 However, the resulting nanoparticles were larger than expected for DENs, and it seems likely they were actually DSNs.
Underpotential deposition
UPD is normally thought of as the reductive electrodeposition of cations at potentials more positive than their standard potential.74 This method provides high surface selectivity and can be used to synthesize core@shell nanoparticles having a single atomic layer shell or in some cases a submonolayer shell.75–78 Furthermore, the UPD monolayer can subsequently be galvanically exchanged for a more noble metal, thereby expanding the scope of this method.75–77,79 The use of UPD for synthesizing nanoparticles having core@shell structures was pioneered by Adzic and co-workers, particularly for synthesizing oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) electrocatalysts having low Pt loadings,75,76,79 and we have adopted this same general approach for synthesizing core@shell DENs.80,81We have used the UPD method to deposit a single monolayer of Cu onto Pt DENs comprised of 55–225 atoms.81 The synthesis is carried out by preparing the Pt DEN cores, immobilizing them onto a glassy carbon electrode (GCE),34 and then depositing a monolayer of Cu onto their surface viaUPD. As shown in Fig. 3, a voltammetric wave having two distinct reduction peaks is observed for UPD onto the largest Pt core, but only a single broad peak is present for the two smaller cores. This suggests that the UPD process is better defined on the larger, more highly faceted core. That is, as the size of the facets increase, UPD occurs at distinct potentials on the 111 and 100 facets of the DENs.
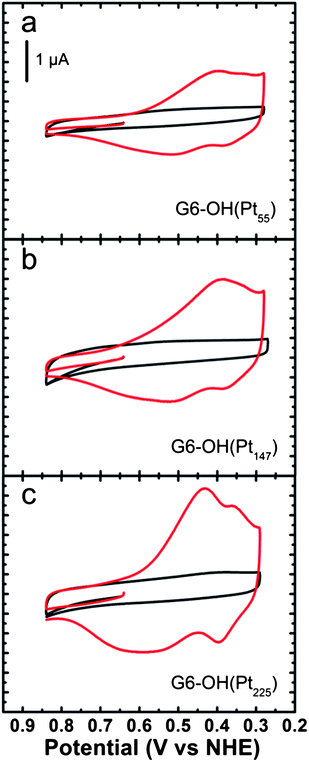 | ||
| Fig. 3 Cyclic voltammograms obtained using GCEs modified with the indicated G6–OH(Ptx) DENs in aqueous electrolyte solutions containing 0.10 M H2SO4 only (black) and 0.10 M H2SO4 + 0.010 M CuSO4 (red). The Cu UPD potential region is shown. The solutions were deoxygenated with Ar. The scans started at 0.64 V and were initially swept in the positive direction at a rate of 10 mV s−1. Reprinted with permission from ref. 81. Copyright 2011 American Chemical Society. | ||
The ratio of Cu shell atoms to Pt atoms on the surface of the core, which we call θCu, was determined by comparing the Pt surface area, measured by H-atom desorption,82 to the amount of Cu deposited. The latter value was found by integrating the area under the Cu UPD peaks and converting this charge to total moles of Cu. The value of θCu is 1.0 for 147- and 225-atom Pt DEN cores, but θCu could be as much as 1.2–1.5 for the 55-atom cores. Note that complete Cu shells for cores containing 55, 147, and 225 Pt atoms have θCu values of 2.2, 1.8, and 1.7, respectively. This suggests that only the facets of the two larger DENs are decorated with Cu, while the facets, edges, and corner sites are all covered on the 55-atom core. As discussed later, EXAFS was also used to confirm the core@shell structure of the DENs.
In a separate UPD study, G6–OH(Au147) DENs were immobilized on a GCE followed by UPD of a Cu monolayer.80 Galvanic exchange of the Cu monolayer for Pt resulted in Au@Pt DENs. The surface composition of these particles was determined by integrating the voltammetric peaks associated with reduction of surface Au oxide and Pt oxide. The Pt shell coverage, θPt, was calculated as 0.85 by this method. The activity of these particles toward the ORR was very close to that of G6–OH(Pt147) DENs synthesized by the usual BH4−reduction method.
The UPD synthetic method presents many new options for core@shell DEN configurations that cannot be achieved by homogeneous reduction methods. For example, it might be possible to prepare core@shell nanoparticle structures having well-defined, facet selective partial coverages of the shell metal.
Characterization of DENs
Accurate characterization of DENs is critical for correlating their structure and function. However, two of the principal attributes of DENs, their small size and their location within the interior of a bulky hydrocarbon framework, make this task difficult. Additionally, as synthesis methods have continued to improve and yield ever more complex DENs, the analytical demands have become correspondingly greater. Accordingly, we have focused substantial effort on improving and expanding methods for characterizing DENs.Structural characterization of DENs
The structural characteristics of DENs include their crystallinity, degree of disorder, and, for bimetallics, degree of spatial segregation of the two metals. An understanding of surface structure is particularly important, because it can directly influence catalytic reactions.The small size of DENs precludes structural characterization techniques that require long-range order, such as typical X-ray diffraction (XRD). However, EXAFS and X-ray diffraction-pair distribution function (XRD-PDF) are useful for analyzing even the smallest DENs. EXAFS provides information about the coordination environment of an absorbing atom, including the number, type, and bond distances of neighboring atoms. EXAFS is particularly powerful for analyzing DENs, because the average CN drops precipitously as particle size decreases and a higher fraction of atoms reside on the particle surface. For example, surface-to-interior atom ratios for 147- and 55-atom cuboctahedra are 1.7 and 4.2, respectively, and therefore EXAFS is quite sensitive to small changes in the size (and shape) of DENs.83 XRD-PDF measures the distribution of mass in a sample and can be used to determine atomic structure in amorphous materials. The experimental PDF, G(r), is given by eqn (7), where ρ(r) and ρ0 are the local and atomic number densities, respectively.
| G(r) = 4πr(ρ(r) − ρ0) | (7) |
A recent study demonstrates the power of combining EXAFS with XRD-PDF and other analytical methods to solve complicated structural problems. In one particular case, the problem was that several studies suggested that the structure of Pt DENs was highly sensitive to the method used to prepare them.8,34,72,84–86 This situation is in contrast to DENs synthesized from most other metals, which is quite straightforward. To better understand the products of the homogeneous-reduction method for preparing Pt DENs, we used a combination of EXAFS and XRD-PDF, as well as UV-vis spectroscopy, TEM, and XPS to characterize both dry and wet (solution-phase) G6–OH(Ptx) (x = 55, 147, 240) DENs.72 The XPS, UV-vis spectroscopy, and EXAFS data indicated incomplete reduction of the G6–OH(Pt2+)x precursor. For example, Fig. 4a and 4b show the Pt–Pt CNs for dry and wet Pt DENs determined using EXAFS. In both cases, the experimentally determined CNs are much lower than those expected on the basis of the precursor stoichiometry (Fig. 4c). However, because EXAFS measures the average coordination environment of an element, it cannot distinguish between a mixture of configurations having high and low CNs and a single configuration having an intermediate CN. Taken together with the XPS and UV-vis spectroscopy results, the seemingly obvious conclusion is that each dendrimer contains some reduced Pt (in the form of a smaller-than-expected nanoparticle) and some unreduced Pt (in the form of the precursor complex in which the Pt–Pt CN = 0). Interestingly, however, TEM micrographs indicated particle sizes close to those expected for fully reduced DENs.
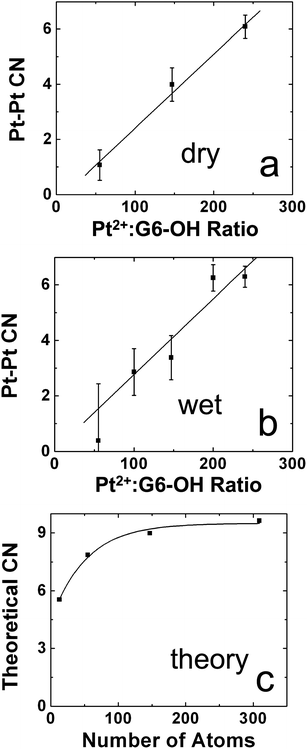 | ||
| Fig. 4 Comparison of the Pt–Pt CNs for (a) dry and (b) wet Pt DENs at the indicated Pt2+:G6–OH ratios. (c) Calculated M–M CNs for cuboctahedral particles in this size range. Reprinted with permission from ref. 72. Copyright 2008 American Chemical Society. | ||
To resolve this apparent inconsistency, we turned to XRD-PDF analysis, which confirmed the TEM results. Both XRD-PDF and TEM are insensitive to the presence of unreduced complex: only nanoparticles will be detected using these techniques. The only model that fit the results from all of these analytical methods is one in which some dendrimers contained fully reduced Pt DENs and others contained only the original precursor ions. This counterintuitive bimodal distribution model was rationalized by invoking a mechanism involving autocatalytic growth of the DENs. That is, zerovalent Pt seeds are formed by chemical reduction in some dendrimers, and these seeds catalyze complete reduction of all Pt2+ present in those dendrimers. However, in other dendrimers these seeds do not form, and hence no subsequent particle growth is observed.
Structural characterization of bimetallic DENs
EXAFS is a suitable probe for distinguishing between certain bimetallic structures. Specifically, small core@shell, alloyed, and cluster-on-cluster nanoparticles have differentiable homo and hetero metal–metal CNs. We have used this fact to investigate the structures of PdAu,12,87PdCu,88 and PtCu81 DENs. For example, 147-atom PdAu DENs having different Pd:Au ratios were synthesized using two different methods: co-complexation and sequential reduction (Scheme 3).12,87EXAFS suggested that DENs synthesized using the co-complexation approach are quasi-random alloys (alloys with partial surface segregation of Pd), whereas DENs prepared by sequential reduction have a core@shell type structure.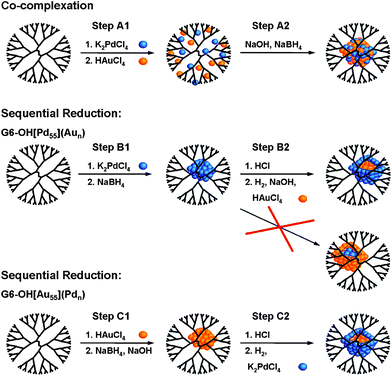 | ||
| Scheme 3 | ||
Fig. 5 shows the metal–metal CNs for DENs prepared by co-complexation as a function of the mole fraction of Pd in the DENs.87 Here, M signifies coordination to both Au and Pd, and so Pd–M is the sum of the Pd–Pd and Pd–Au CNs. The linear relationships between the Pd–Pd, Pd–Au, and Au–Au CNs and the amount of Pd in the DEN are consistent with those expected for an alloyed structure. In contrast, a core@shell configuration would exhibit greater homonuclear-bonding at high and low Pd loadings. Likewise, the Pd–M and Au–M values are not a strong function of the Pd content, which indicates that the relative number of surface and interior atoms of each metal does not change with composition. The slightly higher values of the Au–M CNs relative to the Pd–M CNs suggest some segregation of Pd to the surface of the particle.
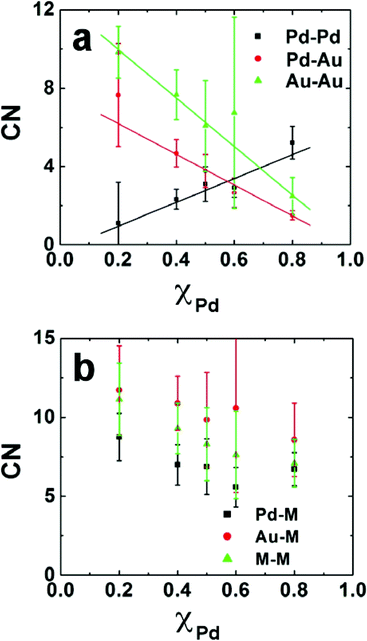 | ||
| Fig. 5 (a) Experimentally obtained partial CNs for 147-atom Pd–Pd, Pd–Au, and Au–Au DENs prepared by co-complexation. (b) Pd–M, Au–M, and M–M CNs as a function of Pd composition. | ||
The sequential reduction method requires synthesis of a monometallic nanoparticle core followed by reduction of a second shell metal (Scheme 3). Accordingly, we prepared 55-atom Pd and Au cores, and then deposited either one or two monolayers of the other metal onto the seed.12 An EXAFS analysis of the metal-metal CNs, similar to that discussed in the previous paragraph, was then carried out. Interestingly, Pd enrichment was observed on the DEN surface regardless of the order of reduction of the two metals (Scheme 3). We also used a surface-specific catalytic reaction to probe the PdAu structure. Specifically, it is know that the catalytic conversion of resazurin to resorufin occurs in the presence of small Au particles but not on similar-sized Pd particles. We found that the PdAu DENs prepared by the sequential reduction method did not catalyze the conversion to resorufin. Like the EXAFS results, this finding also indicates a high degree of Pd segregation to the DEN surface.
In situ structural characterization
To develop meaningful correlations between the structure and function of nanoscale catalysts, it is imperative that the structure of the catalyst be understood during the reaction of interest. Accordingly, we have undertaken spectroelectrochemical studies of electrocatalytic reactions using X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS).81,89 For example, we examined the structure of G6–OH(Pt240) DENs before, during, and after adsorption of a CO monolayer. For these experiments, the DENs were immobilized on a carbon paper electrode, and the XAS measurements were obtained with the electrode (and DENs) under potential control. In contrast to the previously discussed results for Pt DEN precursors reduced using BH4−, in which only a fraction of the total Pt is reduced, the Pt–Pt CN determined by EXAFS indicated complete reduction when the DENs were under electrochemical control. No significant change to the Pt–Pt CN was observed upon adsorption of CO, but a low Z contribution consistent with adsorbed CO was detected. After removing the CO adlayer electrochemically, a small drop in the Pt–Pt CN was observed, although the change was within the uncertainty of the measurements. We concluded that CO adsorption and desorption does not change the structure of Pt DENs.The interesting results described in the previous paragraph laid the groundwork for additional in situ structural studies of DENs. For example, we recently reported an in situXAS analysis of Cu UPD onto G6–OH(Pt225).81 Like the previously discussed CO study, these Pt DENs were immobilized on a carbon paper electrode and XAS spectra were obtained before, during, and after deposition of a single atomic layer of Cu. The experimental results were compared to a theoretical model based on a Pt@Cu DEN composed of a truncated octahedron Pt core having 225 atoms and a Cu shell decorating only the facet positions.81 The Pt–Pt CNs indicated that Cu did not partition from the shell into the core, and the Cu–Cu and Pt–Cu CNs were consistent with the core@shell model. Additionally, some compression of the Pt lattice was observed, which is expected for Pt nanoparticles of this size.90 Tensile strain of the Cu lattice was also observed, due to templating of the Cu shell by the underlying Pt lattice.91,92
Encapsulation
When DENs were first reported, evidence for encapsulation was circumstantial. However, support for this architecture was provided by an early TEM study of Au DENs.13 In this study, the dendrimers were stained with a dye that provided electron contrast, so that colocalization of the nanoparticles and dendrimers could be confirmed. More recent studies of the spatial relationship between the DEN and the surrounding dendrimer have also appeared, and these are discussed next.One of these studies monitored CO adsorption onto the surface of both dried and solution-phase Pt DENs in a variety of solvents.93 It was found that in polar solvents CO adsorbed strongly and extensively to the DEN surface. However, dry DENs exhibited weaker adsorption and lower coverages of CO. This study concluded that in poor solvents (air and low dielectric liquids) the dendrimer collapses onto the surface of the encapsulated DEN and thereby shields it from interactions with adsorbates like CO. In contrast, good solvents for the dendrimer expand its structure and permit interactions between small molecules and the encapsulated nanoparticle. These observations are only consistent with the nanoparticles being fully encapsulated within the dendrimer host.
A similar study used alkanethiols to carry out solvent-selective poisoning of the surface of Pt DEN catalysts.34 In this case, DENs encapsulated in hydroxyl-terminated PAMAM dendrimers were immobilized onto an electrode surface and then exposed to alkanethiols in either polar or nonpolar solvents. In polar solvents, the alkanethiols strongly bound to the Pt DENs and inhibited electrocatalytic reactions. However, in nonpolar solvents, no poisoning was observed. The results were interpreted exactly as described in the previous paragraph, thereby providing additional evidence for nanoparticle encapsulation.
High-resolution NMR studies of Pd DENs also provide evidence for nanoparticle encapsulation.20,94Fig. 6 shows the methylene region of 1H-NMR spectra for G4–OH, G4–OH(Pd2+)55, and G4–OH(Pd55), as well as peak assignments for the PAMAM dendrimer structure. The peak assignments for G4–OH were made using a combination of 1H, 1H–1H correlation spectroscopy (COSY) NMR, 1H–15N heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) NMR, 1H–13C heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) NMR, and 1H–13C HMBC NMR.20 As indicated in Fig. 6, the peak positions of the peripheral methylene groups (those located closest to the terminal functional groups) are shifted relative to the peaks of the interior methylene groups. Interestingly, all of the 1H peaks originating from the dendrimer disappear upon complexation of Pd2+. This is likely a consequence of Pd2+ breaking the symmetry of the dendrimer. However, after reduction with BH4−, the dendrimer peaks return (with slightly decreased intensity), but the relative intensity of the internal methylene peaks to those of the peripheral methylene peaks decreases. This suggests a partial breaking of the interior symmetry of the dendrimer. However, when the Pd DEN is extracted from the dendrimer using short-chain thiols, the peak intensities of the functional groups return to the initial free dendrimer values. This is strong evidence that the Pd particle is encapsulated by the dendrimer.
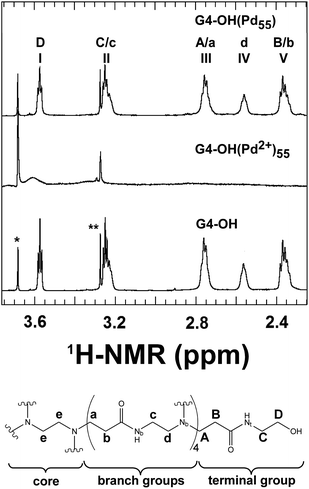 | ||
| Fig. 6 (Top) 1H NMR spectra of G4–OH, G4–OH(Pd2+)55, and G4–OH(Pd55). The peak marked with a single asterisk arises from the dioxane internal standard, and the peak marked with a double asterisk arises from residual methanol. (Bottom) Schematic representation of G4–OH indicating the lettering scheme used to identify the methylene and nitrogen groups. Reprinted with permission from ref. 20. Copyright 2009 American Chemical Society. | ||
The final evidence for encapsulation was demonstrated using two techniques that measure changes to the hydrodynamic radius of the dendrimer after nanoparticle formation: pulsed-field gradient spin-echo (PFGSE) NMR20,94 and quasi-elastic light scattering (QLS).95 The PFGSE NMR results indicated a radius of 2.0 ± 0.2 nm for both G4–OH and G4–OH(Pd55),20 and a radius of 3.3 ± 0.3 nm for G6–OH and G6–OH(Pdx) (x = 55, 147, 200, 250).94 If the nanoparticle is truly encapsulated within the dendrimer, then the hydrodynamic radius of the dendrimer should not be affected by its presence. Clearly, that is the case here.
We also used QLS to determine the hydrodynamic radius of G6–OH(Pd147), and under similar solution conditions the result (3.3 ± 0.3 nm) was the same as determined by PFGSE NMR.95 Similar results were obtained for G6–OH(Au147) (3.2 ± 0.2) and G6–OH(Pt147) (4.0 ± 0.2 nm).95 However, under certain solution conditions, primarily around neutral pH, the hydrodynamic radius of G6–OH(A147) (A = Pd, Au and Pt) was found to nearly double, even though the size of the empty dendrimer (G6–OH) and the precursors (for example, G6–OH(Pt2+)147) maintained a normal radius of around 3.5 nm. Importantly, there was no indication of aggregation in the TEM analysis of G6–OH(A147) (A = Pd, Au and Pt). Thus, the physical phenomenon responsible for the anomalous size increase, measured by QLS, of these DENs at neutral pH remains something of a mystery.
The surface metal atoms of DENs do not seem to be significantly passivated by the interior functional groups of the PAMAM dendrimer. Indirect evidence for this is given by the high catalytic rates exhibited by DENs.14,34 Additionally, a recent EXAFS study of G6–OH(Au147) DENs indicated an upper limit of 15 nitrogen or oxygen interactions with the metal surface.21 This indicates at least 84% of the surface remains accessible for catalytic reactions.
Probes of DEN size
TEM is the most common method for measuring the size of DENs. Other standard characterization techniques for this size regime, for example atomic force microscopy (AFM), are hindered by the presence of the dendrimer shell.96 Although TEM can be an effective means for size determination, it suffers from three drawbacks. First, routine electron microscopy does not provide sufficient resolution to distinguish between particles having sizes that vary by just a few tens of atoms. Aberration-corrected microscopes should provide this level of resolution, but they have only recently become available and are still relatively inaccessible. Second, TEM samples are typically imaged in vacuum or a low-pressure gas, and this excludes (for now) liquid-phase, in situ studies. Third, the sample configuration (for example, apparent agglomeration) can change during TEM sample preparation.There are several indirect measures of particle size that corroborate the TEM findings. For example, the optical plasmon band of solution-phase DENs can be used to estimate, or least set an upper bound, on their size if they are comprised of appropriate metals, such as Ag, Au, or Cu.97 For instance, Cu nanoparticles <3 nm in diameter do not exhibit a plasmon band in the UV-vis.1 As mentioned earlier, size information may also be obtained from EXAFS data. This is because the ratio of surface to interior atoms increases significantly with decreasing size for particles <2 nm in diameter. Accordingly, the predicted CNs for cuboctahedral particles containing 55 and 147 atoms are 7.86 and 8.98, respectively, and such values can usually be distinguished.
As described in the previous section, the relative 1D 1H-NMR peak intensities of the internal dendrimer functional groups are reduced by the presence of DENs. Indeed, a correlation exists between the size of DENs and the damping of the NMR signal.94 To demonstrate this principle, we compared the D/d ratio (Fig. 6) for G6–OH(Pdx) (x = 55, 147, 200, 250) DENs and found it scaled linearly with particle size (Fig. 7). This method of characterization may be useful for research groups without access to high-resolution TEM. Furthermore, this experimental method provides a means for in situ analysis of DENs.
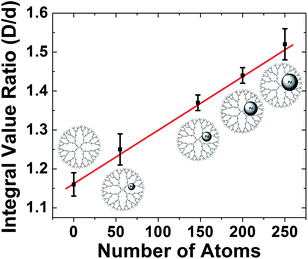 | ||
| Fig. 7 Ratio of the integrated D/d peak intensities of 1H NMR spectra for G6–OH(Pdx) (x = 55, 147, 200, 250) as a function of the average number of atoms in the DENs. | ||
Mass spectrometry (MS) is a powerful method for determining the composition of small nanoparticles.59 The ability of MS for measuring the size of DENs depends upon the nature of the dendrimer encapsulating the particle. For example, Yamamoto and co-workers used matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight (MALDI-TOF) MS to measure the size of Rh DENs synthesized in G4 DPA dendrimers.54 Unfortunately, we have been unable to obtain informative spectra of DENs synthesized in PAMAM dendrimer using either MALDI-TOF98 or electrospray ionization MS. In fact, obtaining reliable MS spectra for high-generation PAMAM dendrimers, even in the absence of an encapsulated nanoparticle, is challenging.99
Catalytic and electrocatalytic DENs
Homogenous catalysis
In our last review of this field14 we discussed how the dendrimer itself could control access of substrates to encapsulated nanoparticles, and hence enhance catalytic selectivity.32,100 DENs can also serve as model catalysts for correlating the effect of nanoparticle size to activity. For example, the effect of DEN size on the rate of catalytic hydrogenation of allyl alcohol was reported for G6–OH(Pdx) (x = 55, 100, 147, 200, 250).101 In these studies, the turnover frequency (TOF) (normalized to the number of moles of Pd) was determined by measuring the rate of H2 consumption. The results showed that the TOF increased with increasing DEN size. Specifically, the TOF directly correlated to the theoretical number of atoms on the DEN facets (excluding edge atoms) for particles >1.5 nm. Hence, this result was attributed to a geometric effect. In contrast, the TOF for the smallest particles did not correlate to any one specific category of surface atoms, and therefore it was postulated that the decreasing catalytic rates for particles <1.5 nm were due to electronic effects.Astruc and co-workers synthesized Pd DENs in methanol using dendrimers containing 1,2,3-triazolyl ligands and terminated with ferrocenyl-triazole groups and used these materials to study olefin hydrogenation.55,56 In accord with previous findings,32,100 they measured dendrimer-induced selectivity effects that depended on the size of the reactant molecule. Interestingly, the redox potential of the terminal ferrocenyl groups could be used to track the complexation of Pd ions to the dendrimer. The results of this study indicated that Pd2+ forms a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 complex with the triazole groups.
1 complex with the triazole groups.
Nakamula et al. synthesized Rh nanoparticles in G4 DPA dendrimers and G4–OH PAMAM dendrimers, and used them to catalyze the hydrogenation of olefins and nitroarenes.54 The metal ion:dendrimer ratio used in these studies was 60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. The average diameters of the Rh nanoparticles in the G4 DPA dendrimers and the G4–OH dendrimers were reported to be 1.2 ± 0.3 nm and 1.8 ± 0.4 nm, respectively. MALDI-TOF-MS was used to corroborate the size of the nanoparticles in the G4 DPA dendrimers. The Rh DENs contained within the DPA dendrimers were found to be considerably more active than the DENs within G4–OH for olefin hydrogenation. However, the latter were found to be better hydrogenation catalysts for nitroarenes. This effect was attributed to the relative hydrophobicity of the dendrimer cavities and the ability of the reactant molecules to access the catalyst surface.
1. The average diameters of the Rh nanoparticles in the G4 DPA dendrimers and the G4–OH dendrimers were reported to be 1.2 ± 0.3 nm and 1.8 ± 0.4 nm, respectively. MALDI-TOF-MS was used to corroborate the size of the nanoparticles in the G4 DPA dendrimers. The Rh DENs contained within the DPA dendrimers were found to be considerably more active than the DENs within G4–OH for olefin hydrogenation. However, the latter were found to be better hydrogenation catalysts for nitroarenes. This effect was attributed to the relative hydrophobicity of the dendrimer cavities and the ability of the reactant molecules to access the catalyst surface.
In addition to hydrogenation reactions, Pd DENs have been used to catalyze carbon-coupling reactions.14,57,102 However, in these instances the active catalytic species may not be the DEN itself, but rather other Pd species leached from the DENs. This point was emphasized by Terreros and co-workers, who found that Pd(OAc)2 has activity for the aqueous Stille reaction similar to that of Pd DENs.102 They also found that Pd DENs increased in size during the Stille reaction. However, the DENs exhibited better cyclability and selectivity compared to Pd(OAc)2. Astruc and co-workers measured the rate of the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction catalyzed by Pd DENs and DSNs synthesized in the triazolylferrocenyl dendrimers described previously.57 They found that the TOF was independent of the amount of Pd used for catalysis and the method of nanoparticle stabilization (DENvs. DSN). In fact, the TOF and stability improved upon dilution of the catalyst. They concluded that the active catalyst is a leached Pd species. Further evidence for this conclusion came from the observation of a Pd precipitate during catalysis.
To better understand the stability of Pd DENs during catalytic reactions, we monitored the degree of metal leaching from G6–OH(Pd147) in aqueous solutions saturated with air, N2 and H2.103 The results showed that Pd DENs are fully stable for at least 36 h when kept under reducing conditions (H2), but that in the presence of N2 or air some oxidation occurs. In the latter case, about half of the oxidized Pd recomplexes to the interior of the dendrimer, as evidenced by regrowth of the LMCT band in the UV-vis spectrum. However, inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) analysis of solutions after filtration through nominal molecular-weight limiting (NMWL) membranes indicated that the other half of the oxidized Pd irreversibly leaches from the dendrimer. Removal of ions present in the Pd DEN solution using dialysis reduced both Pd oxidation and subsequent leaching from the dendrimer, but it did not completely stabilize the DENs against degradation. For example, ∼15% of the Pd in G6–OH(Pd147) DENs oxidized after 12 h in air-saturated, undialyzed aqueous solutions, and about ∼6% of this oxidized Pd leached from the dendrimer. Dialyzed G6-OH(Pd147) DEN solutions that were kept under N2 exhibited ~4% Pd oxidation of which ~2% leached from the dendrimer, and in H2–saturated, dialyzed solutions no leaching was observed. Interestingly, the Pd2+-dendrimer precursor complex is stable under all of these conditions and no detectable leaching of Pd2+ was observed.
Heterogeneous catalysis
As discussed earlier, the dendrimer itself does not significantly block access of small molecules to the surfaces of DENs in aqueous solutions,14,34,101 but upon drying (or in poor solvents) the dendrimer collapses around the encapsulated nanoparticle.93 As a result, gas-phase catalytic reactions usually proceed very slowly.104 One exception to this general rule was reported by Somarjai and co-workers, who found that even after drying Rh and Pt DENs immobilized on a three dimensional silica support exhibited catalytic activity for ethylene hydrogenation.105 They proposed that interactions between G4–OH and the channel walls of the silica support prevented the dried dendrimer from passivating the encapsulated nanoparticles. Further thermal treatment under mildly reducing conditions resulted in higher catalytic activity. However, XPS studies indicated that the DENs were incompletely reduced during synthesis and that further reduction of the metal occurred after heating. Therefore, it was not possible to attribute the enhanced catalytic activity to increased surface exposure of the DEN.Unfortunately, efforts to remove the dendrimer without changing the composition or structure of the DENs within have thus far been unsuccessful.104,106 Clearly, this is a problem that deserves additional study.
Electrocatalysis
DEN-based electrochemical catalysis is a special case of heterogeneous catalysis. In electrocatalysis, DENs are immobilized on an electrode surface, and the catalytic rate is measured as a function of the electrode potential. As for all forms of DEN-based catalysis, the reactants must permeate the dendrimer periphery and interact directly with the surfaces of the encapsulated DENs. However, in electrocatalysis, electrons from the electrode must also access the nanoparticles. How exactly this happens has not been explored, but the fact that it does happen is unambiguous.We commenced our study of DEN-based electrocatalysis by examining the effect of nanoparticle size on the kinetics of the ORR.107 Specifically, G6–OH(Ptx) (x = 55, 100, 147, 200, 240) DENs were immobilized on a glassy carbon rotating disk electrode (GC RDE), and the specific activity of each size DEN was determined using standard electrochemical methods.34 The results indicated that the kinetics of the ORR decreased monotonically with decreasing particle size. It is a testament to the DENs synthetic method that significant and reproducible differences in ORR kinetics are observed when particle sizes are changed by just a few tens of atoms. Interestingly, the smallest two DENs exhibited decreased mass-transfer limited currents, which could represent a change in the product of the ORR from water to peroxide. Note, however, that there are alternative explanations for this observation.
We also examined ORR kinetics using bimetallic PtPd alloy DENs always containing ∼180 atoms but at different ratios of the two metals.11 The PtPd DENs were synthesized using the co-complexation technique (Scheme 3) and immobilized onto the surface of a GC RDE. The kinetic analysis revealed two important results. First, Tafel plots suggested that the ORR mechanism was the same for PtPd DENs having different elemental compositions. Second, when normalized to the mass of Pt present in each composition, DENs containing Pd:Pt atomic ratios of 30![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 150 and 60
150 and 60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 120 exhibited superior activities compared to Pt-only DENs.
120 exhibited superior activities compared to Pt-only DENs.
Some years ago we showed that positively charged amine-terminated dendrimers immobilized onto an electrode surface can act as molecular gates, blocking access of positively charged species in solution while permitting negatively charged ions to access the substrate.108 This effect was attributed to electrostatic interactions between the redox probes and the positive charges on the protonated dendrimer. Kim and co-workers used this effect to confirm immobilization of amine-terminated Au DENs onto a GCE.109 Immobilized G6–NH2(Au147) DENs were also used in this study to catalyze hydrazine oxidation.
In addition to catalysis on planar electrodes, several groups have immobilized DENs on carbon nanotubes (CNTs), which serve as conductive leads to an electrode surface. For example, Stevenson and co-workers outfitted nitrogen-doped CNTs with Pt DENs contained within amine-terminated dendrimers and used the supported nanoparticles to catalyze the ORR.110 Centrifugal separation and UV-vis spectroscopy were used to monitor adsorption of the DENs onto the CNTs. Adsorption isotherms revealed that the affinity of the Pt DENs for the CNTs increased with increasing edge-plane character of the CNTs. In another study, G4–NH2(Pd40) DENs were anchored to chemically oxidized MWNTs through covalent attachment of the terminal amine groups to carboxyl groups on the nanotube.111 These materials were found to be catalytically active for hydrazine oxidation.
Future outlook
Although the dendrimer-templating method is now more than a decade old, it remains the best method for preparing catalytically active nanoparticles in the 1–2 nm size range that have a high degree of compositional and structural fidelity. Moreover, the presence of the dendrimer ensures particle stability, while also providing a means for solubilizing them or anchoring them to surfaces without damaging the nanoparticles or passivating the metal surface. For these reasons, DENs are excellent models for studying homogeneous, heterogeneous, and mixed homogeneous/heterogeneous catalytic reactions. For example, because DENs contain so few atoms, their catalytic properties can be directly compared to results from first-principles theory. Looking to the future, this is certain to be one of the main directions of DENs-related research. Another area of potential interest is the development of synthetic methods for preparing other types of nanoparticles, including semiconductors, mixed metal/metal oxide materials, and more complex multi-shell structures. We are currently devoting substantial effort to the synthesis of semiconductor DENs.112 Finally, exploring the synergistic effects of the dendrimer and the DEN during catalytic reactions is another area ripe for study.Although DENs are typically very easy to synthesize, characterization of nanoparticles in this size regime is challenging. However, there is currently substantial effort being devoted to atom-resolved TEM and other high-resolution imaging techniques that is bound to be very helpful. We and our collaborators have contributed to the development of both in situ and ex-situ XRD and XAS methods for structure determination. Electrochemical methods have turned out to be especially powerful for evaluating surface structure, and further advances along these lines is assured. Development of reliable mass spectrometry methods for analyzing DENs would be very helpful. Finally, serious theoretical studies are just beginning to emerge, and they offer much promise for a better understanding of the structure of DENs.113–116
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the U. S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences (Grant No. DE-FG02-09ER16090); the U. S. National Science Foundation (Grant No. 0847957); and the Robert A. Welch Foundation (Grant No. F-0032). We are particularly grateful to our current and former co-workers who contributed to key aspects of the research described here: Prof. Neer Asherie (Yeshiva University, USA), Prof. Anatoly Frenkel (Yeshiva University, USA), Dr. M. Victoria Gomez and Dr. Javier Guerra (Universidad de Castilla-La Mancha, Spain), Prof. Graeme Henkelman (UT-Austin, USA), Prof. Marc R. Knecht (University of Kentucky, USA), Prof. Aldrik H. Velders (University of Twente, The Netherlands), Ms. Christina Wales, and Dr. Heechang Ye (OCI Corporation, So. Korea). Finally, we thank Dr Mingqi (Mitch) Zhao, whose original discovery of DENs in 1998 made this work possible.References
- M. Zhao, L. Sun and R. M. Crooks, Preparation of Cu Nanoclusters within Dendrimer Templates, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1998, 120, 4877–4878 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Tarazona-Vasquez and P. B. Balbuena, Pt(II) Uptake by Dendrimer Outer Pockets: 1. Solventless Ligand Exchange Reaction, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2008, 112, 4172–4181 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Tarazona-Vasquez and P. B. Balbuena, Pt(II) Uptake by Dendrimer Outer Pockets: 2. Solvent-Mediated Complexation, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2008, 112, 4182–4193 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Sun and R. M. Crooks, Interactions between Dendrimers and Charged Probe Molecules. 1. Theoretical Methods for Simulating Proton and Metal Ion Binding to Symmetric Polydentate Ligands, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106, 5864–5872 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Tarazona-Vasquez and P. B. Balbuena, Complexation of Cu(II) Ions with the Lowest Generation Poly(amido-amine)-OH Dendrimers: A Molecular Simulation Study, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 12480–12490 CrossRef CAS.
- K. A. Krot, A. F. Danil de Namor, A. Aguilar-Cornejo and K. B. Nolan, Speciation, stability constants and structures of complexes of copper(II), nickel(II), silver(I) and mercury(II) with PAMAM dendrimer and related tetraamide ligands, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2005, 358, 3497–3505 CrossRef CAS.
- M. L. Tran, L. R. Gahan and I. R. Gentle, Structural Studies of Copper(II)-Amine Terminated Dendrimer Complexes by EXAFS, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 20130–20136 CrossRef CAS.
- O. S. Alexeev, A. Siani, G. Lafaye, C. T. Williams, H. J. Ploehn and M. D. Amiridis, EXAFS Characterization of Dendrimer-Pt Nanocomposites Used for the Preparation of Pt/γ-Al2O3 Catalysts, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 24903–24914 CrossRef CAS.
- M. S. Diallo, S. Christie, P. Swaminathan, L. Balogh, X. Shi, W. Um, C. Papelis, W. A. Goddard, III and J. H. Johnson, Jr, Dendritic Chelating Agents. 1. Cu(II) Binding to Ethylene Diamine Core Poly(amidoamine) Dendrimers in Aqueous Solutions, Langmuir, 2004, 20, 2640–2651 CrossRef CAS.
- R. W. J. Scott, A. K. Datye and R. M. Crooks, Bimetallic Palladium–Platinum Dendrimer-Encapsulated Catalysts, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 3708–3709 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ye and R. M. Crooks, Effect of Elemental Composition of PtPd Bimetallic Nanoparticles Containing an Average of 180 Atoms on the Kinetics of the Electrochemical Oxygen Reduction Reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 3627–3633 CrossRef CAS.
- M. G. Weir, M. R. Knecht, A. I. Frenkel and R. M. Crooks, Structural Analysis of PdAu Dendrimer-Encapsulated Bimetallic Nanoparticles, Langmuir, 2010, 26, 1137–1146 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Gröhn, B. J. Bauer, Y. A. Akpalu, C. L. Jackson and E. J. Amis, Dendrimer Templates for the Formation of Gold Nanoclusters, Macromolecules, 2000, 33, 6042–6050 CrossRef.
- R. W. J. Scott, O. M. Wilson and R. M. Crooks, Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of Dendrimer-Encapsulated Nanoparticles, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 692–704 CrossRef CAS.
- J. K. Vohs and B. D. Fahlman, Advances in the controlled growth of nanoclusters using a dendritic architecture, New J. Chem., 2007, 31, 1041–1051 RSC.
- X. Peng, Q. Pan and G. L. Rempel, Bimetallic dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles as catalysts: a review of the research advances, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008, 37, 1619–1628 RSC.
- B. D. Chandler and J. D. Gilbertson, Dendrimer-Encapsulated Bimetallic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications to Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis, Top. Organomet. Chem., 2006, 20, 97–120 CrossRef CAS.
- C. M. Aikens, Electronic Structure of Ligand-Passivated Gold and Silver Nanoclusters, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2011, 2, 99–104 CrossRef CAS.
- B. R. Cuenya, Synthesis and catalytic properties of metal nanoparticles: Size, shape, support, composition, and oxidation state effects, Thin Solid Films, 2010, 518, 3127–3150 CrossRef CAS.
- M. V. Gomez, J. Guerra, A. H. Velders and R. M. Crooks, NMR Characterization of Fourth-Generation PAMAM Dendrimers in the Presence and Absence of Palladium Dendrimer-Encapsulated Nanoparticles, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 341–350 CrossRef CAS . Correction: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15564.
- V. Petkov, N. Bedford, M. R. Knecht, M. G. Weir, R. M. Crooks, W. Tang, G. Henkelman and A. Frenkel, Periodicity and Atomic Ordering in Nanosized Particles of Crystals, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 8907–8911 CAS.
- G. A. Somorjai and C. Aliaga, Molecular Studies of Model Surfaces of Metals from Single Crystals to Nanoparticles under Catalytic Reaction Conditions. Evolution from Prenatal and Postmortem Studies of Catalysts, Langmuir, 2010, 26, 16190–16203 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Burda, X. Chen, R. Narayanan and M. A. El-Sayed, Chemistry and Properties of Nanocrystals of Different Shapes, Chem. Rev., 2005, 105, 1025–1102 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Lee, S. E. Habas, S. Kweskin, D. Butcher, G. A. Somorjai and P. Yang, Morphological Control of Catalytically Active Platinum Nanocrystals, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 7824–7828 CrossRef CAS.
- R. M. Crooks, M. Zhao, L. Sun, V. Chechik and L. K. Yeung, Dendrimer-Encapsulated Metal Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications to Catalysis, Acc. Chem. Res., 2001, 34, 181–190 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhao and R. M. Crooks, Intradendrimer Exchange of Metal Nanoparticles, Chem. Mater., 1999, 11, 3379–3385 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhao and R. M. Crooks, Homogeneous Hydrogenation Catalysis with Monodisperse, Dendrimer-Encapsulated Pd and Pt Nanoparticles, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1999, 38, 364–366 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Chechik, M. Zhao and R. M. Crooks, Self-Assembled Inverted Micelles Prepared from a Dendrimer Template: Phase Transfer of Encapsulated Guests, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121, 4910–4911 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Chechik and R. M. Crooks, Dendrimer-Encapsulated Pd Nanoparticles as Fluorous Phase-Soluble Catalysts, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000, 122, 1243–1244 CrossRef CAS.
- L. K. Yeung, C. T. Lee, Jr., K. P. Johnston and R. M. Crooks, Catalysis in supercritical CO2 using dendrimer-encapsulated palladium nanoparticles, Chem. Commun., 2001, 2290–2291 RSC.
- Y. Niu and R. M. Crooks, Dendrimer-Encapsulated Metal Nanoparticles and their applications to Catalysis, C. R. Chim., 2003, 6, 1049–1059 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Niu, L. K. Yeung and R. M. Crooks, Size-Selective Hydrogenation of Olefins by Dendrimer-Encapsulated Palladium Nanoparticles, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123, 6840–6846 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Li and M. A. El-Sayed, The Effect of Stabilizers on the Catalytic Activity and Stability of Pd Colloidal Nanoparticles in the Suzuki Reactions in Aqueous Solution, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, 105, 8938–8943 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ye and R. M. Crooks, Electrocatalytic O2 Reduction at Glassy Carbon Electrodes Modified with Dendrimer-Encapsulated Pt Nanoparticles, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 4930–4934 CrossRef CAS.
- J. C. Garcia-Martinez and R. M. Crooks, Extraction of Au Nanoparticles Having Narrow Size Distributions from within Dendrimer Templates, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 16170–16178 CrossRef CAS.
- B. D. Chandler, C. G. Long, J. D. Gilbertson, C. J. Pursell, G. Vijayaraghavan and K. J. Stevenson, Enhanced Oxygen Activation over Supported Bimetallic Au–Ni Catalysts, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 11498–11508 CAS.
- C. J. Crump, J. D. Gilbertson and B. D. Chandler, CO Oxidation and Toluene Hydrogenation by Pt/TiO2 Catalysts Prepared from Dendrimer Encapsulated Nanoparticle Precursors, Top. Catal., 2008, 49, 233–240 CrossRef CAS.
- N. N. Hoover, B. J. Auten and B. D. Chandler, Tuning Supported Catalyst Reactivity with Dendrimer-Templated Pt–Cu Nanoparticles, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 8606–8612 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Shi, S. H. Wang, I. Lee, M. Shen and J. R. Baker, Jr, Comparison of the internalization of targeted dendrimers and dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles into cancer cells, Biopolymers, 2009, 91, 936–942 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Shi, S. H. Wang, M. Shen, M. E. Antwerp, X. Chen, C. Li, E. J. Petersen, Q. Huang, W. J. Weber, Jr. and J. R. Baker, Jr., Multifunctional Dendrimer-Modified Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes: Synthesis, Characterization, and In Vitro Cancer Cell Targeting and Imaging, Biomacromolecules, 2009, 10, 1744–1750 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Vögtle; G. Richardt; N. Werner. Dendrimer Chemistry: Concepts, Syntheses, Properties, Applications. Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, 2009 Search PubMed.
- D. Méry and D. Astruc, Dendritic catalysis: Major concepts and recent progress, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2006, 250, 1965–1979 CrossRef.
- M. J. Cho, D. H. Choi, P. A. Sullivan, A. J. P. Akelaitis and L. R. Dalton, Recent progress in second-order nonlinear optical polymers and dendrimers, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2008, 33, 1013–1058 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Astruc, C. Ornelas and J. Ruiz, Metallocenyl Dendrimers and Their Applications in Molecular Electronics, Sensing, and Catalysis, Acc. Chem. Res., 2008, 41, 841–856 CrossRef CAS.
- W.-S. Li and T. Aida, Dendrimer Porphyrins and Phthalocyanines, Chem. Rev., 2009, 109, 6047–6076 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Astruc, E. Boisselier and C. Ornelas, Dendrimers Designed for Functions: From Physical, Photophysical, and Supramolecular Properties to Applications in Sensing, Catalysis, Molecular Electronics, Photonics, and Nanomedicine, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 1857–1959 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu, V. S. Bryantsev, M. S. Diallo and W. A. Goddard, III, PAMAM Dendrimers Undergo pH Responsive Conformational Changes without Swelling, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 2798–2799 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Li, K. Hong, L. Porcar, R. Verduzco, P. D. Butler, G. S. Smith, Y. Liu and W.-R. Chen, Assess the Intramolecular Cavity of a PAMAM Dendrimer in Aqueous Solution by Small-Angle Neutron Scattering, Macromolecules, 2008, 41, 8916–8920 CrossRef CAS.
- W.-R. Chen, L. Porcar, Y. Liu, P. D. Butler and L. J. Magid, Small Angle Neutron Scattering Studies of the Counterion Effects on the Molecular Conformation and Structure of Charged G4 PAMAM Dendrimers in Aqueous Solutions, Macromolecules, 2007, 40, 5887–5898 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Li, M. Zamponi, K. Hong, L. Porcar, C.-Y. Shew, T. Jenkins, E. Liu, G. S. Smith, K. W. Herwig, Y. Liu and W.-R. Chen, pH Responsiveness of polyelectrolyte dendrimers: a dynamical perspective, Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 618–622 RSC.
- Y. Niu and R. M. Crooks, Preparation of Dendrimer-Encapsulated Metal Nanoparticles Using Organic Solvents, Chem. Mater., 2003, 15, 3463–3467 CrossRef CAS.
- L. K. Yeung and R. M. Crooks, Heck Heterocoupling within a Dendritic Nanoreactor, Nano Lett., 2001, 1, 14–17 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Satoh, T. Nakashima, K. Kamikura and K. Yamamoto, Quantum size effect in TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by finely controlled metal assembly on dendrimer templates, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2008, 3, 106–111 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Nakamula, Y. Yamanoi, T. Yonezawa, T. Imaoka, K. Yamamoto and H. Nishihara, Nanocagecatalysts—rhodium nanoclusters encapsulated with dendrimers as accessible and stable catalysts for olefin and nitroarene hydrogenations, Chem. Commun., 2008, 5716–5718 RSC.
- C. Ornelas, J. R. Aranzaes, L. Salmon and D. Astruc, “Click” Dendrimers: Synthesis, Redox Sensing of Pd(OAc)2, and Remarkable Catalytic Hydrogenation Activity of Precise Pd Nanoparticles Stabilized by 1,2,3-Triazole-Containing Dendrimers, Chem.–Eur. J., 2008, 14, 50–64 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Ornelas, L. Salmon, J. R. Aranzaes and D. Astruc, Catalytically efficient palladium nanoparticles stabilized by “click” ferrocenyl dendrimers, Chem. Commun., 2007, 4946–4948 RSC.
- A. K. Diallo, C. Ornelas, L. Salmon, J. R. Aranzaes and D. Astruc, “Homeopathic” catalytic activity and atom-leaching mechanism in Miyaura–Suzuki reactions under ambient conditions with precise dendrimer-stabilized Pd nanoparticles, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 8644–8648 CrossRef CAS.
- J. C. Garcia-Martinez, R. W. J. Scott and R. M. Crooks, Extraction of Monodisperse Palladium Nanoparticles from Dendrimer Templates, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 11190–11191 CrossRef CAS.
- J. F. Parker, C. A. Fields-Zinna and R. W. Murray, The Story of a Monodisperse Gold Nanoparticle: Au25L18, Acc. Chem. Res., 2010, 43, 1289–1296 CrossRef CAS.
- M. R. Knecht, J. C. Garcia-Martinez and R. M. Crooks, Hydrophobic Dendrimers as Templates for Au Nanoparticles, Langmuir, 2005, 21, 11981–11986 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-G. Kim, S.-K. Oh and R. M. Crooks, Preparation and Characterization of 1–2 nm Dendrimer-Encapsulated Gold Nanoparticles Having Very Narrow Size Distributions, Chem. Mater., 2004, 16, 167–172 CrossRef CAS.
- M. R. Knecht, J. C. Garcia-Martinez and R. M. Crooks, Synthesis, Characterization, and Magnetic Properties of Dendrimer-Encapsulated Nickel Nanoparticles Containing <150 Atoms, Chem. Mater., 2006, 18, 5039–5044 CrossRef CAS.
- M. R. Knecht and R. M. Crooks, Magnetic properties of dendrimer-encapsulated iron nanoparticles containing an average of 55 and 147 atoms, New J. Chem., 2007, 31, 1349–1353 RSC.
- J. Hassoun, S. Panero and B. Scrosati, Electrodeposited Ni–Sn intermetallic electrodes for advanced lithium ion batteries, J. Power Sources, 2006, 160, 1336–1341 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Hassoun, S. Panero, P. Simon, P. L. Taberna and B. Scrosati, High-Rate, Long-Life Ni–Sn Nanostructured Electrodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries, Adv. Mater., 2007, 19, 1632–1635 CrossRef CAS.
- A. T. Gates, E. G. Nettleton, V. S. Myers and R. M. Crooks, Synthesis and Characterization of NiSn Dendrimer-Encapsulated Nanoparticles, Langmuir, 2010, 26, 12994–12999 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhang, Y. Mo, M. B. Vukmirovic, R. Klie, K. Sasaki and R. R. Adzic, Platinum Monolayer Electrocatalysts for O2 Reduction: Pt Monolayer on Pd(111) and on Carbon-Supported Pd Nanoparticles, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 10955–10964 CrossRef CAS.
- A. J. Bard; L. R. Faulkner. Electrochemical Methods Fundamentals and Application; 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons: New York, 2001 Search PubMed.
- A. C. Curtis, D. G. Duff, P. P. Edwards, D. A. Jefferson, B. F. G. Johnson, A. I. Kirkland and A. S. Wallace, A Morphology-Selective Copper Organosol, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1988, 27, 1530–1533 CrossRef.
- M. P. Pileni and I. Lisiecki, Nanometer metallic copper particle synthesis in reverse micelles, Colloids Surf., A, 1993, 80, 63–68 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Glasner and A. I. Frenkel, Geometrical Characteristics of Regular Polyhedra: Application to EXAFS Studies of Nanoclusters, AIP Conf. Proc., 2007, 882, 746–748 CrossRef CAS.
- M. R. Knecht, M. G. Weir, V. S. Myers, W. D. Pyrz, H. Ye, V. Petkov, D. J. Buttrey, A. I. Frenkel and R. M. Crooks, Synthesis and Characterization of Pt Dendrimer-Encapsulated Nanoparticles: Effect of the Template on Nanoparticle Formation, Chem. Mater., 2008, 20, 5218–5228 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Lang, S. Maldonado, K. J. Stevenson and B. D. Chandler, Synthesis and Characterization of Dendrimer Templated Supported Bimetallic Pt–Au Nanoparticles, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 12949–12956 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Herrero, L. J. Buller and H. D. Abruña, Underpotential Deposition at Single Crystal Surfaces of Au, Pt, Ag and Other Materials, Chem. Rev., 2001, 101, 1897–1930 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhang, F. H. B. Lima, M. H. Shao, K. Sasaki, J. X. Wang, J. Hanson and R. R. Adzic, Platinum Monolayer on Nonnoble Metal-Noble Metal Core-Shell Nanoparticle Electrocatalysts for O2 Reduction, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 22701–22704 CrossRef CAS.
- J. X. Wang, H. Inada, L. Wu, Y. Zhu, Y. Choi, P. Liu, W.-P. Zhou and R. R. Adzic, Oxygen Reduction on Well-Defined Core-Shell Nanocatalysts: Particle Size, Facet, and Pt Shell Thickness Effects, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 17298–17302 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhai, M. Huang and S. Dong, Electrochemical Designing of Au/Pt Core Shell Nanoparticles as Nanostructured Catalyst with Tunable Activity for Oxygen Reduction, Electroanalysis, 2007, 19, 506–509 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Li, J. Liu, W. He, Q. Huang and H. Yang, Influence of the composition of core-shell Au–Pt nanoparticle electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2010, 344, 132–136 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Gong, D. Su and R. R. Adzic, Platinum-Monolayer Shell on AuNi0.5Fe Nanoparticle Core Electrocatalyst with High Activity and Stability for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 14364–14366 CrossRef CAS.
- D. F. Yancey, E. V. Carino and R. M. Crooks, Electrochemical Synthesis and Electrocatalytic Properties of Au@Pt Dendrimer-Encapsulated Nanoparticles, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 10988–10989 CrossRef CAS.
- E. V. Carino and R. M. Crooks, Characterization of Pt@Cu Core@Shell Dendrimer-Encapsulated Nanoparticles Synthesized by Cu Underpotential Deposition, Langmuir, 2011, 27, 4227–4235 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Biegler, D. A. J. Rand and R. Woods, Limiting oxygen coverage on platinized platinum; Relevance to determination of real platinum area by hydrogen adsorption, J. Electroanal. Chem., Interfacial Electrochem., 1971, 29, 269–277 CrossRef CAS.
- A. I. Frenkel, Solving the 3D structure of metal nanoparticles, Z. Kristallogr., 2007, 222, 605–611 CrossRef CAS.
- O. Ozturk, T. J. Black, K. Perrine, K. Pizzolato, C. T. Williams, F. W. Parsons, J. S. Ratliff, J. Gao, C. J. Murphy, H. Xie, H. J. Ploehn and D. A. Chen, Thermal Decomposition of Generation-4 Polyamidoamine Dendrimer Films: Decomposition Catalyzed by Dendrimer-Encapsulated Pt Particles, Langmuir, 2005, 21, 3998–4006 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhao and R. M. Crooks, Dendrimer-Encapsulated Pt Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications to Catalysis, Adv. Mater., 1999, 11, 217–220 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Gu, P. Sanders and H. J. Ploehn, Quantitative analysis of Pt-PAMAM ligand exchange reactions: Time and concentration effects, Colloids Surf., A, 2010, 356, 10–15 CrossRef CAS.
- M. R. Knecht, M. G. Weir, A. I. Frenkel and R. M. Crooks, Structural Rearrangement of Bimetallic Alloy PdAu Nanoparticles within Dendrimer Templates to Yield Core/Shell Configurations, Chem. Mater., 2008, 20, 1019–1028 CrossRef CAS.
- S. V. Myers, A. I. Frenkel and R. M. Crooks, X-ray Absorption Study of PdCu Bimetallic Alloy Nanoparticles Containing an Average of ∼64 Atoms, Chem. Mater., 2009, 21, 4824–4829 CrossRef CAS.
- M. G. Weir, V. S. Myers, A. I. Frenkel and R. M. Crooks, In situ X-ray Absorption Analysis of ∼1.8 nm Dendrimer-Encapsulated Pt Nanoparticles during Electrochemical CO Oxidation, ChemPhysChem, 2010, 11, 2942–2950 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Jiang, L. H. Liang and D. S. Zhao, Lattice Contraction and Surface Stress of fcc Nanocrystals, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, 105, 6275–6277 CrossRef CAS.
- H. S. Yee and H. D. Abruña, Ab initio XAFS Calculations and in situ XAFS Measurements of Copper Underpotential Deposition on Pt(111): A Comparative Study, J. Phys. Chem., 1994, 98, 6552–6558 CrossRef CAS.
- H. S. Yee and H. D. Abruña, In situ X-ray studies of the underpotential deposition of copper on platinum(111), J. Phys. Chem., 1993, 97, 6278–6288 CrossRef CAS.
- M. A. Albiter, R. M. Crooks and F. Zaera, Adsorption of Carbon Monoxide on Dendrimer-Encapsulated Platinum Nanoparticles: Liquid versus Gas Phase, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2010, 1, 38–40 CrossRef CAS.
- M. V. Gomez, J. Guerra, V. S. Myers, R. M. Crooks and A. H. Velders, Nanoparticle Size Determination by 1H NMR Spectroscopy, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 14634–14635 CrossRef CAS.
- C. H. Wales, J. Berger, S. Blass, R. M. Crooks and N. Asherie, Quasi-Elastic Light Scattering of Platinum Dendrimer-Encapsulated Nanoparticles, Langmuir, 2011, 27, 4104–4109 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Gu, H. Xie, J. Gao, D. Liu, C. T. Williams, C. J. Murphy and H. J. Ploehn, AFM Characterization of Dendrimer-Stabilized Platinum Nanoparticles, Langmuir, 2005, 21, 3122–3131 CrossRef CAS.
- O. M. Wilson, R. W. J. Scott, J. C. Garcia-Martinez and R. M. Crooks, Synthesis, Characterization and Structure-Selective Extraction of 1–3 nm AuAg Bimetallic Nanoparticles, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 1015–1024 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhou, D. H. Russell, M. Zhao and R. M. Crooks, Characterization of Poly(amidoamine) Dendrimers and Their Complexes with Cu2+ by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Mass Spectrometry, Macromolecules, 2001, 34, 3567–3573 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Müller, C. Laschober, W. W. Szymanski and G. Allmaier, Determination of Molecular Weight, Particle Size, and Density of High Number Generation PAMAM Dendrimers Using MALDI–TOF–MS and nES–GEMMA, Macromolecules, 2007, 40, 5599–5605 CrossRef.
- S.-K. Oh, Y. Niu and R. M. Crooks, Size-Selective Catalytic Activity of Pd Nanoparticles Encapsulated within End-Group Functionalized Dendrimers, Langmuir, 2005, 21, 10209–10213 CrossRef CAS.
- O. M. Wilson, M. R. Knecht, J. C. Garcia-Martinez and R. M. Crooks, Effect of Pd Nanoparticle Size on the Catalytic Hydrogenation of Allyl Alcohol, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 4510–4511 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Bernechea, E. de Jesús, C. López-Mardomingo and P. Terreros, Dendrimer-Encapsulated Pd Nanoparticles versus Palladium Acetate as Catalytic Precursors in the Stille Reaction in Water, Inorg. Chem., 2009, 48, 4491–4496 CrossRef CAS.
- E. V. Carino, M. R. Knecht and R. M. Crooks, Quantitative Analysis of the Stability of Pd Dendrimer-Encapsulated Nanoparticles, Langmuir, 2009, 25, 10279–10284 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Lang, R. A. May, B. L. Iversen and B. D. Chandler, Dendrimer-Encapsulated Nanoparticle Precursors to Supported Platinum Catalysts, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 14832–14836 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Huang, J. N. Kuhn, C.-K. Tsung, Y. Zhang, S. E. Habas, P. Yang and G. A. Somorjai, Dendrimer Templated Synthesis of One Nanometer Rh and Pt Particles Supported on Mesoporous Silica: Catalytic Activity for Ethylene and Pyrrole Hydrogenation, Nano Lett., 2008, 8, 2027–2034 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Lafaye, A. Siani, P. Marécot, M. D. Amiridis and C. T. Williams, Particle Size Control in Dendrimer-Derived Supported Ruthenium Catalysts, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 7725–7731 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ye, J. A. Crooks and R. M. Crooks, Effect of Particle Size on the Kinetics of the Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalyzed by Pt Dendrimer-Encapsulated Nanoparticles, Langmuir, 2007, 23, 11901–11906 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhao, H. Tokuhisa and R. M. Crooks, Molecule-Sized Gates Based on Surface-Confined Dendrimers, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1997, 36, 2596–2598 CrossRef CAS.
- T. H. Kim, H. S. Choi, B. R. Go and J. Kim, Modification of a glassy carbon surface with amine-terminated dendrimers and its application to electrocatalytic hydrazine oxidation, Electrochem. Commun., 2010, 12, 788–791 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Vijayaraghavan and K. J. Stevenson, Synergistic Assembly of Dendrimer-Templated Platinum Catalysts on Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanotube Electrodes for Oxygen Reduction, Langmuir, 2007, 23, 5279–5282 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Shen, Q. Xu, H. Gao and N. Zhu, Dendrimer-encapsulated Pd nanoparticles anchored on carbon nanotubes for electro-catalytic hydrazine oxidation, Electrochem. Commun., 2009, 11, 1329–1332 CrossRef CAS.
- B. I. Lemon and R. M. Crooks, Preparation and Characterization of Dendrimer-Encapsulated CdS Semiconductor Quantum Dots, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000, 122, 12886–12887 CrossRef CAS.
- C.-Y. Lu and G. Henkelman, The role of geometric relaxation in oxygen binding to metal nanoparticles, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2011, 2, 1237–1240 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Welborn, W. Tang, J. Ryu, V. Petkov and G. Henkelman, A combined density functional and X-ray diffraction study of Pt nanoparticle structure, J. Chem. Phys., 2011 Search PubMed , in press.
- N. S. Froemming and G. Henkelman, Optimizing core-shell nanoparticle catalysts with a genetic algorithm, J. Chem. Phys., 2009, 131, 234103 CrossRef.
- T. H. Kim, H. S. Choi, W. Tang and G. Henkelman, Charge redistribution in core-shell nanoparticles to promote oxygen reduction, J. Chem. Phys., 2009, 130, 194504 CrossRef.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011 |
