Surface structure of Pd(111) with less than half a monolayer of Zn†
Abstract
We have characterized the structural properties of submonolayer amounts of Zn on Pd(111) using scanning tunneling 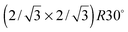 unit cell located near Zn substitutions; SPA-LEED patterns reveal the same periodicity. We attribute this phase to the metastable bonding of atoms or clusters predominantly in hollow sites surrounding Zn substitutions in the surface layer. At ≈0.4 ML,
unit cell located near Zn substitutions; SPA-LEED patterns reveal the same periodicity. We attribute this phase to the metastable bonding of atoms or clusters predominantly in hollow sites surrounding Zn substitutions in the surface layer. At ≈0.4 ML, 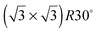 and (2 × 1) ordering on surfaces annealed to 350 K. At coverages near 0.5 ML, both
and (2 × 1) ordering on surfaces annealed to 350 K. At coverages near 0.5 ML, both

- This article is part of the themed collection: Scanning tunneling microscopy: revealing new physical chemistry insight

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...