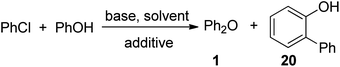
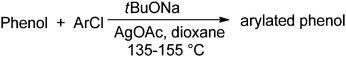Divergent reaction pathways for phenol arylation by arynes: synthesis of helicenes and 2-arylphenols†
Thanh Truong and Olafs Daugulis*
Department of Chemistry, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204-5003, USA. E-mail: olafs@uh.edu
First published on 18th October 2012
Abstract
Two reactions of phenols with arynes have been developed. If LiTMP base is employed, arynes generated from aryl chlorides react with phenols to form helicenes. o-Arylation of phenols can be achieved by employing tBuONa base in the presence of AgOAc. Direct arylation of binol was achieved leading to the shortest pathway to o,o′-diarylbinols.
2-Arylphenol functionality can be found in organocatalysts, sensors, phosphite ligands, and biologically active substances.1 The most common methods for synthesis of these structures involve cross-coupling of an organometallic reagent with an aryl halide or pseudohalide.1a,2 In addition to several step synthesis of both coupling components, the phenol moiety usually has to be protected. Shorter synthetic pathways to 2-arylphenols can be achieved by employing transition-metal catalyzed C–H bond functionalization methodology.3 First palladium-catalyzed phenol ortho-arylations were reported by Miura et al.3a However, in many cases polyarylation was observed. Subsequently, Bedford et al. published a method for rhodium-catalyzed arylation of 2-substituted phenols.3b More recently, Bedford et al., Dong et al., and Liu et al. have shown that phenols possessing ester and carbamate directing groups can be arylated under palladium catalysis by aryl halides or simple arenes.3c–e Gevorgyan has shown that selective phenol derivative ortho-arylation is possible by employing a silicon-based tether that can be subsequently removed.3f Gaunt has reported para-arylation of phenol ethers by diaryliodonium salts.3g Direct intermolecular ortho-arylation of unprotected phenols by aryl chlorides has not yet been disclosed. We report here a method for base- and silver-promoted phenol direct ortho-arylation by aryl chlorides that proceeds via benzyne mechanism. A one-step transition-metal-free synthesis of helicenes is also disclosed.
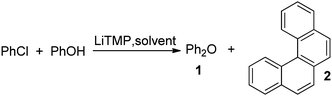
Phenol O-arylation can be accomplished by benzynes.4 Minor amounts of C-arylation products may accompany diaryl ethers.4 Since the ratio of C- vs. heteroatom arylation can be tuned by changing reaction solvent,5a,b we decided to explore phenol o-arylation. Arynes can be generated from silyl aryl triflates under nearly neutral conditions at room temperature.6 These starting materials are expensive and only a few of them are commercially available. Consequently, we used readily accessible and cheap aryl chlorides as aryne sources. Two different reaction conditions were investigated for phenol arylation. The first set of conditions employs lithium 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidide (LiTMP) base. These conditions are based on our earlier report for heterocycle arylation by aryl halides.5a The second set of conditions involves an alkali metal alkoxide base in dioxane and is based on intramolecular arylation of phenol derivatives.5c Very different reaction outcomes were observed depending on the conditions used.
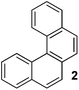
If a solution of phenol and chlorobenzene in THF was treated by TMPLi, diphenyl ether was formed together with a hydrocarbon in 4/1 ratio (Table 1, entry 1). Spectroscopic analysis showed that hydrocarbon product is benzo[c]phenanthrene (tetrahelicene). Helicenes have been used in asymmetric catalysis, as molecular machines, and as organic electronic materials.7 Their syntheses are typically lengthy,8 and one-step access to helicenes from simple, commercially available starting materials would make these interesting structures more available. For example, parent hexahelicene has been prepared in six steps by employing ring-closing metathesis.8c Consequently, we decided to optimize the helicene formation and investigate the reaction mechanism. Optimization of the reaction conditions showed that increase of phenol–chlorobenzene ratio to 1/4 and use of mixed pentane–THF solvent resulted in 80% conversion to tetrahelicene (entry 6).
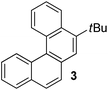
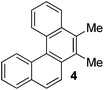
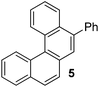
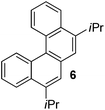
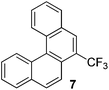
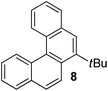
Examples of the helicene synthesis are presented in Table 2. Reaction of phenol with chlorobenzene affords a 67% isolated yield of tetrahelicene (entry 1). If 2-tert-butylphenol is reacted with chlorobenzene, 5-tert-butyltetrahelicene is obtained in 48% yield (entry 2). 5,6-Dimethyltetrahelicene is produced from 2,3-dimethylphenol in 58% yield (entry 3). 2-Phenylphenol is converted to 5-phenyltetrahelicene in 65% yield (entry 4). Hindered 2,6-diisopropylphenol is reactive and 5,8-diisopropyltetrahelicene was formed in 40% yield (entry 5). 6-Trifluoromethyltetrahelicene can be synthesized in 40% yield (entry 6). 3-tert-Butylphenol can be converted to 6-tert-butyltetrahelicene in 51% yield (entry 7).
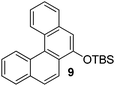
A TBS-protected resorcinol afforded the product in a good yield (entry 8). The reaction of 2,6-dimethylphenol with 1-chloronaphthalene resulted in formation of two isomeric hydrocarbons in 2.1/1 ratio and 60% yield. The major product was hexahelicene 11 that could be isolated in 26% yield by fractional crystallization of the isomer mixture (Scheme 1).
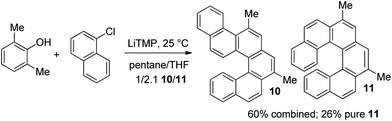 | ||
| Scheme 1 Hexahelicene synthesis. | ||
Analysis of the reaction products shows that helicenes are formed by the reaction of two molecules of aryl chloride with one molecule of phenol. Informative results were obtained in the reaction of 3-tert-butylphenol with 1.6 equiv. chlorobenzene (Scheme 2). Benzocyclooctadienone 12 was obtained in 61% yield. If 3 equiv. of chlorobenzene and 4.2 equiv. of LiTMP were employed, structure 13 was isolated in 64% yield. Compound 12 could be converted to 13 by reaction with 2 equiv. of PhCl in the presence of 3.2 equiv. LiTMP. Both 12 and 13 can be transformed to tert-butyltetrahelicene 8 as shown in Scheme 2. Direct reaction of 4 equiv. chlorobenzene with 3-tert-butylphenol in the presence of 6 equiv. LiTMP affords 8 (entry 7, Table 2). These experiments show that 12 and 13 are competent intermediates en route to 8. In addition, the reaction of 4-hydroxybiphenyl with chlorobenzene afforded 14 which cannot easily aromatize by elimination. X-Ray crystallographic analysis of O-methyl derivative of 14 showed that hydroxyl and phenyl groups are in cis arrangement.
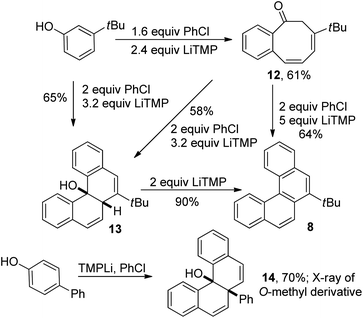 | ||
| Scheme 2 Reaction intermediates. | ||
The following reaction mechanism is proposed (Scheme 3). Reaction of phenol with benzyne generated from chlorobenzene forms a benzocyclobutene 15. Ring-opening affords 16 which undergoes another reaction with benzyne to form 17. Subsequent opening of the strained four-membered ring in 17 gives a ten-membered ring ketone 18. Intramolecular nucleophilic attack followed by dehydration affords tetrahelicene 2. Intermediates related to 16 and 19 have been isolated and characterized (12, 13, and 14, Scheme 1). Benzene cycloaddition with benzyne producing a benzocyclobutane derivative that subsequently ring-opens to give benzocyclooctatetraene in low yield has been reported showing the viability of intermediates such as 15 and 17.9
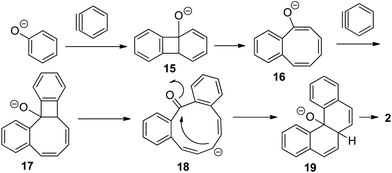 | ||
| Scheme 3 Reaction mechanism. | ||
As described above, use of LiTMP base afforded no detectable phenol C-arylation. The application of tBuONa in dioxane gave minor amounts of C-arylation (Table 3). In enolate chemistry, the C- vs. O-functionalization ratios are influenced by the counterion,10 and C-functionalization of hexafluoroacetylacetone can be achieved via its Ag salt.11a Thus, addition of 0.5–1 equiv. AgOAc resulted in a good selectivity for C-arylation. The optimized conditions include AgOAc additive, 155 °C, dioxane solvent, and NaOtBu base.
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | PhCl/PhOH/base | Solvent, T | 1/20/conv |
| a Solvent (1 mL), 0.25 mmol scale, 24 h. Conversion by GC analysis.b Additive: 1 equiv. AgOAc.c Additive: 0.1 equiv. AgOAc. | |||
| 1 | 2/1/3.9/LiTMP | Et2O, 25 °C | 50/<1/32% |
| 2 | 2/1/3.9/tBuOK | Dioxane, 110 °C | 9/1/91% |
| 3 | 2/1/3.9/tBuONa | Dioxane, 155 °C | 7/1/87% |
| 4b | 2/1/3.9/tBuONa | Dioxane, 155 °C | 1/30/87% |
| 5c | 2/1/3.9/tBuONa | Dioxane, 155 °C | 1/15/65% |
The arylation scope is presented in Table 4. Phenol can be either mono- or diarylated in good yield depending on phenol–chlorobenzene ratio (entries 1 and 2). Introduction of 3-fluorophenyl substituent is possible (entry 3). Reaction of phenol with 2-chloroanisole affords the 3-methoxyphenylated derivative (entry 4).11b Substituted phenols, such as 3-methylphenol (entry 5), 4-hydroxybenzophenone (entry 6), 1-naphthol (entry 7), and 2-naphthol (entry 8) can be phenylated in good to excellent yields.
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Phenol | ArCl | Product | Yield, % |
| a Scale: 0.5 mmol, 48–96 h, 0.5–2 equiv. AgOAc, 1.6–5/1/3.6–8 ratio of ArCl/phenol/base. Yields are isolated yields.b Crude: 9/1 isomer mixture. Yield of pure major isomer.c No AgOAc.d Reaction scale: 10 mmol. | ||||
| 1 | Phenol | PhCl | 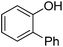 | 78 |
| 2 | Phenol | PhCl | 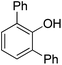 | 60 |
| 3 | Phenol | 1-Cl-3-FC6H4 | 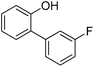 | 72 |
| 4 | Phenol | 2-Cl-1-MeOC6H4 | 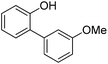 | 64 |
| 5b | 3-Me-phenol | PhCl | 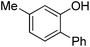 | 80 |
| 6 | 4-OH-benzo-phenone | PhCl | 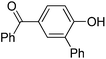 | 58 |
| 7 | 1-Naphthol | PhCl | 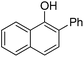 | 82 |
| 8c | 2-Naphthol | PhCl | 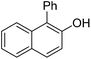 | 80, 77d |
| 9c | 2-Naphthol | 3-Cl-1-CF3C6H4 | 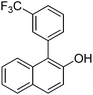 | 74 |
| 10c | 2-Naphthol | 3-Br-1-tBuO2CC6H4 | 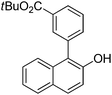 | 66 |
| 11c | 2-Naphthol | 3-Cl-1-CNC6H4 | 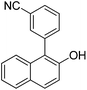 | 65 |
The reaction is surprisingly functional group tolerant despite the use of strong tert-butoxide base. Thus, fluoride (entry 3), ether (entry 4), ketone (entry 6), trifluoromethyl (entry 9), ester (entry 10), and cyano groups (entry 11) are tolerated. Arylation of 2-naphthol (entries 8–11) does not require AgOAc additive. Phenylation of 2-naphthol on a 10 mmol scale afforded product in 77% yield (entry 8).
Arylated binol derivatives are used as organocatalysts.1a Their syntheses require several steps from relatively expensive starting materials.1a Direct C-arylation of binol is the shortest possible route to such compounds. This pathway should also allow introduction of two different aryl groups into binol moiety, thus allowing access to structurally diverse organocatalysts. Diarylation of binol with excess chlorobenzene afforded 21 in 51% yield (Scheme 4). A two-step synthesis of an unsymmetrical diarylbinol was also achieved. Thus, binol was phenylated to afford 3-phenylbinol 22 in 67% yield. Subsequently, 22 was arylated by 1-chloro-3-fluorobenzene to afford 3,3′-diarylbinol 23 in 60% yield. Additionally, arylation of enantiopure (R)-binol with 3-chloroanisole afforded product 24 in 50% yield and 95 % ee, showing the applicability of the method to synthesis of enantioenriched organocatalysts.
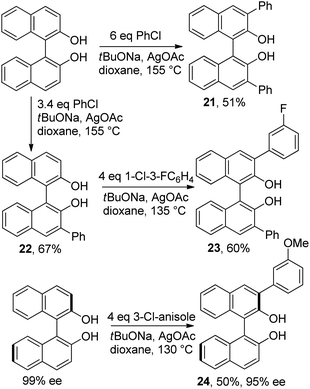 | ||
| Scheme 4 Binaphthol arylation. | ||
In conclusion, we have described two reactions of phenols with arynes. If LiTMP base is employed, arynes generated from aryl chlorides react with phenols to form helicene derivatives. If tBuONa base is used in dioxane at elevated temperature in the presence of AgOAc, selective o-arylation of phenols can be achieved. Diarylation of binol was demonstrated resulting in the shortest pathway to o,o′-diarylbinols. Enantiopure binol was o-arylated by 3-chloroanisole affording 3-(3-methoxyphenyl)binol in 95% ee.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Welch Foundation (grant no. E-1571), NIGMS (grant no.R01GM077635), and Camille and Henry Dreyfus Foundation for supporting this research. We also thank Dr James Korp for collecting and solving the X-ray structure of methyl ether of 14.Notes and references
- (a) M. Rueping, B. J. Nachtsheim, R. M. Koenigs and W. Ieawsuwan, Chem.–Eur. J., 2010, 16, 13116 CrossRef CAS; (b) H. Maeda, Y. Bando, K. Shimomura, I. Yamada, M. Naito, K. Nobusawa, H. Tsumatori and T. Kawai, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 9266 CrossRef CAS; (c) M. Englert, P. W. Jolly and G. Wilke, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1971, 10, 77 CrossRef CAS; (d) W. Schuehly, J. M. V. Paredes, J. Kleyer, A. Huefner, S. Anavi-Goffer, S. Raduner, K.-H. Altmann and J. Gertsch, Chem. Biol., 2011, 18, 1053 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Ackermann, A. R. Kapdi, S. Fenner, C. Kornhaaß and C. Schulzke, Chem.–Eur. J., 2011, 17, 2965 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) T. Satoh, Y. Kawamura, M. Miura and M. Nomura, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1997, 36, 1740 CrossRef CAS; (b) R. B. Bedford, S. J. Coles, M. B. Hursthouse and M. E. Limmert, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2003, 42, 112 CrossRef CAS; (c) R. Bedford, R. L. Webster and C. J. Mitchell, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2009, 7, 4853 RSC; (d) X. Zhao, C. S. Yeung and V. M. Dong, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 5837 CrossRef CAS; (e) B. Xiao, Y. Fu, J. Xu, T.-J. Gong, J.-J. Dai, J. Yi and L. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 468 CrossRef CAS; (f) C. Huang and V. Gevorgyan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 10844 CrossRef CAS; (g) C.-L. Ciana, R. J. Phipps, J. R. Brandt, F.-M. Meyer and M. J. Gaunt, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 458 CrossRef CAS; (h) A. Kirste, B. Elsler, G. Schnakenburg and S. R. Waldvogel, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 3571 CrossRef CAS; (i) L. Ackermann, E. Diers and A. Manvar, Org. Lett., 2012, 14, 1154 CrossRef CAS; (j) A. Wetzel, G. Pratsch, R. Kolb and M. R. Heinrich, Chem.–Eur. J., 2010, 16, 2547 CrossRef CAS. Tritylaniline o-arylation by benzynes: (k) T. Pirali, F. Zhang, A. H. Miller, J. L. Head, D. McAusland and M. F. Greaney, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 1006 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Huisgen and J. Sauer, Angew. Chem., 1960, 72, 91 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) T. Truong and O. Daugulis, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 4243 CrossRef CAS; (b) T. Truong and O. Daugulis, Org. Lett., 2011, 13, 4172 CrossRef CAS; (c) G. Bajracharya and O. Daugulis, Org. Lett., 2008, 10, 4625 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Himeshima, T. Sonoda and H. Kobayashi, Chem. Lett., 1983, 1211 CrossRef CAS.
- Review: Y. Shen and C.-F. Chen, Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 1463 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) J. Meisenheimer and K. Witte, Chem. Ber., 1903, 36, 4153 CrossRef CAS; (b) L. Liu, B. Yang, T. J. Katz and M. K. Poindexter, J. Org. Chem., 1991, 56, 3769 CrossRef CAS; (c) S. K. Collins, A. Grandbois, M. P. Vachon and J. Côté, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 2923 CrossRef CAS; (d) I. G. Stará, I. Starý, A. Kollárovič, F. Teplý, D. Šaman and M. Tichý, J. Org. Chem., 1998, 63, 4046 CrossRef. Other PAH syntheses via benzynes: (e) I. Fleming and T. Mah, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1975, 964 RSC; (f) S. A. Worlikar and R. C. Larock, J. Org. Chem., 2009, 74, 9132 CrossRef CAS; (g) S. Bhuvaneswari, M. Jeganmohan and C.-H. Cheng, Org. Lett., 2006, 8, 5581 CrossRef CAS.
- R. G. Miller and M. Stiles, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1963, 85, 1798 CrossRef CAS.
- L. M. Jackman and B. C. Lange, Tetrahedron, 1977, 33, 2737 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) L. Zhang, M. Brookhart and P. S. White, Organometallics, 2006, 25, 1868 CrossRef CAS; (b) G.-Y. J. Im, S. M. Bronner, A. E. Goetz, R. S. Paton, P. H.-Y. Cheong, K. N. Houk and N. K. Garg, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 17933 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. CCDC 897191. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c2sc21288a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2013 |

![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
: