Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleHigh adsorptive properties of covalent triazine-based frameworks (CTFs) for surfactants from aqueous solution†
Asamanjoy
Bhunia
a,
Subarna
Dey
a,
Maria
Bous
b,
Chenyang
Zhang
b,
Wolfgang
von Rybinski
*b and
Christoph
Janiak
*a
aInstitute for Inorganic and Structural Chemistry, University Düsseldorf, D-40204 Düsseldorf, Germany. E-mail: janiak@uni-duesseldorf.de
bInstitute for Physical Chemistry, University Düsseldorf, D-40204 Düsseldorf, Germany. E-mail: vonRybinski@uni-duesseldorf.de
First published on 7th November 2014
Abstract
Carbonaceous covalent triazine-based frameworks from 1,4-dicyanobenzene (CTF-1) can adsorb up to about 4 g g−1 of the surfactants alkyl polyglycolether, C12EO7 and sodium dodecylsulfate, SDS from aqueous solution (c = 8.0 mmol L−1) which is more than 20-times the gravimetric uptake capacity of a carbon black (Printex L from Evonik). This high uptake is due to CTF sheet exfoliation. Taking into account the thermal and chemical stability of CTFs this first surfactant adsorption study with CTFs shows that CTFs are especially interesting for the uptake of substances from solution.
The adsorptive properties of porous solid substances are of great importance for many applications.1 Solids based on carbon black structures and graphitic carbons which have a surface area between 100 and 500 m2 g−1 are especially interesting as key sorbents,2inter alia for separation processes and gas storage.3,4
Covalent triazine-based frameworks (CTFs) were developed by Kuhn, Antonietti and Thomas et al. as permanently porous substances.5 They constitute a subclass of POMs (Porous Organic Materials) and possess high chemical and thermal stability. Classes of POMs are often differentiated according to their building units such as benzimidazole-linked polymers (BILPs),6 hyper-crosslinked polymers (HCPs),7 polymers of intrinsic microporosity (PIMs),8 porous aromatic frameworks (PAFs),9 conjugated microporous polymers (CMPs)10 and covalent organic frameworks (COFs).11
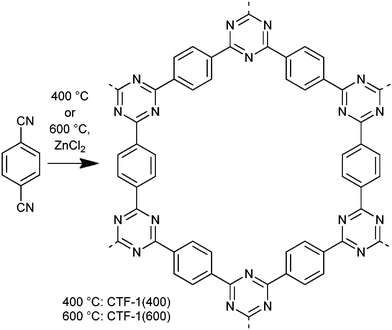
CTFs are made by the idealized trimerization reaction of carbonitriles to triazine rings (Scheme 1). The resulting sheets of CTF-1 can form a hexagonal lattice with an eclipsed AAA structure and tubular channels of 1.2 nm diameter.5 CTFs are interesting because of cheap and readily available starting materials, facile synthesis and certain hydrophilicity. From their elemental composition, we view CTFs from ionothermal reaction with ZnCl2 as in-between well-defined COFs and porous carbon materials. So far, CTFs have been used in heterogeneous catalysis,12 as catalytic support in liquid phase reactions,13 for gas storage and for separation.14
For applications of CTFs as adsorbents in liquids,15 the interaction with substances from solution is decisive.16 Important substances from solution which strongly interact with surfaces are surfactants. Surfactant adsorption at solid–liquid or liquid–liquid interfaces is crucial in industrial processes such as corrosion inhibition, dispersion stabilization, detergency, crude oil refining, purification and lubrication.17 Adsorption studies from solution for many types of surfactants and numerous surfaces18 showed that the adsorbed amounts and the structure within the adsorbed layer depend on the properties of the surfaces, the type of the surfactants and parameters like temperature and pH. Typical gravimetric surfactant uptake capacities for porous graphitized carbon black with a specific surface area of about 100 m2 g−1 were in the range of 0.1 to 0.2 g g−1.19
Here we investigate for the first time the adsorptive properties of a CTF member (CTF-1 synthesized from 1,4-dicyanobenzene, Scheme 1; see ESI† for further details) towards a non-ionic and an anionic surfactant (alkyl polyglycolether, C12EO7 and sodium dodecylsulfate, SDS, respectively) from aqueous solution and compare it with a typical carbon black with a specific surface area of 150 m2 g−1.
The amount of surfactant adsorbed on CTFs was determined from the surface tension of the solutions which correlates to the surfactant equilibrium concentration from a calibration curve (see Fig. S8 and details in ESI†). The CTF alone did not influence the surface tension of the aqueous solution.
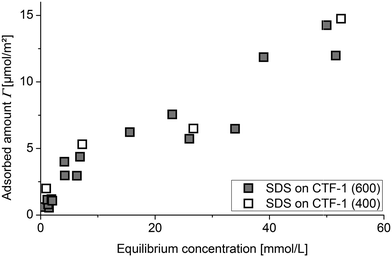
The adsorption isotherms for SDS onto CTFs (Fig. 1) show two regions. At low SDS concentrations, the adsorbed amount of SDS increases gradually and then the isotherm reaches a plateau and is nearly constant up to an SDS equilibrium concentration of 30 mmol L−1. At higher surfactant content, adsorption again increases nearly linearly up to high equilibrium concentrations. The course of the adsorbed amounts in dependence on SDS equilibrium concentration in the low concentration region corresponds to the formation of a first adsorption layer of SDS on CTF. The almost linear increase of adsorbed SDS amounts at higher SDS concentrations in the second regime correlates with a second adsorption process on the first SDS layer. It is interesting to see that for both CTF-1 samples the adsorbed SDS amounts are the same. Therefore the surface characteristics should be similar despite the different surface area. In desorption experiments, we have seen almost no hysteresis, so that the adsorption process is reversible (data not shown). A more detailed insight into the adsorption mechanism is given by the section of the adsorption isotherm for low solution concentrations (Fig. 2). It shows more clearly the typical shape of an adsorption isotherm in the monolayer region during formation of a surfactant layer on a surface.16 If compared to the SDS adsorption on a typical carbon black, one can conclude that the adsorption behaviour on CTF at low surfactant concentrations is similar to that of carbon black albeit with higher adsorbed amounts. Typical carbon black adsorbs about 2 μmol(SDS) m−2 in the plateau region (Fig. 2).
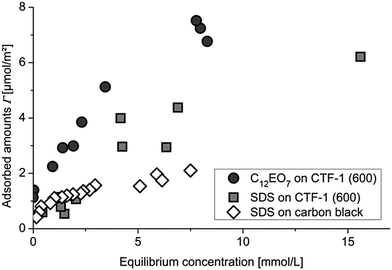 | ||
| Fig. 2 Adsorption isotherms of SDS and C12EO7 on CTF-1(600) and SDS on carbon black in the low concentration range. | ||
The adsorbed amounts Γ (in mol m−2) represent the number of adsorbed molecules per area on a solid. In Table 1 the values for the area per adsorbed molecule calculated according to eqn (1) are given, assuming that the BET surface area of the CTFs is accessible for the surfactant molecules.
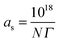 | (1) |
| Surfactanta | Solid [SBET/m2 g−1] | Adsorbed amount Γb | Area per molecule, asc (nm2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (μmol m−2) | (mg m−2) | (g g−1) | |||
| a SDS = sodium dodecylsulfate; C12EO7 = alkyl polyglycolether. b Adsorbed amount Γ at c = 8.0 mmol L−1 from eqn (S1) (ESI). c From the adsorption isotherms, eqn (1). To be compared with a limiting area per molecule of 1.05 nm2 in the horizontal orientation and 0.2 nm2 in the vertical orientation from Langmuir film balance measurements.20 d Printex L from Evonik. | |||||
| SDS | CTF-1(600) [1390] | 5.0 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 0.33 |
| SDS | CTF-1(400) [970] | 5.0 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 0.33 |
| SDS | Carbon blackd [150] | 2.0 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.83 |
| C12EO7 | CTF-1(600) [1390] | 7.0 | 3.5 | 4.9 | 0.24 |
| C12EO7 | Carbon blackd [150] | 2.5 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.66 |
Also the formation of hemimicelles on the surface can be possible which was shown by measurements with atomic force microscopy on graphite surfaces.21 If one considers the cross section area of the surfactant with 0.2 nm2 for the alkyl chain and about 0.5 nm2 for the ethylenoxide chain,22 both surfactants could be included into the channels of the solid (cross section area about 1.4 nm2). On the other hand the fast and thorough desorption of the long chain surfactants suggest no or little adsorption in the channels. Instead of channel filling the layer structure of CTF-1 can lead to interlayer surfactant insertion (similar to graphite) as evidenced by a shift of the (001) peak from 2θ ≈ 25° (3.6 Å) to 2θ ≈ 20° (4.4 Å) in the powder X-ray pattern (Fig. S2, ESI†). Exfoliation can explain the strong increase of the adsorbed amounts at higher concentrations as multilayer formation or adsorption of micelles which has been claimed for other surfaces23 becomes possible on the CTF sheet surfaces.
Fig. 2 shows the adsorption of the non-ionic surfactant C12EO7 on CTF-1(600) in comparison to anionic SDS. The adsorption of the non-ionic one is slightly higher than that of the anionic surfactant which could be also shown for the adsorption on carbon black. The reason for the lower adsorption of the anionic compared to the non-ionic surfactant is the electrostatic repulsion of the polar group of the anionic surfactant which leads to lower packing density of the surfactant molecules on the surface.
From the gravimetric adsorption of the surfactants (Table 1) related to surface area and mass of the solid adsorbent it is evident that the gravimetric uptake capacity of CTFs is up to 20-times the amount of carbon black by weight (g g−1) and about 2.5 times the amount by surface area (mg m−2) for the ionic SDS surfactant. For the non-ionic C12EO7 surfactant the adsorbed amounts by weight (g g−1) are even increased due to the higher molecular mass of the non-ionic surfactant compared to the anionic surfactant and the higher uptake of the non-ionic surfactant by surface area (mol m−2).
In summary, this comparative study demonstrates the potential for unusually high adsorbed amounts of surfactants on CTF solids due to their high surface area. Hence, CTFs are not only interesting for gas adsorption but also show interesting properties for the application as adsorbents from solutions, taking into account their solvothermal chemical stability. SEM images of before and after SDS adsorption show no evident change in microscopic CTF morphology (Fig. S5, ESI†).
Notes and references
- F. Rouquerol, J. Rouquerol and K. Sing, Adsorption by Powders and Porous Solids Principles, Methodology and Applications, Elsevier, 1999 Search PubMed.
- Introduction to themed issue on porous carbon materials: A.-H. Lu and S. Dai, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1, 932 Search PubMed.
- J. R. Morris, C. I. Contescu, M. F. Chisholm, V. R. Cooper, J. Guo, L. He, Y. Ihm, E. Mamontov, Y. B. Melnichenko, R. J. Olsen, S. J. Pennycook, M. B. Stone, H. Zhang and N. C. Gallego, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1, 9341–9350 CAS; Y. Xia, Z. Yang and Y. Zhu, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1, 9365–9381 Search PubMed; N. Fechler, S.-A. Wohlgemuth, P. Jäker and M. Antonietti, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1, 9418–9421 Search PubMed; S. J. Yang, J. H. Kang, H. Jung, T. Kim and C. R. Park, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1, 9427–9432 Search PubMed; L. Huang and D. Cao, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1, 9433–9439 Search PubMed.
- A. G. Hsieh, C. Punckt, S. Korkut and I. A. Aksay, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2013, 117, 7950–7958 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Kuhn, M. Antonietti and A. Thomas, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 3450–3453 CrossRef CAS PubMed; P. Kuhn, A. l. Forget, D. Su, A. Thomas and M. Antonietti, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 13333–13337 CrossRef PubMed; M. J. Bojdys, J. Jeromenok, A. Thomas and M. Antonietti, Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 2202–2205 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. G. Rabbani and H. M. El-Kaderi, Chem. Mater., 2012, 24, 1511–1517 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Germain, J. Hradil, J. M. J. Fréchet and F. Svec, Chem. Mater., 2006, 18, 4430–4435 CrossRef CAS.
- B. S. Ghanem, K. J. Msayib, N. B. McKeown, K. D. M. Harris, Z. Pan, P. M. Budd, A. Butler, J. Selbie, D. Book and A. Walton, Chem. Commun., 2007, 67–69 RSC.
- H. Zhao, Z. Jin, H. Su, J. Zhang, X. Yao, H. Zhao and G. Zhu, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 2780–2782 RSC.
- J.-X. Jiang, F. Su, A. Trewin, C. D. Wood, N. L. Campbell, H. Niu, C. Dickinson, A. Y. Ganin, M. J. Rosseinsky, Y. Z. Khimyak and A. I. Cooper, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 8574–8578 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S.-Y. Ding and W. Wang, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 548–568 RSC ; introduction to themed issue on COFs: A. I. Cooper, CrystEngComm, 2013, 15, 1483 RSC; S. Kandambeth, A. Mallick, B. Lukose, M. V. Mane, T. Heine and R. Banerjee, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 19524–19527 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Katekomol, J. Roeser, M. Bojdys, J. Weber and A. Thomas, Chem. Mater., 2013, 25, 1542–1548 CrossRef CAS; J. Roeser, K. Kailasam and A. Thomas, ChemSusChem, 2012, 5, 1793–1799 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Hug, M. E. Tauchert, S. Li, U. E. Pachmayr and B. V. Lotsch, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 13956–13964 RSC; C. E. Chan-Thaw, A. Villa, P. Katekomol, D. Su, A. Thomas and L. Prati, Nano Lett., 2010, 10, 537–541 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Hug, M. B. Mesch, H. Oh, N. Popp, M. Hirscher, J. Senker and B. V. Lotsch, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 5928–5936 Search PubMed; A. Bhunia, V. Vasylyeva and C. Janiak, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 3961–3963 RSC; A. Bhunia, I. Boldog, A. Möller and C. Janiak, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1, 14990–14999 Search PubMed.
- T. Wang, K. Kailasam, P. Xiao, G. Chen, L. Chen, L. Wang, J. Li and J. Zhu, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2014, 187, 63–70 CrossRef CAS PubMed; J. Liu, H. Chen, S. Zheng and Z. Xu, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2013, 58, 3557–3562 CrossRef; J. Liu, E. Zong, H. Fu, S. Zheng, Z. Xu and D. Zhu, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2012, 372, 99–107 CrossRef PubMed; W. Zhang, F. Liang, C. Li, L.-G. Qiu, Y.-P. Yuan, F.-M. Peng, X. Jiang, A.-J. Xie, Y.-H. Shen and J.-F. Zhu, J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 186, 984–990 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Dobias, X. Qiu and W. von Rybinski, Solid-Liquid Dispersions, Surfactant Science Series, Marcel Dekker, 1999 Search PubMed.
- M. J. Rosen and M. Dahanayake, Industrial Utilization of Surfactants: Principles and Practice, AOCS Press, Illinois, 2001 Search PubMed.
- W. von Rybinski and M. J. Schwuger, Adsorption and Wetting, Nonionic Surfactants, ed. M. J. Schick, Marcel Dekker, 1987, pp. 45–107 Search PubMed.
- J. M. Corkill, J. F. Goodman and J. R. Tate, Trans. Faraday Soc., 1966, 62, 979–986 RSC.
- H. D. Dörfler, Grenzflächen und kolloid-disperse Systeme, Springer, Heidelberg, 2002, p. 143 Search PubMed.
- E. J. Wanless and W. A. Ducker, Langmuir, 1997, 13, 1463–1474 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Lange and P. Jeschke, in Nonionic Surfactants, ed. M. Schick, Surfactant Science Series, Marcel Dekker, 1987, pp. 1–44 Search PubMed.
- X. Liu, D. Wu, S. Turgman-Cohen, J. Genzer, T. W. Theyson and O. J. Rojas, Langmuir, 2010, 26, 9565–9574 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Synthesis, IR, powder XRD, elemental analysis, TG analysis, SEM images, N2 and CO2 sorption and pore size distribution, adsorption of surfactants. See DOI: 10.1039/c4cc06393g |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |