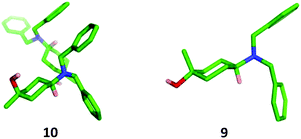Synthesis of dibenzylamino-1-methylcyclohexanol and dibenzylamino-1-trifluoromethylcyclohexanol isomers†
D. Heulyn
Jones
a,
Stefano
Bresciani
a,
James P.
Tellam
a,
Justyna
Wojno
a,
Anthony W. J.
Cooper
b,
Alan R.
Kennedy
a and
Nicholas C. O.
Tomkinson
*a
aWestCHEM, Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Thomas Graham Building, University of Strathclyde, 295 Cathedral Street, Glasgow, G1 1XL, UK. E-mail: Nicholas.Tomkinson@strath.ac.uk
bMolecular Discovery Research, GlaxoSmithKline, Medicines Research Centre, Hertfordshire, SG1 2NY, UK
First published on 8th October 2015
Abstract
The isomers of dibenzylamino-1-methylcyclohexan-1-ol and dibenzylamino-1-trifluoromethylcyclohexan-1-ol have been prepared. The stereochemistry of these compounds was unequivocally assigned through a combination of NMR spectroscopy and single crystal X-ray analysis. The cis-isomer of 3-N,N-dibenzylamino-1-trifluoromethylcyclohexanol and its derivatives display an unusual conformational behaviour in both solution-phase and the solid-state, where the amino group usually adopts an axial conformation.
Introduction
The introduction of three-dimensional shape through an increase in the proportion of sp3 hybridised centres (Fsp3) has been correlated to compound progress in a drug-discovery setting.1–5 The reduction of aromatic ring count has also been shown to have beneficial effects on the development properties of oral drug candidates, including aqueous solubility, lipophilicity, serum albumin binding, CyP450 inhibition and hERG inhibition.6 Based upon these important factors there has been significant interest in robust synthetic routes to building blocks and fragments which confer both shape and fixed conformation on a molecule through the introduction of saturation.7–9Whilst there are advantages to the reduction in the number of aromatic rings within a compound,6 the conformational constraints of a ring provide clear benefits in a medicinal chemistry setting, where functional groups can be held in positions to maximise ligand–receptor interaction.10 For this reason the introduction of functional groups on an aromatic scaffold has provided significant benefits within drug-discovery. In addition, there are many simple and effective procedures for the formation of carbon–carbon and carbon–heteroatom bonds on aromatic and heteroaromatic rings allowing for the rapid introduction of diversity and complexity on these frameworks to establish and probe structure activity knowledge.11
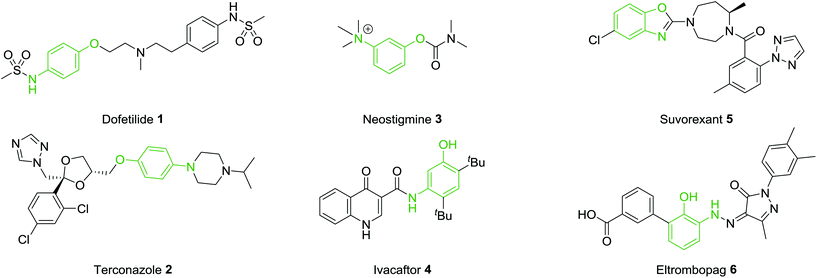
A common motif found in many drug molecules is the aminophenol functionality. This can easily be introduced through a variety of bond construction procedures and both the amine and hydroxyl groups provide excellent synthetic handles through which to selectively introduce a variety of additional groups. Introduction of this functionality on a rigid aromatic scaffold can provide both hydrogen bond donor and hydrogen bond acceptor properties along with the provision of mildly basic and acidic functional groups. Therefore, this pharmacophore is prevalent in many bioactive molecules. A selection of marketed drugs which contain a 1,4-, 1,3- or 1,2-aminophenol functionality are collected in Fig. 1. Dofetilide 1 is a class III antiarrhythmic used for the maintenance of sinus rhythm.12 Terconazole 2 is a broad spectrum antifungal agent which ultimately inhibits the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway.13 Neostigmine 3 is a reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor which stimulates both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors.14 Ivacaftor 4 is effective in the treatment of cystic fibrosis.15 Suvorexant 5 is a orexin receptor antagonist,16 approved for the treatment of insomnia and Eltombopag 6, interacts with the thrombopoietin receptor and leads to an increased platelet count in patients.17 These selected examples show the diversity in protein targets for this class of compound and highlight the importance and prevalence of the aminophenol functionality in compounds with profound biological activities.
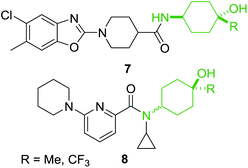
From the examples outlined in Fig. 1 there are clear benefits to the use of aromatic rings to fix the aminophenol functionality in space. However, the correlation between developing an oral drug candidate and the number of aromatic rings in a compound provides a strong impetus to develop saturated analogues of common aromatic motifs found in drug molecules.6 As part of an ongoing investigation we hypothesised that saturation of the aminophenol framework would provide a particularly useful series of aminocyclohexanol fragments for discovery research. Examination of the patent literature reveals a number of compounds which contain the aminocyclohexanol functionality suggesting that this grouping also has potential in the drug-discovery setting. Recent examples include the benzoxazole 7 which has been shown to be an mPGES-1 inhibitor and the 2-amidopyridine derivative 8, synthesised as a potential 11β-HSD1 inhibitor (Fig. 2).18,19
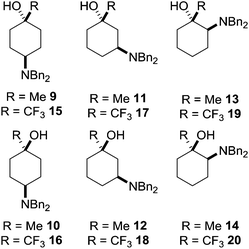
A convenient synthetic precursor to the amino cyclohexanol framework would be a suitably N-protected derivative. A typical example that can readily be unmasked to reveal the desired functionality is dibenzylamino-1-methylcyclohexan-1-ol and dibenzylamino-1-trifluoromethylcyclohexan-1-ol, which each have six structural isomers 9–20 (Fig. 3).
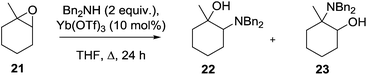
Despite the prevalence of this framework in the patent literature relatively few syntheses of this scaffold have been reported in the primary literature. In an isolated report, Yamamoto described the ytterbium triflate-mediated ring opening of epoxide 21 with dibenzylamine to give the amino alcohol 22 together with 23 as a 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of regioisomers (Scheme 1).20 Although the stereochemistry of this product was not unequivocally assigned it is expected that this would be the trans-isomer 13.
1 mixture of regioisomers (Scheme 1).20 Although the stereochemistry of this product was not unequivocally assigned it is expected that this would be the trans-isomer 13.
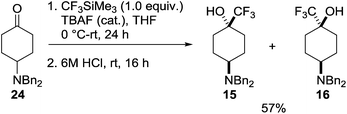
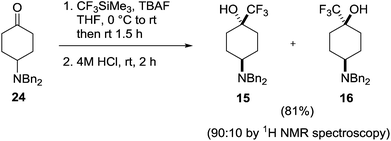
In the trifluoromethyl series (15–20) only the 4-amino-1-trifluoromethylcyclohexanol 15 has been reported, as a mixture along with minor isomer 16.19 This mixture was prepared through reaction of the dibenzylamino ketone 24 with Ruppert's reagent (CF3SiMe3) in the presence of tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride (TBAF) followed by acidic cleavage of the siloxy intermediate to give the products 15 and 16 as a 6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of diastereoisomers (Scheme 2), the trans-isomer 15 predominating.
1 mixture of diastereoisomers (Scheme 2), the trans-isomer 15 predominating.
Whilst these isolated reports are of use to those wishing to exploit this functionality in their efforts, the synthesis and stereochemical assignment of all twelve isomers of this cyclohexyl motif would be of direct use in adding stereochemical complexity and 3-dimensional shape to discovery projects. Within this paper we describe the synthesis, isolation and purification of all 1-methyl- and 1-trifluoromethyl dibenzylaminocyclohexan-1-ol isomers 9–20 in three steps or fewer from readily available precursors, and unequivocally assign their stereochemistry based upon NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallographic experiments.
Results and discussion
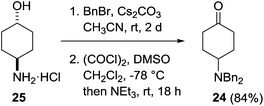
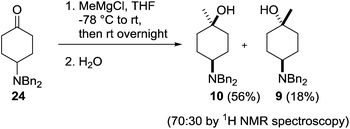
Our investigations began with the preparation of the 4-dibenzylamino derivatives 9, 10, 15 and 16 which were accessed from the common intermediate 24. Dibenzylation of 4-aminocyclohexanol hydrochloride 25 followed by Swern oxidation provided the known ketone 24 in 84% yield (Scheme 3).21Treatment of a THF solution of 24 with methylmagnesium chloride at −78 °C and allowing the reaction mixture to warm slowly to room temperature followed by an acidic workup provided access to the two diastereoisomers 10 and 9 in a 70![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30 ratio, which were separated by column chromatography providing the products in 56% (10) and 18% (9) isolated yields (Scheme 4).
30 ratio, which were separated by column chromatography providing the products in 56% (10) and 18% (9) isolated yields (Scheme 4).
The stereochemistry of each isomer was confirmed by X-ray crystallographic analysis (Fig. 4). The cis-isomer 10 showed two crystallographically independent molecules within the unit cell characterised by slightly different conformations of the cyclohexane ring which formed a hydrogen-bonded closed tetramer of molecules.
Introduction of the trifluoromethyl group was achieved under standard conditions using Ruppert's reagent in the presence of TBAF, delivering the two diastereomeric products 15 and 16 in a 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 ratio as determined by 1H NMR and 19F NMR spectroscopy (Scheme 5). Although a small amount of the major diastereomer was purified by column chromatography, efficient separation of 15 and 16 could not be achieved due to their similar affinities to silica, and the mixture of diastereomers was isolated in 81% yield. X-Ray crystallography showed the major diastereoisomer from this transformation to be the trans-isomer 15 where the trifluoromethyl group had been introduced in an axial position.
1 ratio as determined by 1H NMR and 19F NMR spectroscopy (Scheme 5). Although a small amount of the major diastereomer was purified by column chromatography, efficient separation of 15 and 16 could not be achieved due to their similar affinities to silica, and the mixture of diastereomers was isolated in 81% yield. X-Ray crystallography showed the major diastereoisomer from this transformation to be the trans-isomer 15 where the trifluoromethyl group had been introduced in an axial position.
The complete reversal of cis/trans selectivity when compared to methyl analogues 9 and 10 is likely due to pre-complexation of the approaching nucleophile in the addition of the Grignard reagent, whereas the axial addition of the trifluoromethyl group relieves gauche interactions within the transition state.22–24
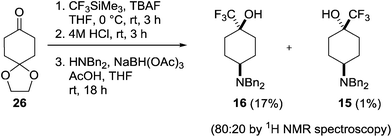
Although the cis-diastereoisomer 16 was present within the crude reaction mixture, its isolation proved challenging. We therefore examined alternative synthetic strategies to access this isomer. Initial attempts at using stoichiometric amounts of the bulky Lewis acid methylaluminium bis(2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methyl)phenoxide to encourage the equatorial approach of the nucleophile were unsuccessful.25 In addition, the more sterically demanding trifluoromethylating agent hexafluoroacetone hydrate-1,8-diaza-bicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene salt only returned starting materials.26 However, 16 was successfully prepared through the sequence outlined in Scheme 6. Trifluoromethylation of the mono-protected cyclohexanedione 26 followed by deprotection and subsequent reductive amination27 gave the diastereomeric cis- and trans-isomers 16 and 15 in an 80![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
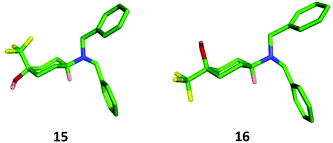
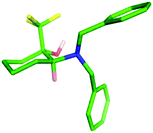
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 ratio, from which the required cis-isomer 16 could be isolated through purification by column chromatography in a poor but acceptable yield for the three steps (17%). The relative configuration of both the trans- and cis-diastereoisomers 15 and 16 was confirmed through X-ray crystallography (Fig. 5).
20 ratio, from which the required cis-isomer 16 could be isolated through purification by column chromatography in a poor but acceptable yield for the three steps (17%). The relative configuration of both the trans- and cis-diastereoisomers 15 and 16 was confirmed through X-ray crystallography (Fig. 5).
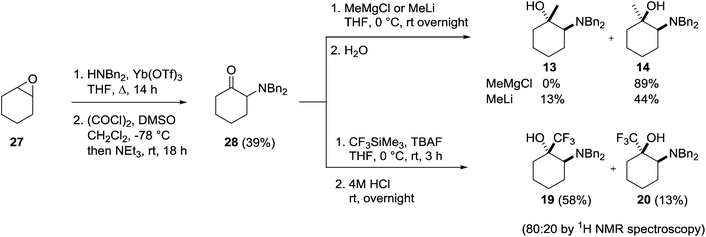
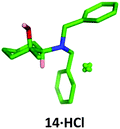
Conveniently, the four possible 1,2-isomers 13, 14, 19 and 20 could be prepared and isolated from a common intermediate, greatly simplifying the synthesis of these compounds (Scheme 7). Intermediate 28 was prepared through a two-step literature procedure involving the ring opening of cyclohexene oxide 27 followed by Swern oxidation of the resulting aminoalcohol to give 28 in 39% isolated yield (Scheme 7).20 Addition of methylmagnesium chloride to 28 at 0 °C gave the cis-aminoalcohol 14 in 89% isolated yield as a single isomer. Single crystal X-ray analysis of the hydrochloride salt of 14 confirmed the relative stereochemistry of this compound (Fig. 6) with the methyl group adopting an equatorial position. Chelation of the Grignard reagent to the carbonyl oxygen and the secondary amine would be expected to deliver the methyl group from an equatorial position, as was observed.
Changing the nucleophile to methyllithium resulted in the formation of both the cis- and trans-products 14 and 13 in a 80![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 ratio (1H NMR analysis of the crude reaction mixture). The isomers were separated by column chromatography, and the 1H NMR spectrum of the minor trans-isomer 13 agreed with the values reported for the product from ring-opening of 1-methylcyclohexene oxide by dibenzylamine.20 Therefore, the diastereomers 13 and 14 can be accessed as single isomers in good yield via two complimentary routes.
20 ratio (1H NMR analysis of the crude reaction mixture). The isomers were separated by column chromatography, and the 1H NMR spectrum of the minor trans-isomer 13 agreed with the values reported for the product from ring-opening of 1-methylcyclohexene oxide by dibenzylamine.20 Therefore, the diastereomers 13 and 14 can be accessed as single isomers in good yield via two complimentary routes.
Treatment of 28 with Ruppert's reagent and TBAF resulted in a 80![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 mixture of the expected products 19 and 20, which were purified by column chromatography and isolated in 58% and 13% yields respectively (Scheme 7). The major diastereomer was shown to be the trans-isomer 19 by single crystal X-ray analysis (Fig. 7), and was supported by the observation of long range splitting of the axial NC-H proton by the trans-CF3 group in the 1H NMR spectrum. This coupling was not observed for the cis-isomer 20.
20 mixture of the expected products 19 and 20, which were purified by column chromatography and isolated in 58% and 13% yields respectively (Scheme 7). The major diastereomer was shown to be the trans-isomer 19 by single crystal X-ray analysis (Fig. 7), and was supported by the observation of long range splitting of the axial NC-H proton by the trans-CF3 group in the 1H NMR spectrum. This coupling was not observed for the cis-isomer 20.
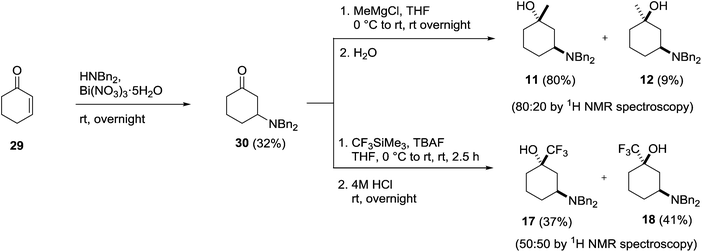
Having successfully prepared each of the 1,4- and 1,2-isomers our attention moved to the synthesis of the 1,3-substituted amino alcohols 11, 12, 17 and 18. Once again, these could be prepared from a common intermediate (30), which itself was prepared using a bismuth nitrate catalysed conjugate addition of dibenzylamine to cyclohexenone 29 (Scheme 8).28 Isolation of the key intermediate 30 by chromatography proved problematic due to decomposition of the adduct on silica, however, direct crystallisation from the crude reaction mixture using petroleum ether gave the amino ketone in 32% yield on scale without the need for chromatography.
Addition of methylmagnesium chloride to 30 gave a 80![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
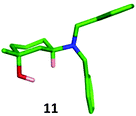
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 diastereomeric mixture of the expected trans-11 and cis-12 products, which were separated by column chromatography and isolated in 80% and 9% yields respectively. The identity of the major trans-isomer 11 was confirmed by single crystal X-ray analysis where the dibenzylamino group adopted an equatorial position (Fig. 8).
20 diastereomeric mixture of the expected trans-11 and cis-12 products, which were separated by column chromatography and isolated in 80% and 9% yields respectively. The identity of the major trans-isomer 11 was confirmed by single crystal X-ray analysis where the dibenzylamino group adopted an equatorial position (Fig. 8).
Treatment of 30 with Ruppert's reagent in the presence of TBAF gave a 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
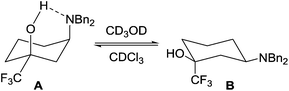
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 mixture of the diastereomeric products 17 and 18, which were separated by column chromatography and isolated in 37% and 41% yields respectively (Scheme 8). The stereochemistry of cis-isomer 18 was deduced by 1H NMR spectroscopy due to its intriguing behaviour in solution. In CDCl3, 18 adopted a conformation (A) where the large dibenzylamino group resided in an axial position due to an intramolecular hydrogen bond, whereas in the H-bonding deuterated solvent CD3OD the amino group adopted the more common equatorial conformation (B) (Fig. 9).
50 mixture of the diastereomeric products 17 and 18, which were separated by column chromatography and isolated in 37% and 41% yields respectively (Scheme 8). The stereochemistry of cis-isomer 18 was deduced by 1H NMR spectroscopy due to its intriguing behaviour in solution. In CDCl3, 18 adopted a conformation (A) where the large dibenzylamino group resided in an axial position due to an intramolecular hydrogen bond, whereas in the H-bonding deuterated solvent CD3OD the amino group adopted the more common equatorial conformation (B) (Fig. 9).
This solvent-dependant conformational change has been observed previously for cis-1,5,5-trimethylcyclohexane-1,3-diol and cis-1,5,5-trimethyl-3-aminocyclohexanol in CDCl3/D2O,29 but it is impressive that such a bulky dibenzylamino group displays this strong conformational fluxionality. The effect can in part be attributed to the size of the trifluoromethyl group, although the fact that the effect is reversed in CD3OD suggests there is a hydrogen-bonding interaction involved (Fig. 9). Interestingly, this is not seen in the methyl analogue 12 which suggests that the trifluoromethyl group plays a pivotal role in the conformation adopted by 18 in solution, presumably by tuning the acidity of the alcohol.301H NMR analysis of 18·HCl (in CDCl3) showed the dibenzylamino group in an equatorial position, supporting the proposal that an intramolecular hydrogen bond alters the conformational preference of 18 in non-polar solvents.
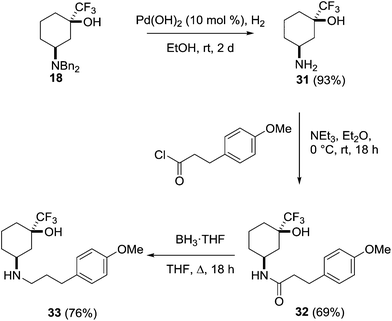
This behaviour was further investigated through the preparation of a series of analogues of 18 (Scheme 9). Deprotection of the amine through hydrogenolysis gave the amine 31 (94%) which was acylated under standard conditions to give the amide 32 (69%). Reduction of the amide with borane gave the secondary amine 33 (76%).
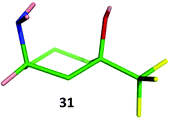
The relative stereochemistry of amine 31 was confirmed by single crystal X-ray where the amine substituent adopts an axial conformation (Fig. 10). 1H NMR analysis of 31 showed the NH2 group adopts an axial conformation in solution in both CDCl3 and CD3OD showing the subtle interplay of sterics and electronics in the benzylated analogue 18. Amide 32 and secondary amine 33 displayed the same conformational behaviour, suggesting that all cis-3-amino-1-trifluoromethylcyclohexanols possessing groups bonded to nitrogen that are less bulky than two benzyl groups are likely to always adopt a conformation with the amino functionality axial. This has interesting implications for adopting these monomers in a drug-discovery setting, where functional group disposition is critical to ligand–receptor interaction. It is entirely feasible that for compounds containing the cis-3-amino-cyclohexan-1-ol motif as exemplified by 12 and 18, axial/equatorial conformation could be controlled through incorporation of either a methyl or a trifluoromethyl group.
Conclusion
The twelve isomers of amino-1-methylcyclohexan-1-ol and amino-1-trifluoromethylcyclohexan-1-ol were successfully prepared in three-steps or fewer from commercially available starting materials. The stereochemistry of each isomer was assigned via a combination of 1H NMR spectroscopy and single crystal X-ray analysis. An interesting conformational behaviour was observed and investigated for cis-3-amino-1-trifluoromethylcyclohexan-1-ol derivatives, which could have structural implications for molecules containing this motif. This work provides robust routes to the isomers of amino-1-methylcyclohexan-1-ol and amino-1-trifluoromethylcyclohexan-1-ol, which will be of use for introducing 3D shape to drug-like molecules.Experimental
Materials and methods
All commercial materials were used as received without further purification. THF was dried using a solvent purification system. Flash chromatography was carried out using Merck Kieselgel 60 H silica. Analytical thin layer chromatography was carried out using aluminum-backed plates coated with Merck Kieselgel 60 GF254 that were visualized under UV light (at 254 nm) or stained using KMnO4. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance III or a Bruker Avance spectrometer, operating at 400 MHz (1H), 376 MHz (19F) and 101 MHz (13C). Chemical shifts were reported in parts per million (ppm) in the scale relative to residual solvent signals. Multiplicities are abbreviated as: s, singlet; d, doublet; t, triplet; q, quartet; dd, doublet of doublets; tt, triplet of triplets; pent; pentet; hept, heptet; m, multiplet; br, broad. Coupling constants are measured in Hertz (Hz). High-resolution mass spectra (HRMS) were obtained courtesy of the EPSRC National Mass Spectrometry Facility at Swansea University, U.K.trans-4-(Dibenzylamino)cyclohexan-1-ol
Cesium carbonate (51.4 g, 158 mmol) was added to a solution of trans-4-aminocyclohexanol (7.9 g, 52.3 mmol) in acetonitrile (150 mL). Benzyl bromide (12.7 mL, 106 mmol) was added and the mixture left to stir at room temperature for 2 days. The crude reaction mixture was filtered, and the solid washed with additional acetonitrile (100 mL). The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, dissolved in dichloromethane (100 mL) and washed with water (3 × 50 mL). The organic extract was dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give trans-4-(dibenzylamino)cyclohexan-1-ol as a colourless solid (15.1 g, 98%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.37 (4H, d, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.29 (4H, ddd, J = 7.1, 6.1 Hz), 7.19–7.24 (2H, m), 3.62 (4H, s), 3.54 (1H, tt, J = 10.9, 4.3 Hz), 2.53 (1H, tt, J = 11.8, 3.5 Hz), 1.95–2.04 (2H, m), 1.87–1.94 (2H, m), 1.36–1.61 (1H, br s), 1.36–1.49 (2H, m), 1.12–1.30 (2H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 141.0 (quat C), 128.5 (CH), 128.3 (CH), 126.8 (CH), 71.0 (CH), 56.9 (CH), 54.1 (CH2), 35.0 (CH2), 26.0 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C20H26ON 296.2009 (M+ + 1), found 296.2011.General Procedure 1. Swern oxidation
A solution of DMSO (11.6 mL, 163 mmol) in anhydrous dichloromethane (20 mL) was added drop-wise via a dropping funnel to a cooled solution of oxalyl chloride (6.8 mL, 80.8 mmol) in anhydrous dichloromethane (100 mL) at −78 °C. The reaction mixture was left to stir for an additional 15 minutes following completion of addition, and a solution of trans-4-(dibenzylamino)cyclohexan-1-ol (14.0 g, 47.5 mmol) in anhydrous dichloromethane (50 mL) was added drop-wise via a dropping funnel. Following completion of addition, the reaction mixture was stirred for 30 minutes before triethylamine (46 mL, 328 mmol) was added slowly drop-wise via syringe, and the cooling bath removed to allow the reaction mixture to warm to room temperature. The rubber septa were removed to allow the evaporation of SMe2, and the mixture left to stir overnight at room temperature. The crude reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure, dissolved in ethyl acetate (150 mL) and washed with water (3 × 100 mL). The organic extract was dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude product, which was purified by column chromatography on silica (8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 petroleum ether
1 petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate) to give 24 as peach coloured solid (13.9 g, 86%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38 (4H, d, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.29–7.34 (4H, m), 7.21–7.26 (2H, m), 3.66 (4H, s), 3.02 (1H, tt, J = 11.5, 3.4 Hz), 2.37–2.45 (2H, m), 2.12–2.33 (4H, m), 1.76–1.89 (2H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 211.1 (quat C), 140.4 (quat C), 128.5 (CH), 128.4 (CH), 127.0 (CH), 55.9 (CH), 54.2 (CH2), 40.3 (CH2), 27.5 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C20H24ON 294.1852 (M+ + 1), found 294.1854.
ethyl acetate) to give 24 as peach coloured solid (13.9 g, 86%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38 (4H, d, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.29–7.34 (4H, m), 7.21–7.26 (2H, m), 3.66 (4H, s), 3.02 (1H, tt, J = 11.5, 3.4 Hz), 2.37–2.45 (2H, m), 2.12–2.33 (4H, m), 1.76–1.89 (2H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 211.1 (quat C), 140.4 (quat C), 128.5 (CH), 128.4 (CH), 127.0 (CH), 55.9 (CH), 54.2 (CH2), 40.3 (CH2), 27.5 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C20H24ON 294.1852 (M+ + 1), found 294.1854.
General Procedure 2. Addition of methylmagnesium chloride
To a solution of 24 (4.41 g, 15.05 mmol) in anhydrous THF (45 mL) cooled to −78 °C under a N2 atmosphere, was added 3.0 M MeMgCl in THF (8.02 mL, 24.06 mmol) drop-wise. Following completion of addition, the cooling bath was removed and the reaction mixture left to warm to room temperature and stirred overnight. Water (10 mL) was added drop-wise, and the aqueous layer extracted with diethyl ether (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic extracts were washed with water (20 mL) and brine (20 mL), dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude products, which were purified by column chromatography on silica (5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 petroleum ether
1 petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate followed by 4
ethyl acetate followed by 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 and finally 3
1 and finally 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to give 10 as a colourless solid (2.62 g, 56%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38 (4H, d, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.29 (4H, app t, J = 7.6 Hz), 7.21 (2H, t, J = 7.3 Hz), 3.67 (4H, s), 2.43–2.53 (1H, m), 1.62–1.83 (6H, m), 1.25–1.38 (2H, m), 1.17 (3H, s); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 141.2 (quat C), 128.5 (CH), 128.2 (CH), 126.7 (CH), 69.2 (quat C), 57.2 (CH), 54.1 (CH2), 38.5 (CH2), 31.4 (CH3), 23.5 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C21H28ON 310.2165 (M+ + 1), found 310.2157. A sample was crystallised by slow evaporation of a solution in cyclohexane. Followed by 9 as a colourless solid (0.85 g, 18%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.36 (4H, d, J = 7.1 Hz), 7.26–7.31 (4H, m), 7.21 (2H, dt, J = 7.2, 1.3 Hz), 3.63 (4H, s), 2.56 (1H, tt, J = 11.6, 3.7 Hz), 1.78–1.88 (2H, m), 1.67–1.77 (2H, m), 1.32–1.55 (4H, m), 1.25 (3H, s); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 141.0 (quat C), 128.5 (CH), 128.3 (CH), 126.8 (CH), 71.0 (quat C), 57.5 (CH), 54.3 (CH2), 39.8 (CH2), 25.6 (CH2), 25.5 (CH3); HRMS calc. for C21H28ON 310.2165 (M+ + 1), found 310.2168. Crystals were grown by slow evaporation of a solution in cyclohexane.
1) to give 10 as a colourless solid (2.62 g, 56%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38 (4H, d, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.29 (4H, app t, J = 7.6 Hz), 7.21 (2H, t, J = 7.3 Hz), 3.67 (4H, s), 2.43–2.53 (1H, m), 1.62–1.83 (6H, m), 1.25–1.38 (2H, m), 1.17 (3H, s); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 141.2 (quat C), 128.5 (CH), 128.2 (CH), 126.7 (CH), 69.2 (quat C), 57.2 (CH), 54.1 (CH2), 38.5 (CH2), 31.4 (CH3), 23.5 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C21H28ON 310.2165 (M+ + 1), found 310.2157. A sample was crystallised by slow evaporation of a solution in cyclohexane. Followed by 9 as a colourless solid (0.85 g, 18%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.36 (4H, d, J = 7.1 Hz), 7.26–7.31 (4H, m), 7.21 (2H, dt, J = 7.2, 1.3 Hz), 3.63 (4H, s), 2.56 (1H, tt, J = 11.6, 3.7 Hz), 1.78–1.88 (2H, m), 1.67–1.77 (2H, m), 1.32–1.55 (4H, m), 1.25 (3H, s); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 141.0 (quat C), 128.5 (CH), 128.3 (CH), 126.8 (CH), 71.0 (quat C), 57.5 (CH), 54.3 (CH2), 39.8 (CH2), 25.6 (CH2), 25.5 (CH3); HRMS calc. for C21H28ON 310.2165 (M+ + 1), found 310.2168. Crystals were grown by slow evaporation of a solution in cyclohexane.
General Procedure 3. Reaction with Ruppert's reagent
To a solution of 24 (2.0 g, 6.83 mmol) in anhydrous THF (15 mL) cooled to 0 °C, was added trifluoromethyltrimethylsilane (1.2 mL, 8.20 mmol) under a N2 atmosphere. The mixture was stirred rapidly, and a solution of TBAF (5 mg, cat) in anhydrous THF (1 mL) was added slowly drop-wise. Following completion of addition, the cooling bath was removed and the reaction mixture left to warm to room temperature and stirred until consumption of starting material was apparent by TLC (1.5 h). The reaction mixture was exposed to air, 4 M HCl (aq) solution (10 mL) was added and the reaction mixture left to stir at room temperature until consumption of the siloxy intermediate was apparent by TLC (2 h). The pH was adjusted to 7 by the drop-wise addition of a saturated solution of K2CO3, and dichloromethane (30 mL) was added. The mixture was washed with water (3 × 15 mL), dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude product, which was purified by column chromatography on silica (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 petroleum ether
1 petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate) to give 15 and 16 as a colourless solid as a 9
ethyl acetate) to give 15 and 16 as a colourless solid as a 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 trans
1 trans![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) cis mixture of diastereomers (2.0 g, 81%). A small amount of pure trans-15 was obtained and used for characterisation purposes; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.27–7.36 (8H, m), 7.19–7.24 (2H, m), 3.65 (4H, s), 2.73 (1H, pent, J = 6.3 Hz), 2.18 (2H, app dt, J = 10.7, 4.5 Hz), 1.83 (4H, app q, J = 6.7 Hz), 1.52–1.57 (1H, br s), 1.47 (2H, app dt, J = 14.0, 7.0 Hz); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 140.3 (quat C), 128.6 (CH), 128.3 (CH), 126.9 (CH), 126.8 (quat C, q, J = 283 Hz), 72.4 (quat C, q, J = 30.3 Hz), 55.3 (CH), 53.9 (CH2), 29.9 (CH2), 23.5 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −80.1; HRMS calc. for C21H25ONF3 364.1883 (M+ + 1), found 364.1882; Crystals obtained from cold toluene.
cis mixture of diastereomers (2.0 g, 81%). A small amount of pure trans-15 was obtained and used for characterisation purposes; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.27–7.36 (8H, m), 7.19–7.24 (2H, m), 3.65 (4H, s), 2.73 (1H, pent, J = 6.3 Hz), 2.18 (2H, app dt, J = 10.7, 4.5 Hz), 1.83 (4H, app q, J = 6.7 Hz), 1.52–1.57 (1H, br s), 1.47 (2H, app dt, J = 14.0, 7.0 Hz); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 140.3 (quat C), 128.6 (CH), 128.3 (CH), 126.9 (CH), 126.8 (quat C, q, J = 283 Hz), 72.4 (quat C, q, J = 30.3 Hz), 55.3 (CH), 53.9 (CH2), 29.9 (CH2), 23.5 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −80.1; HRMS calc. for C21H25ONF3 364.1883 (M+ + 1), found 364.1882; Crystals obtained from cold toluene.
4-Oxo-1-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexan-1-ol
4-Oxo-1-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexan-1-ol was prepared using General Procedure 3 (reaction mixture was stirred overnight at rt following addition of 4 M HCl (aq) solution) from 1,4-dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-8-one (2.00 g, 12.8 mmol), trifluoromethyltrimethylsilane (2.08 mL, 14.1 mmol), anhydrous THF (30 mL) and a solution of TBAF (5 mg) in THF (1.0 mL) to give the crude product, which was purified by column chromatography on silica (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 petroleum ether
1 petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate) to give 4-oxo-1-trifluoromethylcyclohexan-1-ol as a colourless solid (1.28 g, 55%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, d6-Acetone) δ 5.30 (1H, s), 2.69 (2H, ddd, J = 14.4, 6.4, 6.4 Hz), 2.06–2.27 (6H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, d6-Acetone) δ 208.3 (quat C), 127.7 (quat C, q, J = 308 Hz), 71.8 (quat C, q, J = 22 Hz), 35.8 (CH2), 30.4 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, d6-Acetone) δ −93.4; HRMS calc. for C7H8O2F3 181.0482 (M+ − 1), found 181.0485.
ethyl acetate) to give 4-oxo-1-trifluoromethylcyclohexan-1-ol as a colourless solid (1.28 g, 55%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, d6-Acetone) δ 5.30 (1H, s), 2.69 (2H, ddd, J = 14.4, 6.4, 6.4 Hz), 2.06–2.27 (6H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, d6-Acetone) δ 208.3 (quat C), 127.7 (quat C, q, J = 308 Hz), 71.8 (quat C, q, J = 22 Hz), 35.8 (CH2), 30.4 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, d6-Acetone) δ −93.4; HRMS calc. for C7H8O2F3 181.0482 (M+ − 1), found 181.0485.
cis-4-(Dibenzylamino)-1-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexan-1-ol 16
Following the procedure reported by Abdel-Magid,27 4-oxo-1-trifluoromethylcyclohexan-1-ol (0.20 g, 1.1 mmol), dibenzylamine (0.21 mL, 1.1 mmol), NaBH(OAc)3 (0.33 g, 1.5 mmol) and acetic acid (0.13 mL, 2.2 mmol) were mixed in anhydrous THF (5 mL). The resulting mixture was stirred under an Ar atmosphere for 16 h, before further portions of NaBH(OAc)3 (0.33 g, 1.5 mmol) and acetic acid (0.13 mL, 2.2 mmol) were added and the mixture stirred for a further 6 h. The reaction mixture was quenched with 1 M NaOH (aq) solution (20 mL), poured into a separating funnel and extracted with dichloromethane (3 × 15 mL). The combined organic extract was washed with water (20 mL), dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude product, which was purified by column chromatography on silica (6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 petroleum ether
1 petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate) to give cis16 (0.12 g, 31%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38 (4H, d, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.31 (4H, app t, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.23 (2H, t, J = 7.2 Hz), 3.68 (4H, s), 2.46–2.62 (1H, m), 1.72–1.90 (6H, m), 1.67 (1H, br s), 1.55 (1H, app td, J = 12.5, 5.1 Hz); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 140.8 (quat C), 128.5 (CH), 128.4 (CH), 126.9 (CH), 126.4 (quat C, q, J = 280 Hz), 72.5 (quat C, q, J = 30 Hz), 56.6 (CH), 54.0 (CH2), 29.7 (CH2), 22.0 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −84.5; HRMS calc. for C21H25ONF3 364.1883 (M+ + 1), found 364.1880. Crystals were grown by slow evaporation of a saturated solution in CHCl3.
ethyl acetate) to give cis16 (0.12 g, 31%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38 (4H, d, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.31 (4H, app t, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.23 (2H, t, J = 7.2 Hz), 3.68 (4H, s), 2.46–2.62 (1H, m), 1.72–1.90 (6H, m), 1.67 (1H, br s), 1.55 (1H, app td, J = 12.5, 5.1 Hz); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 140.8 (quat C), 128.5 (CH), 128.4 (CH), 126.9 (CH), 126.4 (quat C, q, J = 280 Hz), 72.5 (quat C, q, J = 30 Hz), 56.6 (CH), 54.0 (CH2), 29.7 (CH2), 22.0 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −84.5; HRMS calc. for C21H25ONF3 364.1883 (M+ + 1), found 364.1880. Crystals were grown by slow evaporation of a saturated solution in CHCl3.
trans-2-(Dibenzylamino)cyclohexan-1-ol
Following the procedure reported by Yamamoto,20 dibenzylamine (3.9 mL, 20.0 mmol) was added to a mixture of cyclohexene oxide (1.0 mL, 10.0 mmol), ytterbium triflate (0.62 g, 1.0 mmol) and anhydrous THF (10 mL). The mixture was refluxed under an Ar atmosphere for 14 h. Ethyl acetate (30 mL) was added, and the solution was washed with a saturated solution of K2CO3 (20 mL), dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude product, which was purified by column chromatography on silica (9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 petroleum ether
1 petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate) to give trans-2-(dibenzylamino)cyclohexan-1-ol as a colourless solid (1.5 g, 50%); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.22–7.36 (10H, m), 3.87 (2H, d, J = 13.3 Hz), 3.73–3.77 (1H, br s), 3.52 (1H, app td, J = 10.1, 4.5 Hz), 3.40 (2H, d, J = 13.3 Hz), 2.37 (1H, ddd, J = 10.9, 10.6, 3.5 Hz), 2.04–2.12 (1H, m), 1.96–2.02 (1H, m), 1.75–1.85 (1H, m), 1.61–1.72 (1H, m), 1.05–1.33 (4H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 139.6 (quat C), 129.1 (CH), 128.6 (CH), 127.3 (CH), 69.2 (CH), 64.3 (CH), 53.7 (CH2), 33.3 (CH2), 25.6 (CH2), 24.2 (CH2), 22.2 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C20H26ON 296.2009 (M+ + 1), found 296.2010.
ethyl acetate) to give trans-2-(dibenzylamino)cyclohexan-1-ol as a colourless solid (1.5 g, 50%); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.22–7.36 (10H, m), 3.87 (2H, d, J = 13.3 Hz), 3.73–3.77 (1H, br s), 3.52 (1H, app td, J = 10.1, 4.5 Hz), 3.40 (2H, d, J = 13.3 Hz), 2.37 (1H, ddd, J = 10.9, 10.6, 3.5 Hz), 2.04–2.12 (1H, m), 1.96–2.02 (1H, m), 1.75–1.85 (1H, m), 1.61–1.72 (1H, m), 1.05–1.33 (4H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 139.6 (quat C), 129.1 (CH), 128.6 (CH), 127.3 (CH), 69.2 (CH), 64.3 (CH), 53.7 (CH2), 33.3 (CH2), 25.6 (CH2), 24.2 (CH2), 22.2 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C20H26ON 296.2009 (M+ + 1), found 296.2010.
2-(Dibenzylamino)cyclohexan-1-one 28
Compound 28 was prepared using General Procedure 1 from trans-2-(dibenzylamino)cyclohexan-1-ol (1.20 g, 4.1 mmol), oxalyl chloride (0.48 mL, 5.6 mmol), DMSO (1.00 mL, 14.1 mmol), triethylamine (3.92 mL, 28.1 mmol) and anhydrous dichloromethane (30 mL in total) to give the crude product, which was purified by column chromatography on silica (8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 petroleum ether
1 petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate) to give 28 as a light yellow solid (0.93 g, 78%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.39 (4H, d, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.26–7.32 (4H, m), 7.18–7.24 (2H, m), 4.00 (2H, d, J = 14.3 Hz), 3.76 (2H, d, J = 14.3 Hz), 3.31 (1H, dd, J = 12.4, 5.7), 2.34–2.44 (1H, m), 2.10–2.25 (2H, m), 1.76–2.02 (3H, m), 1.44–1.66 (2H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 212.2 (quat C), 140.8 (quat C), 128.5 (CH), 128.3 (CH), 126.9 (CH), 66.6 (CH), 54.9 (CH2), 42.6 (CH2), 31.7 (CH2), 27.2 (CH2), 25.1 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C20H24ON 294.1852 (M+ + 1), found 294.1852.
ethyl acetate) to give 28 as a light yellow solid (0.93 g, 78%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.39 (4H, d, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.26–7.32 (4H, m), 7.18–7.24 (2H, m), 4.00 (2H, d, J = 14.3 Hz), 3.76 (2H, d, J = 14.3 Hz), 3.31 (1H, dd, J = 12.4, 5.7), 2.34–2.44 (1H, m), 2.10–2.25 (2H, m), 1.76–2.02 (3H, m), 1.44–1.66 (2H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 212.2 (quat C), 140.8 (quat C), 128.5 (CH), 128.3 (CH), 126.9 (CH), 66.6 (CH), 54.9 (CH2), 42.6 (CH2), 31.7 (CH2), 27.2 (CH2), 25.1 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C20H24ON 294.1852 (M+ + 1), found 294.1852.
cis-2-(Dibenzylamino)-1-methylcyclohexan-1-ol 14
Compound 14 was prepared following General Procedure 2 at a reduced temperature of 0 °C, from 28 (0.25 g, 0.85 mmol), anhydrous THF (10 mL) and 3.0 M MeMgCl in THF (0.45 mL, 1.35 mmol), and was isolated as a yellow oil (0.23 g, 89%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.39 (4H, d, J = 7.3 Hz), 7.30 (4H, app t, J = 7.3 Hz), 7.22 (2H, t, J = 7.3 Hz), 4.14 (2H, d, J = 13.8 Hz), 3.39 (2H, d, J = 13.8 Hz), 2.29 (1H, dd, J = 12.2, 3.4 Hz), 1.80–1.90 (2H, m), 1.65–1.79 (1H, m), 1.48–1.57 (2H, m), 1.38–1.48 (1H, m), 1.08–1.27 (5H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 141.2 (quat C), 129.0 (CH), 128.2 (CH), 126.7 (CH), 74.3 (quat C), 63.1 (CH), 55.9 (CH2), 41.4 (CH2), 29.2 (CH3), 26.4 (CH2), 21.8 (CH2), 20.1 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C21H28ON 310.2165 (M+ + 1), found 310.2166. The HCl salt of 14 was prepared by forming a saturated HCl solution in diethyl ether. Crystals were grown by the slow evaporation of a concentrated solution of the salt 14·HCl in methanol.trans-2-(Dibenzylamino)-1-methylcyclohexan-1-ol 13 and cis-2-(dibenzylamino)-1-methylcyclohexan-1-ol 14
Compounds 13 and 14 were prepared following General Procedure 2 at a reduced temperature of 0 °C, using 28 (0.050 g, 0.17 mmol), dry THF (10 mL) and a 1.6 M solution of MeLi in diethyl ether (0.16 mL, 0.26 mmol) to give the crude products, which were purified by column chromatography on silica (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 petroleum ether
1 petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate) to give 14 (0.023 g, 44%) which was identical to an authentic sample, followed by 13 as a colourless residue (0.007 g, 13%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.17–7.46 (10H, m), 3.85 (2H, d, J = 13.7 Hz), 3.42 (2H, d, J = 13.7 Hz), 2.61 (1H, app d, J = 10.6 Hz, CH), 1.84, (2H, app d, J = 8.8 Hz), 1.50–1.72 (4H, m), 1.36–1.47 (2H, m), 1.27 (3H, s); HRMS calc. for C21H28ON 310.2165 (M+ + 1), found 310.2166.
ethyl acetate) to give 14 (0.023 g, 44%) which was identical to an authentic sample, followed by 13 as a colourless residue (0.007 g, 13%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.17–7.46 (10H, m), 3.85 (2H, d, J = 13.7 Hz), 3.42 (2H, d, J = 13.7 Hz), 2.61 (1H, app d, J = 10.6 Hz, CH), 1.84, (2H, app d, J = 8.8 Hz), 1.50–1.72 (4H, m), 1.36–1.47 (2H, m), 1.27 (3H, s); HRMS calc. for C21H28ON 310.2165 (M+ + 1), found 310.2166.
trans-2-(Dibenzylamino)-1-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexan-1-ol 19 and cis-2-(dibenzylamino)-1-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexan-1-ol 20
Compounds 19 and 20 were prepared using General Procedure 2 in which 4 M HCl was added after 3 h, using 28 (0.234 g, 0.80 mmol), trifluoromethyltrimethylsilane (0.14 mL, 0.95 mmol), anhydrous THF (10 mL) and a solution of TBAF (5 mg) in THF (1.0 mL) to give the crude products, which were purified by column chromatography on silica (5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, followed by 5
1, followed by 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 petroleum ether
2 petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate) to give 19 as a colourless solid (0.167 g, 58%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.26–7.44 (10H, m), 3.69–4.15 (2H, br s), 3.63 (1H, s), 3.36 (2H, d, J = 13.3 Hz), 2.78–2.89 (1H, m), 2.21–2.31 (1H, m), 1.91–2.01 (2H, m), 1.75–1.91 (1H, m), 1.28–1.69 (3H, m), 1.19 (1H, dddd, J = 16.4, 9.4, 4.6, 2.3 Hz); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 139.4 (quat C), 129.2 (CH), 128.7 (CH), 127.6 (CH), 127.2 (quat C, q, J = 293.0 Hz), 72.3 (quat C, q, J = 20.1 Hz), 66.3 (CH), 55.9 (CH2, br), 34.1 (CH2), 26.0 (CH2), 21.5 (CH2), 21.4 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −69.4; HRMS calc. for C21H25ONF3 364.1883 (M+ + 1), found 364.1878; crystallised from cold MeOH. Followed by 20 as a colourless solid (0.037 g, 13%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38–7.46 (4H, m), 7.35 (4H, app t, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.28 (2H, t, J = 7.2 Hz), 3.66–4.38 (2H, br s), 3.52 (2H, d, J = 13.8 Hz), 3.00 (1H, dd, J = 10.1, 4.4 Hz), 2.31–2.58 (1H, m), 1.72–1.94 (4H, m), 1.47–1.64 (3H, m), 1.16–1.40 (1H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 139.7 (quat C), 129.2 (CH), 128.4 (CH), 127.1 (CH), 126.4 (quat C, q, J = 293.0 Hz), 76.3 (quat C, q, J = 20.2 Hz), 58.6 (CH), 55.5 (CH2, br), 32.8 (CH2), 25.2 (CH2), 20.8 (CH2), 20.5 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −78.2; HRMS calc. for C21H25ONF3 364.1883 (M+ + 1), found 364.1883.
ethyl acetate) to give 19 as a colourless solid (0.167 g, 58%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.26–7.44 (10H, m), 3.69–4.15 (2H, br s), 3.63 (1H, s), 3.36 (2H, d, J = 13.3 Hz), 2.78–2.89 (1H, m), 2.21–2.31 (1H, m), 1.91–2.01 (2H, m), 1.75–1.91 (1H, m), 1.28–1.69 (3H, m), 1.19 (1H, dddd, J = 16.4, 9.4, 4.6, 2.3 Hz); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 139.4 (quat C), 129.2 (CH), 128.7 (CH), 127.6 (CH), 127.2 (quat C, q, J = 293.0 Hz), 72.3 (quat C, q, J = 20.1 Hz), 66.3 (CH), 55.9 (CH2, br), 34.1 (CH2), 26.0 (CH2), 21.5 (CH2), 21.4 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −69.4; HRMS calc. for C21H25ONF3 364.1883 (M+ + 1), found 364.1878; crystallised from cold MeOH. Followed by 20 as a colourless solid (0.037 g, 13%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38–7.46 (4H, m), 7.35 (4H, app t, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.28 (2H, t, J = 7.2 Hz), 3.66–4.38 (2H, br s), 3.52 (2H, d, J = 13.8 Hz), 3.00 (1H, dd, J = 10.1, 4.4 Hz), 2.31–2.58 (1H, m), 1.72–1.94 (4H, m), 1.47–1.64 (3H, m), 1.16–1.40 (1H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 139.7 (quat C), 129.2 (CH), 128.4 (CH), 127.1 (CH), 126.4 (quat C, q, J = 293.0 Hz), 76.3 (quat C, q, J = 20.2 Hz), 58.6 (CH), 55.5 (CH2, br), 32.8 (CH2), 25.2 (CH2), 20.8 (CH2), 20.5 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −78.2; HRMS calc. for C21H25ONF3 364.1883 (M+ + 1), found 364.1883.
3-(Dibenzylamino)cyclohexan-1-one 30
Following the procedure reported by Banik and Srivastava,28 bismuth(III) nitrate pentahydrate (10.0 g, 21 mmol) was added to a solution of cyclohexen-1-one (10 mL, 103 mmol) and dibenzylamine (20 mL, 104 mmol) in dichloromethane (80 mL). Most of the dichloromethane was removed under reduced pressure, and the resulting slurry stirred at room temperature overnight. Dichloromethane (100 mL) was added and the resulting suspension filtered by gravity filtration through filter paper. The filtrate was washed with sat. NaHCO3 (2 × 30 mL) and brine (2 × 30 mL), dried over MgSO4, filtered once again and the dichloromethane removed under reduced pressure (taking care not to heat above 40 °C) to give the crude product. Purification was achieved by twice recrystallising from warm petroleum ether to give 30 as colourless crystals (9.7 g, 32%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.36 (4H, d, J = 7.0 Hz), 7.27–7.33 (4H, m), 7.20–7.25 (2H, m), 3.72 (2H, d, J = 14.0 Hz), 3.62 (2H, d, J = 14.0 Hz), 2.95 (1H, app tt, J = 12.2, 3.7 Hz), 2.61–2.69 (1H, m), 2.39–2.49 (1H, m), 2.27–2.36 (1H, m), 2.15–2.27 (1H, m), 1.95–2.13 (2H, m), 1.65–1.78 (1H, m), 1.61–1.69 (1H, br s), 1.33–1.48 (1H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 210.8 (quat C), 140.0 (quat C), 128.5 (CH), 128.4 (CH), 127.1 (CH), 58.2 (CH), 53.8 (CH2), 44.3 (CH2), 41.3 (CH2), 27.9 (CH2), 22.6 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C20H24ON 294.1852 (M+ + 1), found 294.1855.trans-3-(Dibenzylamino)-1-methylcyclohexan-1-ol 11 and cis-3-(dibenzylamino)-1-methylcyclohexan-1-ol 12
Compounds 11 and 12 were prepared following General Procedure 2 at a reduced temperature of 0 °C, using 30 (0.40 g, 1.36 mmol), anhydrous THF (15 mL) and 3.0 M MeMgCl in THF (0.73 mL, 2.18 mmol), and the products purified by column chromatography on silica (6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 petroleum ether
1 petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate) to give 11 as a colourless solid (0.34 g, 80%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.36 (4H, d, J = 7.4 Hz), 7.28 (4H, app t, J = 7.4 Hz), 7.19 (2H, t, J = 7.4 Hz), 3.63 (3H, s), 2.92 (1H, app tt, J = 12.2, 3.4 Hz), 1.80–1.95 (2H, m), 1.36–1.67 (4H, m), 1.15–1.30 (5H, m), 0.98 (1H, br s); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 141.1 (quat C), 128.6 (CH), 128.3 (CH), 126.7 (CH), 71.0 (quat C), 54.0 (CH2), 53.7 (CH), 41.1 (CH2), 38.7 (CH2), 32.1 (CH3), 27.7 (CH2), 20.7 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C21H28ON 310.2165 (M+ + 1), found 310.2164; crystallised from cold MeOH. Followed by 12 as a colourless oil that solidified on standing (0.04 g, 9%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.27–7.39 (8H, m), 7.22 (2H, t, J = 7.0 Hz), 3.71 (2H, d, J = 14.0 Hz), 3.65 (2H, d, J = 14.0 Hz), 2.74 (1H, app tt, J = 9.4, 3.4 Hz), 1.64–1.85 (4H, m), 1.39–1.62 (3H, m), 1.17–1.30 (1H, m), 1.12 (3H, s, CH3); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 140.0 (quat C), 128.9 (CH), 128.3 (CH), 126.9 (CH), 71.6 (quat C), 55.3 (CH), 53.6 (CH2), 41.1 (CH2), 40.4 (CH2), 28.6 (CH2), 27.4 (CH3), 21.0 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C21H28ON 310.2165 (M+ + 1), found 310.2160.
ethyl acetate) to give 11 as a colourless solid (0.34 g, 80%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.36 (4H, d, J = 7.4 Hz), 7.28 (4H, app t, J = 7.4 Hz), 7.19 (2H, t, J = 7.4 Hz), 3.63 (3H, s), 2.92 (1H, app tt, J = 12.2, 3.4 Hz), 1.80–1.95 (2H, m), 1.36–1.67 (4H, m), 1.15–1.30 (5H, m), 0.98 (1H, br s); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 141.1 (quat C), 128.6 (CH), 128.3 (CH), 126.7 (CH), 71.0 (quat C), 54.0 (CH2), 53.7 (CH), 41.1 (CH2), 38.7 (CH2), 32.1 (CH3), 27.7 (CH2), 20.7 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C21H28ON 310.2165 (M+ + 1), found 310.2164; crystallised from cold MeOH. Followed by 12 as a colourless oil that solidified on standing (0.04 g, 9%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.27–7.39 (8H, m), 7.22 (2H, t, J = 7.0 Hz), 3.71 (2H, d, J = 14.0 Hz), 3.65 (2H, d, J = 14.0 Hz), 2.74 (1H, app tt, J = 9.4, 3.4 Hz), 1.64–1.85 (4H, m), 1.39–1.62 (3H, m), 1.17–1.30 (1H, m), 1.12 (3H, s, CH3); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 140.0 (quat C), 128.9 (CH), 128.3 (CH), 126.9 (CH), 71.6 (quat C), 55.3 (CH), 53.6 (CH2), 41.1 (CH2), 40.4 (CH2), 28.6 (CH2), 27.4 (CH3), 21.0 (CH2); HRMS calc. for C21H28ON 310.2165 (M+ + 1), found 310.2160.
trans-3-(Dibenzylamino)-1-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexan-1-ol 17 and cis-3-(dibenzylamino)-1-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexan-1-ol 18
Compounds 17 and 18 were prepared following General Procedure 3 quenching with 4 M HCl after 2.5 h, from 30 (1.40 g, 4.75 mmol), trifluoromethyltrimethylsilane (0.77 mL, 5.21 mmol), anhydrous THF (20 mL) and a solution of TBAF (5 mg) in THF (1.0 mL) to give the crude products, which were purified by column chromatography on silica (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 petroleum ether
1 petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate) to give 17 as a colourless solid (0.64 g, 37%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.36 (4H, d, J = 7.3 Hz), 7.30 (4H, app t, J = 7.4 Hz), 7.22 (2H, t, J = 7.4 Hz), 3.62 (4H, br s), 1.89–2.03 (1H, m), 1.89–2.02 (2H, m), 1.42–1.79 (6H, m), 1.27–1.41 (1H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 140.5 (quat C), 128.6 (CH), 128.4 (CH), 126.9 (CH), 126.1 (quat C, q, J = 283 Hz), 74.5 (quat C, q, J = 30.3 Hz), 53.9 (CH2), 52.3 (CH), 32.1 (CH2), 29.7 (CH2), 27.4 (CH2), 19.7 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −84.8; HRMS calc. for C21H25ONF3 364.1883 (M+ + 1), found 364.1885. Followed by 18 as a colourless solid (0.70 g, 41%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.39–7.48 (1H, br s), 7.29–7.36 (4H, m), 7.22–7.29 (6H, m), 3.81 (2H, d, J = 14.3 Hz), 3.76 (2H, d, J = 14.3 Hz), 3.19 (1H, app pent, J = 3.2 Hz), 2.48 (1H, app d, J = 14.1 Hz), 2.03–2.17 (1H, app d, J = 14.3 Hz), 1.83–1.95 (1H, app d, J = 11.6 Hz), 1.44–1.82 (5H, m); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ 7.25–7.34 (8H, m), 7.17–7.23 (2H, m), 3.68 (2H, d, J = 13.8 Hz), 3.61 (2H, d, J = 13.8 Hz), 2.91 (1H, app tt, J = 10.8, 3.6 Hz), 2.18–2.28 (1H, m), 1.95–2.05 (1H, m), 1.75–1.84 (1H, m), 1.62–1.74 (2H, m), 1.26–1.60 (3H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 137.3 (quat C), 129.5 (CH), 128.7 (CH), 127.6 (CH), 126.0 (quat C, q, J = 284 Hz), 73.8 (quat C, q, J = 28.7 Hz), 54.9 (CH), 53.2 (CH2), 31.2 (CH2), 30.2 (CH2), 28.3 (CH2), 16.4 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −84.4; HRMS calc. for C21H25ONF3 364.1883 (M+ + 1), found 364.1885.
ethyl acetate) to give 17 as a colourless solid (0.64 g, 37%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.36 (4H, d, J = 7.3 Hz), 7.30 (4H, app t, J = 7.4 Hz), 7.22 (2H, t, J = 7.4 Hz), 3.62 (4H, br s), 1.89–2.03 (1H, m), 1.89–2.02 (2H, m), 1.42–1.79 (6H, m), 1.27–1.41 (1H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 140.5 (quat C), 128.6 (CH), 128.4 (CH), 126.9 (CH), 126.1 (quat C, q, J = 283 Hz), 74.5 (quat C, q, J = 30.3 Hz), 53.9 (CH2), 52.3 (CH), 32.1 (CH2), 29.7 (CH2), 27.4 (CH2), 19.7 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −84.8; HRMS calc. for C21H25ONF3 364.1883 (M+ + 1), found 364.1885. Followed by 18 as a colourless solid (0.70 g, 41%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.39–7.48 (1H, br s), 7.29–7.36 (4H, m), 7.22–7.29 (6H, m), 3.81 (2H, d, J = 14.3 Hz), 3.76 (2H, d, J = 14.3 Hz), 3.19 (1H, app pent, J = 3.2 Hz), 2.48 (1H, app d, J = 14.1 Hz), 2.03–2.17 (1H, app d, J = 14.3 Hz), 1.83–1.95 (1H, app d, J = 11.6 Hz), 1.44–1.82 (5H, m); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ 7.25–7.34 (8H, m), 7.17–7.23 (2H, m), 3.68 (2H, d, J = 13.8 Hz), 3.61 (2H, d, J = 13.8 Hz), 2.91 (1H, app tt, J = 10.8, 3.6 Hz), 2.18–2.28 (1H, m), 1.95–2.05 (1H, m), 1.75–1.84 (1H, m), 1.62–1.74 (2H, m), 1.26–1.60 (3H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 137.3 (quat C), 129.5 (CH), 128.7 (CH), 127.6 (CH), 126.0 (quat C, q, J = 284 Hz), 73.8 (quat C, q, J = 28.7 Hz), 54.9 (CH), 53.2 (CH2), 31.2 (CH2), 30.2 (CH2), 28.3 (CH2), 16.4 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −84.4; HRMS calc. for C21H25ONF3 364.1883 (M+ + 1), found 364.1885.
cis-3-Amino-1-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexan-1-ol 31
Pearlman's catalyst (10% palladium hydroxide on carbon, 0.49 g, 5.38 mmol) and 18 (1.96 g, 0.538 mmol) were added to a Schlenk flask which was evacuated and back-filled with N2. Ethanol (20 mL) was added and the flask evacuated using a diaphragm pump and back-filled with H2 from a balloon three times. The reaction mixture was left to stir vigorously until consumption of starting material was apparent by TLC analysis (2 days at room temperature). Ethyl acetate (20 mL) was added, and the mixture passed through a short Celite plug using additional ethyl acetate. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to give 31 as a light yellow oil, which crystallised upon standing (0.93 g, 93%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 3.35–3.30 (1H, m), 1.86–1.96 (2H, m), 1.79–1.82 (2H, m,), 1.74–1.78 (1H, m), 1.64–1.74 (2H, m), 1.54–1.63 (1H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 127.5 (quat C, q, J = 283.0 Hz), 74.0 (quat C, q, J = 30.3 Hz), 46.8 (CH), 35.3 (CH2), 32.9 (CH2), 31.2 (CH2), 16.5 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −85.2; HRMS calc. for C7H13ONF3 184.0944 (M+ + 1), found 184.0941.N-cis-3-Hydroxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexyl)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)propanamide 32
3-(4-Methoxyphenyl)propionic acid (0.79 g, 4.38 mmol) was refluxed in thionyl chloride (0.58 mL, 8.0 mmol) under an atmosphere of N2 for 2 h. Excess thionyl chloride was removed under reduced pressure to give the crude acid chloride, which was used without further purification. In a separate flask, a solution of 31 (0.73 g, 3.99 mmol) and triethylamine (0.61 mL, 4.38 mmol) in anhydrous diethyl ether (20 mL) under a N2 atmosphere was cooled to 0 °C. A solution of the freshly prepared acid chloride in anhydrous ether (2 mL) was added drop-wise with vigorous stirring of the reaction mixture. Upon completion of addition, the cooling bath was removed and the mixture left to stir overnight at room temperature. The reaction mixture was poured into a separating funnel containing water (20 mL), and was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 15 mL). The combined organic extract was washed with 1 M HCl (2 × 20 mL), water (20 mL), dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude product, which was purified by column chromatography on silica (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 9 methanol
9 methanol![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate) to give 32 as a yellow oil (0.96 g, 69%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.10 (2H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 6.81 (2H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 6.77 (1H, br d, J = 8.2 Hz), 4.28–4.36 (1H, m), 3.76 (3H, s), 2.88 (2H, t, J = 7.4 Hz), 2.40 (2H, t, J = 7.4 Hz), 1.67–1.83 (4H, m), 1.48–1.64 (3H, m), 1.32–1.42 (1H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 171.3 (quat C), 158.3 (quat C), 132.9 (quat C), 129.5 (CH), 125.8 (quat C, q, J = 289 Hz), 114.1 (CH), 73.6 (quat C, q, J = 28 Hz), 55.4 (CH3), 42.9 (CH), 39.3 (CH2), 32.3 (CH2), 31.2 (CH2), 29.8 (CH2), 29.3 (CH2), 15.1 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −85.1; HRMS calc. for C17H23O3NF3 346.1625 (M+ + 1), found 346.1626.
ethyl acetate) to give 32 as a yellow oil (0.96 g, 69%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.10 (2H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 6.81 (2H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 6.77 (1H, br d, J = 8.2 Hz), 4.28–4.36 (1H, m), 3.76 (3H, s), 2.88 (2H, t, J = 7.4 Hz), 2.40 (2H, t, J = 7.4 Hz), 1.67–1.83 (4H, m), 1.48–1.64 (3H, m), 1.32–1.42 (1H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 171.3 (quat C), 158.3 (quat C), 132.9 (quat C), 129.5 (CH), 125.8 (quat C, q, J = 289 Hz), 114.1 (CH), 73.6 (quat C, q, J = 28 Hz), 55.4 (CH3), 42.9 (CH), 39.3 (CH2), 32.3 (CH2), 31.2 (CH2), 29.8 (CH2), 29.3 (CH2), 15.1 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −85.1; HRMS calc. for C17H23O3NF3 346.1625 (M+ + 1), found 346.1626.
cis-3-((3-(4-Methoxyphenyl)propyl)amino)-1-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexan-1-ol 33
To a solution of 32 (0.93 g, 2.69 mmol) in anhydrous THF (25 mL) under a N2 atmosphere, was added drop-wise a 1 M solution of BH3·THF (27.0 mL, 27.0 mmol). Upon completion of addition, the mixture was heated at reflux overnight. The reaction mixture was cooled to 0 °C and methanol (5 mL) was added carefully drop-wise and the mixture stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. 2 M HCl (aq) (5 mL) was added, and the mixture was stirred for an additional 30 minutes at room temperature, after which the volatiles were removed under reduced pressure to give the aqueous residue. The aqueous residue was adjusted to pH 10 using 2 M NaOH (aq), and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 mL). The combined organic extracts were washed with brine (20 mL), dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude product, which was purified by column chromatography on silica (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 dichloromethane
1 dichloromethane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) methanol) to give 33 as a light yellow oil (0.68 g, 76%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.10 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.83 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 3.78 (3H, s), 3.65 (1H, app t, J = 6.4 Hz), 3.14 (1H, app pent, J = 3.0 Hz), 2.46–2.77 (4H, m), 1.67–2.03 (7H, m), 1.43–1.65 (4H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 158.0 (quat C), 133.7 (quat C), 129.4 (CH), 125.8 (quat C, q, J = 281 Hz), 114.0 (CH), 73.4 (quat C, q, J = 30 Hz), 55.4 (CH3), 53.0 (CH), 47.0 (CH2), 34.5 (CH2), 32.6 (CH2), 31.8 (CH2), 31.3 (CH2), 30.6 (CH2), 15.3 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −85.2; HRMS calc. for C17H25O2NF3 332.1832 (M+ + 1), found 332.1836.
methanol) to give 33 as a light yellow oil (0.68 g, 76%); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.10 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.83 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 3.78 (3H, s), 3.65 (1H, app t, J = 6.4 Hz), 3.14 (1H, app pent, J = 3.0 Hz), 2.46–2.77 (4H, m), 1.67–2.03 (7H, m), 1.43–1.65 (4H, m); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 158.0 (quat C), 133.7 (quat C), 129.4 (CH), 125.8 (quat C, q, J = 281 Hz), 114.0 (CH), 73.4 (quat C, q, J = 30 Hz), 55.4 (CH3), 53.0 (CH), 47.0 (CH2), 34.5 (CH2), 32.6 (CH2), 31.8 (CH2), 31.3 (CH2), 30.6 (CH2), 15.3 (CH2); 19F{1H} NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −85.2; HRMS calc. for C17H25O2NF3 332.1832 (M+ + 1), found 332.1836.
Acknowledgements
We thank the EPSRC for financial support and the Mass Spectrometry Service, Swansea, for high-resolution spectra.Notes and references
- F. Lovering, J. Bikker and C. Humblet, J. Med. Chem., 2009, 52, 6752 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Aldeghi, S. Malhotra, D. L. Selwood and A. W. E. Chan, Chem. Biol. Drug Des., 2014, 83, 450 CAS.
- C. M. Marson, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 5514 RSC.
- P. A. Clemons, J. A. Wilson, V. Dančík, S. Muller, H. A. Carrinski, B. K. Wagner, A. N. Koehler and S. L. Schreiber, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2011, 108, 6817 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Kim, M. A. Arai, T. Arai, J. O. Lamenzo, E. F. Dean, N. Patterson, P. A. Clemons and S. L. Schreiber, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 14740 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. J. Ritchie and S. J. F. Macdonald, Drug Discovery Today, 2009, 14, 1011 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. D. Sunderhaus and S. F. Martin, Chem. – Eur. J., 2009, 15, 1300 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. S. Tan, Nat. Chem. Biol., 2005, 1, 74 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. L. Schreiber, Science, 2000, 287, 1964 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. E. Welsch, S. A. Snyder and B. R. Stockwell, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2010, 14, 347 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. B. Smith, March's Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms and Structure, Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, 2013 Search PubMed.
- P. E. Cross, J. E. Arrowsmith, G. N. Thomas, M. Gwilt, R. A. Burges and A. J. Higgins, J. Med. Chem., 1990, 33, 1151 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Heeres, R. Hendrickx and J. Van Cutsem, J. Med. Chem., 1983, 26, 611 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. J. Petcher and P. Pauling, J. Med. Chem., 1971, 14, 1 CrossRef CAS.
- B. W. Ramsey, J. Davies, N. G. McElvaney, E. Tullis, S. C. Bell, P. Dřevínek, M. Griese, E. F. McKone, C. E. Wainwright, M. W. Konstan, R. Moss, F. Ratjen, I. Sermet-Gaudelus, S. M. Rowe, Q. Dong, S. Rodriguez, K. Yen, C. Ordoñez and J. S. Elborn, N. Engl. J. Med., 2011, 365, 1663 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. D. Cox, M. J. Breslin, D. B. Whitman, J. D. Schreier, G. B. McGaughey, M. J. Bogusky, A. J. Roecker, S. P. Mercer, R. A. Bednar, W. Lemaire, J. G. Bruno, D. R. Reiss, C. M. Harrell, K. L. Murphy, S. L. Garson, S. M. Doran, T. Prueksaritanont, W. B. Anderson, C. Tang, S. Roller, T. D. Cabalu, D. Cui, G. D. Hartman, S. D. Young, K. S. Koblan, C. J. Winrow, J. J. Renger and P. J. Coleman, J. Med. Chem., 2010, 53, 5320 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. M. Jenkins, D. Williams, Y. Deng, J. Uhl, V. Kitchen, D. Collins and C. L. Erickson-Miller, Blood, 2007, 109, 4739 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. H. Ryu, S. A. Kim, K. H. Ryu, J. S. Kim, N. H. Kim, H. Y. Han, Y. K. Kim, W. Youn, Y. Lee, H. J. Son, B. Lee, S. H. Park, J. Y. Lee, H. J. Lee, H. C. Jung, Y. A. Shin, J. A. Lee, B. R. Lee, J. H. Sa and O. Kwon, Picolinamide and Pyrimidine-4-carboxamide compounds, process for preparing and pharmaceutical composition comprising the same, WO2011139107A2, 2011 Search PubMed.
- D. P. Walker, G. B. Arhancet, H. F. Lu, S. E. Heasley, S. Metz, N. M. Kablaoui, F. M. Franco, C. E. Hanau, J. A. Scholten, J. R. Springer, Y. M. Fobian, J. S. Carter, L. Xing, S. Yang, A. F. Shaffer, G. M. Jerome, M. T. Baratta, W. M. Moore and M. L. Vazquez, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2013, 23, 1120 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Meguro, N. Asao and Y. Yamamoto, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1994, 2597 RSC.
- J. A. Albers, L. Ayala, S. S. Clareen, M. M. D. Mederos, R. Hilgraf, S. G. Hegde, K. Hughes, A. Kois, V. Plantevin-Krenitsky, M. McCarrick, L. Nadolny, M. S. S. Palanki, K. Sahasrabudhe, J. Sapienza, Y. Satoh, M. K. Sloss, E. Sudbeck and J. Wright, Haloaryl substituted Aminopurines, compositions thereof, and methods of treatment therewith, US20070060598A1, 2007 Search PubMed.
- B. W. Gung, Tetrahedron, 1996, 52, 5263 CrossRef CAS.
- J. R. Boone and E. C. Ashby, in Top. Stereochem, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2007, p. 53 Search PubMed.
- D. H. R. Barton, J. Chem. Soc., 1953, 1027 RSC.
- K. Maruoka, T. Itoh, M. Sakurai, K. Nonoshita and H. Yamamoto, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1988, 110, 3588 CrossRef CAS.
- M. V. Riofski, A. D. Hart and D. A. Colby, Org. Lett., 2012, 15, 208 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. F. Abdel-Magid, K. G. Carson, B. D. Harris, C. A. Maryanoff and R. D. Shah, J. Org. Chem., 1996, 61, 3849 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Srivastava and B. K. Banik, J. Org. Chem., 2003, 68, 2109 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. W. Nader, W. Heinrich, M. Baar-Schäfer and E. Hangel, Chem. Ber., 1985, 118, 4314 CrossRef CAS.
- For the effect of fluorine on both conformation and acidity of an alternative H-bond donor see: E. Bogdan, G. Compain, L. Mtashobya, J.-Y. Le Questel, F. Besseau, N. Galland, B. Linclau and J. Graton, Chem. – Eur. J., 2015, 21, 11462 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: 1H, 13C and 19F spectra for compounds reported. CCDC 1064075–1064082. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c5ob01924a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |