Medium bandgap copolymers based on carbazole and quinoxaline exceeding 1.0 V open-circuit voltages†
Kyu Cheol Lee‡
a,
Taehyo Kim‡a,
Seyeong Songa,
Yiho Kima,
Gitish. K. Duttab,
Dong Suk Kim*c,
Jin Young Kim*a and
Changduk Yang*a
aDepartment of Energy Engineering, School of Energy and Chemical Engineering, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), Ulsan 689-798, South Korea. E-mail: jykim@unist.ac.kr; yang@unist.ac.kr
bDepartment of Chemistry, National Institute of Technology Meghalaya Bijini Complex, Laitumkhrah, Shillong, 793003 Meghalaya, India
cKIER-UNIST Advanced Center for Energy, Korea Institute of Energy Research, Ulsan 689-798, South Korea. E-mail: kimds@kier.re.kr
First published on 3rd February 2016
Abstract
Open-circuit voltage (VOC) is an important parameter in determining the performance of polymer solar cells (PSCs). Given the desire for superior VOC values in PSCs, we have designed and synthesized a series of ‘medium bandgap’ donor–acceptor (D–A) copolymers containing carbazole (Cz) and quinoxaline (Qx) (PCzDT-Qx, PCzDT-fQx, and PCzDT-ffQx). As a result of their deep-lying HOMO levels (−5.45 to −5.61 eV), high VOC values are achieved in PSCs with the resulting copolymers, despite the expense of short-circuit current density (JSC) and fill factor (FF) parameters. In this study, in addition to the best power-conversion efficiency (PCE) of up to 4.03% from PCzDT-fQx-based on PSCs, we have demonstrated a VOC value exceeding 1.0 V with PSCs of PCzDT-ffQx, which is among the highest VOC values achieved to date. Moreover, a comprehensive investigation on the mechanism of charge recombination and transport characteristics can determine a clear structure–property correlation in this class of molecules, which is helpful for designing better materials with maximum VOC without scarifying other key photovoltaic parameters.
1. Introduction
In the research community of bulk-heterojunction (BHJ)-based polymer solar cells (PSCs), the majority of synthetic efforts and structure–property studies have been devoted to “low bandgap” donor–acceptor (D–A) copolymers with increased light-harvesting capability to improve short-circuit current density (JSC), which essentially enables high power-conversion efficiencies (PCEs) over 9% in certain systems.1–6 However, the low bandgap D–A copolymers possess usually higher-than-optimal highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) energy levels, which consequently limits the open-circuit voltage (VOC) of the resulting PSCs. Therefore, some recent studies have begun to focus on ‘medium bandgap’ D–A copolymers, due to their deep-lying HOMO levels and potential application in tandem PSCs,7–10 though they relatively suffer from light absorption in visible wavelength range.11,12Since the impressive performance of PSCs based on a quinoxaline (Qx) unit reported by Andersson et al.,13 a series of conjugated materials that belong to the family of D–A copolymers based on Qx have been investigated, which showed their obvious potential for achieving high PCEs in PSCs.14,15 Independently, we also studied a family of Qx-containing D–A copolymers and found that they had very deep-lying HOMO levels, providing a significantly larger VOC of up to 1.00 V.16–18
Seeking to further enhance the VOC values in PSCs, here we attempt to extend the molecular design approach to D–A platform associated with Qx unit; to date, thiophene-based moieties as the natural choice for strong donor portions within the main backbone have been predominantly implemented in constructing Qx-based D–A copolymers for applications in PSCs.19–22
To this end, we have designed and synthesized three medium bandgap D–A copolymers, PCzDT-Qx, PCzDT-fQx, and PCzDT-ffQx (Fig. 1), by copolymerizing tricyclic 2,7-carbazole (Cz) as the donor moiety with either Qx or its fluorinated analogs (fQx (1F) and ffQx (2F)) as the acceptor for the following reasons: (i) taking into account the verified high VOC values generated from D–A copolymers based on Cz donor unit,23–25 we surmise that outgrowth via a synergistic effect of combining Cz and Qx moieties in the main backbone can contribute to the realization of superior VOC. (ii) It is also expected to further improve VOC in the devices of F-containing copolymers, as a results of the more lowered HOMO levels induced by the electron-withdrawing effect of the F substituents. (iii) In addition, the two flanking thienyl spacers can relieve the steric hindrance between the conjugated units, thereby enhancing co-planarity of the backbone, which would in turn help charge transport property by hopping.26,27 Herein, detailed optical, electrochemical, and BHJ morphology, as well as PSC characteristics derived from this series of copolymers are studied and analysed. To our delight, we find that the PSCs based on fluorinated copolymers (PCzDT-fQx, and PCzDT-ffQx) show very high VOC values exceeding 1.0 V, which, to the best of our knowledge, are among the highest values, though they suffer somewhat from poor JSC and fill factor (FF). A best PCE of 4.03% is realized in PSCs based on PCzDT-fQx, which can be attributed to the combined effects of the proper HOMO level and relatively improved charge transport characteristics in the BHJ system.
2. Results and discussion
2.1 Synthesis and characterization
Diboronic ester monomer (M1) and dibromide co-monomers (M2, M3, and M4) were synthesized according to previously reported procedures.28 Scheme 1 shows the synthetic routes for the copolymers. The copolymerizations were accomplished via Pd2(dba)3-catalyzed Suzuki coupling of the monomer M1 with the corresponding co-monomers M2, M3, and M4, respectively. The resulting copolymers were precipitated in methanol![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ammonia solution (9
ammonia solution (9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), collected by filtration, and purified by Soxhlet extraction, using different organic solvents, to remove impurities and/or low molecular weight fractions (see ESI for details†). The remaining part was extracted with chloroform. The purified copolymers exhibit comparable molar masses (Mn) with polydispersity indexes (PDI), determined by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) with THF as an eluent against polystyrene standards, as summarized in Table 1. All copolymers have good solubility in common organic solvents such as chloroform, THF, and chlorobenzene at room temperature. The thermogravimetric analysis measurements (TGA) showed that the onset temperatures with 5% weight-loss (Td) of the copolymers are all over 415 °C, which indicates their excellent thermal stability (see Fig. S1 in ESI†).
1), collected by filtration, and purified by Soxhlet extraction, using different organic solvents, to remove impurities and/or low molecular weight fractions (see ESI for details†). The remaining part was extracted with chloroform. The purified copolymers exhibit comparable molar masses (Mn) with polydispersity indexes (PDI), determined by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) with THF as an eluent against polystyrene standards, as summarized in Table 1. All copolymers have good solubility in common organic solvents such as chloroform, THF, and chlorobenzene at room temperature. The thermogravimetric analysis measurements (TGA) showed that the onset temperatures with 5% weight-loss (Td) of the copolymers are all over 415 °C, which indicates their excellent thermal stability (see Fig. S1 in ESI†).
| Polymer | Mn [kDa]/PDIa | λsolmaxb (nm) | λfilmmax (nm) | Eoptgc (eV) | HOMOd (eV) | LUMOe (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Determined by GPC (THF) against PS standards.b Determined from chloroform solution.c Determined from the onset of the absorption of the thin film.d Determined by equation HOMO = −e(Eox + 4.80) (eV).e Determined by equation LUMO = (HOMO + Eoptg) eV. | ||||||
| PCzDT-Qx | 28/2.8 | 525 | 555 | 1.83 | −5.45 | −3.61 |
| PCzDT-fQx | 39/1.9 | 519 | 548 | 1.95 | −5.49 | −3.53 |
| PCzDT-ffQx | 39/2.3 | 510 | 543 | 1.98 | −5.61 | −3.62 |
2.2 Optical and electrochemical properties, as well as theoretical studies
The UV-vis absorption spectra of three copolymers in chloroform solution and thin film are shown in Fig. 2, and the detailed data obtained from these absorption spectra are summarized in Table 1.All three copolymers exhibit dual characteristic absorption bands, where the short-wavelength absorbance (350–400 nm) originated from the π–π* transition of the main backbone, while the long-wavelength (450–650 nm) absorbance could be ascribed to the intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) between the donor to acceptor segments. With respect to the absorption characteristics in solution, the lower-energy bands of the three copolymers slightly broaden in thin films, indicating that strong intermolecular interaction exists in the film. Note that increasing the number of F substituents from 0 to 2 led to blue shift in the ICT transitions of the copolymers. These phenomena should be related to strong electronegativity of F atom, which matches previously reported results based on copolymers with F substituents,29 Consequently, the optical bandgaps of PCzDT-Qx, PCzDT-fQx, and PCzDT-ffQx are −1.83, −1.95, and −1.98 eV, respectively, as estimated from the absorption onsets in the film. Interestingly, we also observed that the ICT absorption coefficients of the fluorinated copolymers in both solution and thin film are higher than those of the non-fluorinated analogue, implying the increased intra/inter-chain interacts, as a result of the effects of C–F⋯H and F⋯S.29,30
The electrochemical study of these three copolymers was conducted by using cyclic voltammetry (CV) to measure their energy levels; the corresponding redox curves are shown in Fig. 2 and the relevant data are summarized in Table 1. The onset of oxidation potentials (Eox) of PCzDT-Qx, PCzDT-fQx, and PCzDT-ffQx referred to ferrocene/ferrocenium (Fc/Fc+) were 0.197, 0.202, and 0.207 V, respectively, with corresponding calculated HOMO energy levels of −5.45, −5.49, and −5.61 eV, respectively, according to the equation of HOMO = −e(Eox + 4.80) (eV). The LUMO energy levels were calculated from the difference of the HOMO energy levels and optical bandgaps according to the equation of LUMO = (HOMO + Eoptg) eV, which lies in the range of −3.53 to −3.62 eV. It is realized that Cz–Qx-containing copolymers offer significant deep-lying HOMO levels (below −5.45 eV). Furthermore, the HOMO levels scale with increasing the number of F substituents, which correlates well with the observed increase in the optical bandgaps above, as a function of the number of F substituents. Therefore, we can anticipate high VOC in the PSCs with the copolymers as our proposed strategy in the introduction.
To elucidate the molecular orbital geometry and electrical property of these copolymers, the dimer models were computerized by using density functional theory (DFT) at the B3LYP/6-31G* level. For all copolymers, the LUMOs are mainly located around the Qx derivative units, while the HOMOs are delocalized over the backbones. The torsional angles (θ) between the Qx and neighboring thienyl units in PCzDT-Qx, PCzDT-fQx, and PCzDT-ffQx models are calculated to be 12.37, 8.06, and 8.03°, respectively (Fig. 3), supporting that the fluorinated copolymers have better co-planarity for π–π stacking than the non-fluorinated copolymer does. Therefore, it is expected that both PCzDT-fQx, and PCzDT-ffQx show the relatively enhanced charge transport.
2.3 Photovoltaic characteristics
BHJ PSCs were fabricated with a device structure of ITO/PEDOT:PSS/copolymer:PC71BM/Al. The active layers of these devices were spin-coated from o-dichlorobenzene (o-DCB) solutions of these copolymers, wherein the weight ratios of polymer![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) PC71BM varied from 1
PC71BM varied from 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to 1
1 to 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3. The device fabrication process is described in detail in the experimental section. The optimized ratios were found to be 1
3. The device fabrication process is described in detail in the experimental section. The optimized ratios were found to be 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3, 1
3, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2.5, and 1
2.5, and 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 (w/w) for PCzDT-Qx, PCzDT-fQx, and PCzDT-ffQx, respectively. The representative current density–voltage characteristics (J–V) of the each optimized device under illumination of simulated 1.5G condition (100 mW cm−2) are shown in Fig. 4a, and the device parameters are summarized in Table 2.
2 (w/w) for PCzDT-Qx, PCzDT-fQx, and PCzDT-ffQx, respectively. The representative current density–voltage characteristics (J–V) of the each optimized device under illumination of simulated 1.5G condition (100 mW cm−2) are shown in Fig. 4a, and the device parameters are summarized in Table 2.
The detailed photovoltaic data of the optimization process for the PSCs are listed in Table S1 in the ESI.† Under the optimal conditions without thermal annealing, PCEs of the copolymer devices ranged from 2.01 to 2.83%. The photovoltaic parameters of all the devices were improved as a result of thermal annealing (110 °C, 10 min). Particularly in the cases of fluorinated copolymers, the VOC values tended to be more sensitive with respect to the thermal treatment. Best device performance was achieved based on PCzDT-fQx:PC71BM with thermal annealing, which showed a VOC of 1.00 V, a JSC of 8.51 mA cm−2, an FF of 45%, and a PCE of 3.80%. Although the PCE of PCzDT-ffQx-based devices was inferior to those of the devices with other copolymers due to the loss in JSC and FF, it is intriguing to note that PCzDT-ffQx achieved a highest VOC of 1.04 V, which is mainly attributed to its relatively deeper-lying HOMO level. To the best of our knowledge, this is among the best VOC values obtained from single junction BHJ PSCs. The corresponding incident photon-to-current efficiency (IPCE) spectra of the best devices are shown in Fig. 4b. The intensity distributions of IPCE spectra are well-matched with their absorption spectra. The JSC values calculated from IPCE data are consistent with J–V characteristics within 5% error limit.
To verify changes on VOC upon thermal annealing, we also measured the dark J−V curves of PSCs and the resulting dark current density versus bias voltage curves of each optimized copolymer:PC71BM blend film with and without the thermal treatment are shown in Fig. 5. The VOC depends on the saturation current density (J0), and JSC can be calculated by using the following the eqn (1),31,32
 | (1) |
 | ||
| Fig. 5 Current density–voltage (J–V) characteristics of copolymer:PC71BM-based devices for (a) PCzDT-Qx, (b) PCzDT-fQx, and (c) PCzDT-ffQx with and without thermal treatment in the dark condition. | ||
It is well known that processing additives can significantly enhance device performance.19 Thus, we have also studied the effect of several additives (1,8-octanedithiol (ODT), 1,8-diiodooctane (DIO), diphenylether (DPE), and 1-chloronaphthalene (CN)) on the optimized blend films annealed at 110 °C. All the device data with various additives are summarized in Table S1.†
Disappointingly, the introduction of various additives (2%, v/v) has no positive effect on the device performance of the three copolymers. The PCEs of the relevant devices exhibited a reduction mainly due to the decrease of JSC (Table S1†). However, there was an exceptional case of PCzDT-fQx-based PSCs with DPE; the highest PCE of 4.03% was achieved with JSC of 8.63 mA cm−2, VOC of 0.96 V, and FF of 49%.
2.4 Morphology studies
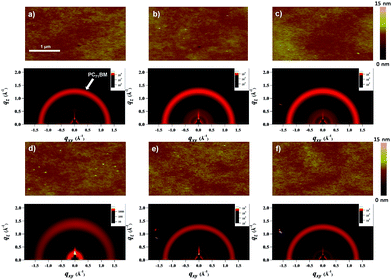
The nanoscale morphology of polymer:PC71BM blend films was studied by tapping mode atomic force microscopy (AFM). In Fig. 6, AFM images of all BHJ films showed uniform and smooth films with a small root-mean-squared (RMS) of 0.29–0.33 nm, indicating homogeneous mixing of copolymers and PC71BM. Only a minor increase (0.41–0.47 nm) in RMS values was observed in the annealed films, which could account for the observed similar JSC and FF in the PSCs processed with and without thermal treatments. In addition, we also recorded gazing-incidence wide-angle X-ray scattering (GIWAXS) measurement to gain additional structural insight into crystallites of the blend films (Fig. 6). In all cases, only the integrated intensities associated with PC71BM were visible, indicating their amorphous nature, in agreement with what is observed in the AFM images.2.5 Charge transport characteristics
The space-charge-limited-current (SCLC, JSCL) measurement is used to investigate hole (μh) and electron (μe) mobilities perpendicular to substrates since they can explain the direct relationship between charge-carrier mobilities and photovoltaic device characteristics. The hole-only (ITO/PEDOT:PSS/copolymer:PC71BM/Al) and electron-only (FTO/copolymer:PC71BM/Al) devices were prepared by using the optimized BHJ films with thermal annealing (Fig. 7). The potential loss due to the series resistance of the ITO and the built-in potential were carefully considered in order to ensure accuracy in the measurement. The J–V characteristics showed a quadratic dependence on voltage over a range of several volts and an inverse cubic dependence on the film thickness, consistent with the Mott–Gurney relationship, shown in eqn (2),
 | (2) |
 | ||
| Fig. 7 Measured J–V characteristics by the space-charge-limited current (SCLC) method with copolymer:PC71BM films under dark condition for (a) hole-only devices and (b) electron-only devices. | ||
| BHJ layer | μh [cm2 V−1 s−1] | Thickness (hole) | μe [cm2 V−1 s−1] | Thickness (electron) | μh/μe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCzDT-Qx:PC71BM | 6.86 × 10−6 | 125 | 2.44 × 10−5 | 110 | 0.281 |
| PCzDT-fQx:PC71BM | 2.15 × 10−5 | 123 | 7.21 × 10−5 | 90 | 0.298 |
| PCzDT-ffQx:PC71BM | 1.25 × 10−5 | 115 | 3.62 × 10−5 | 98 | 0.345 |
2.6 Charge recombination characteristics
We analysed the light intensity dependence of the J–V characteristics in order to quantify recombination and charge extraction within the devices. PSCs based on copolymers were characterized under various illumination intensities in the range of 10–100 mW cm−2. The dependence of JSC on light intensity can be used to determine whether JSC is limited by bimolecular recombination and/or trap-assisted recombination. Fig. 8a shows a log–log plot of JSC as a function of light intensity. By fitting the curve to the power-law dependence of JSC on light intensity, expressed as the following eqn (3).33,34| JSC ∝ Iα | (3) |
To investigate the charge generation and extraction process, photocurrent (Jph) versus effective voltage (Veff) is plotted for BHJ PSCs based on illuminated and dark J–V curves (Fig. 8b). Jph is given by Jph = JL − JD, where JL is illuminated current density and JD is dark current density of BHJ PSCs. Veff is given by Veff = V0 − V, where V0 is compensation voltage at Jph = 0 and V is applied bias voltage. log–log plot of Jph–Veff shows a transition to saturation region at certain Veff, where it is getting limited by the field and G. The BHJ PSCs of both fluorinated copolymers reached a saturated region around 1.0 V, while the non-fluorinated system exhibited no clear saturation with over 1.1 V, where Jph is still increased. Note that the value of the saturated photocurrent for PCzDT-fQx is higher than those of others, which is directly related with G. In other words, not only is the free charges extraction to the electrodes more efficient, but also the charge generation rate is better in BHJ PSCs with PCzDT-fQx compared with others.35,36 This result is consistent with the charge transport and recombination studies above.
3. Experimental section
The reagents and all starting materials were purchased from Aldrich Co., Alfa Aesar. and TCI Co. used without further purification. All solvents are ACS grade unless otherwise noted. Anhydrous THF was obtained by solvent purification system.1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on an Agilent 400 MHz spectrophotometer using CDCl3 as solvent and tetramethylsilane (TMS) as the internal standard. UV-vis-NIR spectra were taken on UV-1800 (SHIMADZU) spectrometer and DFT calculations were performed using the Gaussian 09 package with the nonlocal hybrid Becke three-parameter Lee–Yang–Parr (B3LYP) function and the 6-31G* basis set to elucidate the HOMO and LUMO levels after optimizing the geometry of all copolymers using the same method. Number-average (Mn) and weight average (Mw) molecular weights, and polydispersity index (PDI) of the copolymer products were determined by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) with Perkin-Elmer Series 200 using a series of mono disperse polystyrene as standards in THF (HPLC grade) at 313 K. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) measurements were performed on Solartron electrochemical station (METEK, Versa STAT3) with a three-electrode cell in a 0.1 M tetra-n-butylammonium hexafluorophosphate (n-Bu4NPF6) solution in acetonitrile at a scan rate of 100 mV s−1 at room temperature under argon. Ag/Ag+ electrode, a platinum wire and a glass carbon disk were used as the reference, counter, and working electrode, respectively. The Ag/Ag+ reference electrode was calibrated using a ferrocene/ferrocenium redox couple as an internal standard, whose oxidation potential is set at −4.8 eV with respect to zero vacuum level. The HOMO energy levels were obtained from the equation HOMO (eV) = −(Eonset(ox) − Eonset(ferrocene) + 4.8). The LUMO levels of polymers were obtained from the equation LUMO = (HOMO + Eoptg). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed by Simultaneous DSC/TGA instrument (TA Instruments, USA) at the heating rate of 10 °C min−1. Elemental analyses were performed with Flash 2000 (Thermo Scientific, Netherlands).3.1 General procedure for Suzuki polymerization
M1 (0.25 mmol) and either M2, M3, or M4 (0.25 mmol) were placed in a Schlenk tube under an argon atmosphere with 5 mL of anhydrous toluene. After that a solution of K3PO4 (1.25 mmol), tri-o-tolylphosphine (0.038 mmol) and deionized water (1.5 mL) was added. The mixture was vigorously stirred at room temperature under argon. After 30 min, Pd2(dba)3 (3 mol%) was added to the reaction mixture and stirred at 110 °C for 48 h. The crude product was poured into the mixture of methanol and ammonia solution (9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). The resulting solid was filtered off and subjected to sequential Soxhlet extraction with methanol, acetone, and hexane to afford comparable molecular weight fractions. The residue was extracted with chloroform and precipitated from methanol before drying final product.
1). The resulting solid was filtered off and subjected to sequential Soxhlet extraction with methanol, acetone, and hexane to afford comparable molecular weight fractions. The residue was extracted with chloroform and precipitated from methanol before drying final product.
3.2 PSC fabrication
The ITO-coated glasses were cleaned with detergent and ultra-sonicated in deionized water, acetone and isopropyl alcohol sequentially and dried in an oven for 12 h. The substrates were subjected to UV-ozone treatment for 15 min and then PEDOT:PSS (Al4083) was spin-coated on ITO and were dried at 140 °C to remove moisture. The substrates were transferred to globe box that is filled in N2 and spin-casted with active layer in o-dichlorobenzene. 100 nm of Al was evaporated on top of the active layer under high vacuum (<10−6 torr). The area of Al electrode is 13 mm2. The photovoltaic characteristics were measured in glove box by using a high quality optical fiber to guide light from the solar simulator. The J–V characteristics of the PSC were measured using a Keithley 2635A source measurement unit under AM 1.5G illumination at 100 mW cm−2. The incident photon-to-current efficiency (IPCE) was measured by using a QEX7 from PV measurement Inc. The space-charge-limited-current (SCLC) mobilities were calculated by using Mott–Gurney relationship.3.3 AFM characterization
An Agilent 5500 scanning probe microscope (SPM) running with a Nanoscope V controller was used to obtain AFM images of polymer thin films. AFM images were recorded in high-resolution tapping mode under ambient conditions. Premium silicon cantilevers (TESP-V2) were used with a rotated tip to provide more symmetric representation of features over 200 nm.3.4 GIWAXS characterization
Grazing-incidence wide-angle X-ray scattering (GIWAXS) measurements were conducted at PLS-II 9A U-SAXS beamline of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory in Korea. X-rays coming from the in-vacuum undulator (IVU) were monochromated (wavelength λ = 1.10994 Å) using a double crystal monochromator and focused both horizontally and vertically (450 (H) × 60 (V) μm2 in FWHM @ sample position) using K-B type mirrors. The GIWAXS sample stage was equipped with a 7-axis motorized stage for the fine alignment of sample, and the incidence angle of X-ray beam was set to be 0.13° to 0.135° for IIGDT-based polymer films and blended films. GIWAXS patterns were recorded with a 2D CCD detector (Rayonix SX165) and X-ray irradiation time was 6–9 s, dependent on the saturation level of the detector. Diffraction angles were calibrated using a sucrose standard (Monoclinic, P21, a = 10.8631 Å, b = 8.7044 Å, c = 7.7624 Å, β = 102.938°) and the sample-to-detector distance was ∼231 mm.4. Conclusions
In summary, three medium bandgap D–A copolymers based on Cz and Qx (PCzDT-Qx, PCzDT-fQx, and PCzDT-ffQx) have been designed and synthesized by Suzuki polymerization, seeking to achieve outstanding VOC values in PSCs. All copolymers show deep-lying HOMO levels (−5.45 to −5.61 eV) that consequently can translate into high VOC values in optimized BHJ PSCs with the copolymers. In particular, a pleasant surprise comes from the PCzDT-ffQx with a peak VOC as high as 1.04 V observed, though the JSC and FF are relatively reduced. The best PCSs derived from PCzDT-fQx show a PCE of 3.80% while maintaining high VOC of 1.0 V, in which, moreover, PCE of up to 4.03% with DPE additive is achieved. By using dark J−V curves and SCLC in combination with detailed light-intensity-dependent JSC and photocurrent measurements, we are able to disclose a precise picture of structure–property relationships in this system. We anticipate that in-depth studies (on the mechanism of charge recombination and transport characteristics) combined with further adopting molecular design strategies will be the key to obtain maximum VOC and PCE simultaneously.Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the International Research & Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST) of Korea (2014K1A3A1A19066591), grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (2015R1A2A1A10053397) and (NRF-2013R1A2A2A01015342), and development Program of the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) (B6-2431). Experiments at PLS-II 6D UNIST-PAL beamline were supported in part by MEST, POSTECH, and UNIST UCRF.Notes and references
- L. Lu and L. Yu, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 4413–4430 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, Acc. Chem. Res., 2012, 45, 723–733 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. He, C. Zhong, S. Su, M. Xu, H. Wu and Y. Cao, Nat. Photonics, 2012, 6, 593–597 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Dou, J. You, Z. Hong, Z. Xu, G. Li, R. A. Street and Y. Yang, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25, 6642–6671 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhou, L. Yang and W. You, Macromolecules, 2012, 45, 607–632 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Fan, Y. Liu, M. Xiao, W. Su, H. Gao, J. Chen, H. Tan, Y. Wang, R. Yang and W. Zhu, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2015, 3, 6240–6248 RSC.
- H. Zhou, L. Yang, S. C. Price, K. J. Knight and W. You, Angew. Chem., 2010, 122, 8164–8167 CrossRef.
- R. He, L. Yu, P. Cai, F. Peng, J. Xu, L. Ying, J. Chen, W. Yang and Y. Cao, Macromolecules, 2014, 47, 2921–2928 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Li, Z. Li, K. Feng, X. Xu, L. Wang and Q. Peng, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 13549–13557 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhou, L. Yang and W. You, Macromolecules, 2012, 45, 607–632 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Fan, M. Xiao, Y. Liu, W. Su, H. Gao, H. Tan, Y. Wang, G. Lei, R. Yang and W. Zhu, Polym. Chem., 2015, 6, 4290–4298 RSC.
- D. Liu, W. Zhao, S. Zhang, L. Ye, Z. Zheng, Y. Cui, Y. Chen and J. Hou, Macromolecules, 2015, 48, 5172–5178 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Wang, L. Hou, Z. Wang, S. Hellström, F. Zhang, O. Inganäs and M. R. Andersson, Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 5240–5244 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-C. Chen, Y.-H. Chen, C.-H. Liu, Y.-H. Hsu, Y.-C. Chien, W.-T. Chuang, C.-Y. Cheng, C.-L. Liu, S.-W. Chou and S.-H. Tung, Polym. Chem., 2013, 4, 3411–3418 RSC.
- W. Su, M. Xiao, Q. Fan, J. Zhong, J. Chen, D. Dang, J. Shi, W. Xiong, X. Duan and H. Tan, Org. Electron., 2015, 17, 129–137 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Dang, W. Chen, S. Himmelberger, Q. Tao, A. Lundin, R. Yang, W. Zhu, A. Salleo, C. Müller and E. Wang, Adv. Energy Mater., 2014, 4, 1400680 Search PubMed.
- G. K. Dutta, T. Kim, H. Choi, J. Lee, D. S. Kim, J. Y. Kim and C. Yang, Polym. Chem., 2014, 5, 2540–2547 RSC.
- M. Zhang, X. Guo, S. Zhang and J. Hou, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 1118–1123 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Kim, H. R. Yeom, J. Y. Kim and C. Yang, Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, 6, 1909–1916 CAS.
- J. Kim, M. H. Yun, G.-H. Kim, J. Lee, S. M. Lee, S.-J. Ko, Y. Kim, G. K. Dutta, M. Moon, S. Y. Park, J. Y. Kim and C. Yang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 7523–7534 CAS.
- Y.-J. Cheng, J.-S. Wu, P.-I. Shih, C.-Y. Chang, P.-C. Jwo, W.-S. Kao and C.-S. Hsu, Chem. Mater., 2011, 23, 2361–2369 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Liand and A. C. Grimsdale, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39, 2399–2410 RSC.
- J. Kim, M. H. Yun, G.-H. Kim, J. Y. Kim and C. Yang, Polym. Chem., 2012, 3, 3276–3281 RSC.
- C. Gu, M. Xiao, X. Bao, L. Han, D. Zhu, N. Wang, S. Wen, W. Zhu and R. Yang, Polym. Chem., 2014, 5, 6551–6557 RSC.
- H. Zhou, L. Yang, S. Stoneking and W. You, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2010, 2, 1377–1383 CAS.
- J. Lee, A.-R. Han, H. Yu, T. J. Shin, C. Yang and J. H. Oh, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 9540–9547 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Kim, A.-R. Han, H. R. Lee, J. H. Oh and C. Yang, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17, 26512–26518 RSC.
- B. Kim, H. R. Yeom, M. H. Yun, J. Y. Kim and C. Yang, Macromolecules, 2012, 45, 8658–8664 CrossRef CAS.
- A. C. Stuart, J. R. Tumbleston, H. Zhou, W. Li, S. Liu, H. Ade and W. You, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 1806–1815 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhou, L. Yang, A. C. Stuart, S. C. Price, S. Liu and W. You, Angew. Chem., 2011, 123, 3051–3054 CrossRef.
- M. H. Yun, E. Lee, W. Lee, H. Choi, B. R. Lee, M. H. Song, J.-I. Hong, T.-H. Kwon and J. Y. Kim, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2014, 2, 10195–10200 RSC.
- S. M. Sze and K. K. Ng, Physics of semiconductor devices, John Wiley & Sons, 2006 Search PubMed.
- L. Lu, T. Xu, W. Chen, E. S. Landry and L. Yu, Nat. Photonics, 2014, 8, 716–722 CrossRef CAS.
- A. K. K. Kyaw, D. H. Wang, V. Gupta, W. L. Leong, L. Ke, G. C. Bazan and A. J. Heeger, ACS Nano, 2013, 7, 4569–4577 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Ren, C. W. Schlenker, E. Ahmed, S. Subramaniyan, S. Olthof, A. Kahn, D. S. Ginger and S. A. Jenekhe, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013, 23, 1238–1249 CrossRef CAS.
- E. T. Hoke, K. Vandewal, J. A. Bartelt, W. R. Mateker, J. D. Douglas, R. Noriega, K. R. Graham, J. M. Fréchet, A. Salleo and M. D. McGehee, Adv. Energy Mater., 2013, 3, 220–230 CrossRef CAS.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: TGA and GIWAXS data as well as photovoltaic parameters by various device conditions. See DOI: 10.1039/c5ra25088a |
| ‡ These authors contributed equally. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |