Bio-chemical characterization of a β-mannanase from Bacillus licheniformis HDYM-04 isolated from flax water-retting liquid and its decolorization ability of dyes
J. P. Ge†
,
R. P. Du†,
D. Zhao,
G. Song,
M. Jin and
W. X. Ping*
Key Laboratory of Microbiology, College of Life Science, Heilongjiang University, Harbin 150080, China. E-mail: wenxiangp@aliyun.com; durenpeng20096292@163.com; Fax: +86-0451-86608046
First published on 26th February 2016
Abstract
A β-mannanase was purified from the bacteria, Bacillus licheniformis HDYM-04, which was a high β-mannanase-producing strain (576.16 U mL−1 at 48 h during fermentation). The optimal temperature and pH for this enzyme activity were 60 °C and 8.0, respectively. The enzyme activity was significantly enhanced by Co2+, Mg2+, K+, Ba2+ and Na+ while inhibited by β-mercaptoethanol, DTT, SDS, Tween and EDTA. It was also noticed that the enzyme did not lose its activity in a wide interval such as high NaCl concentration (5 mol L−1) and high urea concentration (5 mol L−1). When amino acid residues were modified with NEM, N-AI and NBS, the enzyme activities significantly decreased. CD spectra demonstrated that the secondary structure of β-mannanase consists of 0% α-helix, 27.9% β-sheet, 24.4% turn and 47.7% random coil. CD spectra also supported that β-mannanase was stable under temperature and pH variation. Ten structurally different dyes could be effectively decolorized by β-mannanase within 24 h, in which Congo red (100%), malachite green (100%), titan yellow (98.6%) and phenol red (91%) had high decolorization rates. This property showed the compound's potential application in textile and paper-making industries to decolorize redundant dyes on them.
1 Introduction
Mannans, which are the major hemicellulose components of softwoods, are heteropolysaccharides composed of a β-1,4-linked backbone containing D-mannose or a combination of D-glucose and D-mannose units. Due to the complex nature of these polysaccharides, a combination of endo and exo acting enzymes such as β-1,4-mannanase, β-mannosidase and α-galactosidases are required for their complete degradation.1 endo-1,4-β-Mannanases (E.C 3.2.1.78, mannan endo-β-1,4-mannosidase) can randomly cleave within the main chain of β-1,4-D-mannan and heteromannans, which can produce manno-oligosaccharides, and it could be classed to the glycosyl hydrolase (GH) families 5 and 26 according to the amino acid sequences similarities.2 The β-mannanases have been purified and characterized from a wide range of fungi such as Trichoderma reesei, Aspergillus oryzae, etc.3,4, some types of bacteria such as B. subtilis, Cellulosimicrobium sp. and Sphingomonas5–7 and some other organisms such as Lycopersicon esculentum (plant), Gastropoda pulmonata (snail), Littorina brevicula (mollusk).8,9 Most microbial mannanases are extracellular and can act in a wide range of pH and temperature so that they have been found various applications in pharmaceutical, food and feed technology, coffee extraction, biological bleaching, bioethanol production, pulp and paper industry, oil and textile industries.10,11Synthetic dyes are extensively used in several industries including textile, paper, printing, leather-dyeing, cosmetic, pharmaceutical and food industries. Approximately 10–15% of these dyes are released into environment after manufacturing processes.12 Moreover, the exiting dyes usually have complicate molecular structures, which making them difficult to be biodegraded. So far, the dye decolorization using microbial enzymes has received a great attention in recent years due to its efficient applications.13 However, no report is about decolorization of dyes by β-mannanase produced by B. licheniformis.
In this present investigation, a β-mannanase from B. licheniformis HDYM-04 was purified and characterized. The fundamental characteristics of the purified enzyme such as effect of pH, temperature, chemical modification of amino acid residues on the enzyme activity and stability, effect of different additives and inhibitors on enzyme activity were also studied. In addition, the secondary structure and the application of the purified β-mannanase from HDYM-04 in the decolorization of various dyes were also reported.
2 Experimental
2.1 Microorganism and cultivation
B. licheniformis HDYM-04 was isolated from flax-retting water in Bayan County, Heilongjiang Province, P. R. China. This strain was preserved in Key Laboratory of Microbiology, College of Life Science, Heilongjiang University. For the seed culture, one colony was inoculated into 200 mL/250 mL liquid medium (1% peptone, 0.5% yeast extract and 1% NaCl; w/v) and incubated at 37 °C overnight. For purification of the β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04, 2 mL seed liquid of strain HDYM-04 was inoculated into the liquid KGM medium which contained (1% konjac powder, 1% peptone, 0.5% K2HPO4·3H2O, 0.02% MgSO4·7H2O, pH 8.0; w/v). The incubation lasted 48 h under the conditions at 37 °C with agitation speed of 160 rpm. The crude β-mannanase from HDYM-04 could be obtained by centrifugation (Beckman, American) of the 40 mL of culture broth at 5000 rpm for 20 min at 4 °C.2.2 Enzyme assay and protein estimation
The β-mannanase activity of HDYM-04 was assayed by measuring the amount of reducing sugars released by the enzyme using dinitrosalicylic (DNS) method.14 One unit of β-mannanase activity was defined as the amount of enzyme that produced 1 μmol of reducing sugar as a D-mannose standard per minute by 1 mL of enzyme.14 Protein concentration was determined according to the method of Bradford using bovine serum albumin (BSA) as the standard.152.3 Enzyme purification
The crude β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was obtained according to “Microorganism and cultivation”. The precipitated enzyme was dialysed and monitored at 550 nm followed by activity assay. The crude enzyme was purified to homogeneity by using combination of acetone precipitation, ion-exchange chromatography (DEAE-cellulose, D3764, Sigma, USA) and gel filtration (Sephadex G-75, Sigma, USA). The final purified fraction of enzyme was subsequently used for further characterization. SDS-PAGE was carried out to determine the homogeneity and apparent molecular mass of the purified β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04. The purified enzyme band was cut and sent to Gene Create Company (P. R. China) for protein determination. The amino acid sequence was determined by LC-MS/MS (ekspertTM nanoLC; AB Sciex Triple TOF 500-PLUS). Homology modeling of the catalytic domain of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was performed using Bioedit software (http://www.uniport.org/).2.4 Effect of pH and temperature on the activity and stability of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04
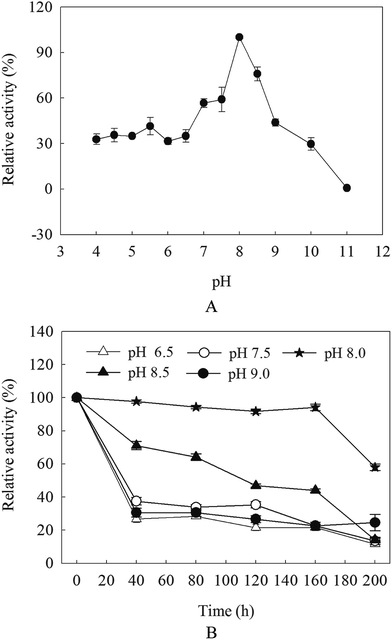
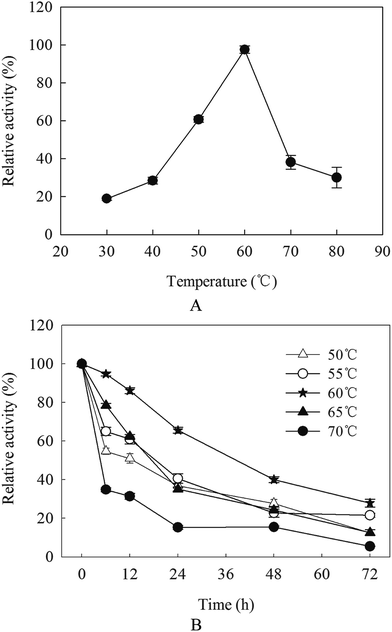
The optimal pH of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was examined at pH 4.0–11.0 under standard assay conditions: the enriched 0.5 mL of purified β-mannanase fraction produced by HDYM-04 was mixed (0.19 mg mL−1 final concentration) with each of the different pH-buffer systems: citric acid–sodium citrate (pH 4–6.5), Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.0–9), and glycine–NaOH (pH 9.5–11) to obtain the corresponding pH. The β-mannanase-buffer mixtures were left for 10 min at room temperature under optimum pH, and assayed for enzyme activity as described above. The highest value of enzyme activity was considered as 100% and the activity of the other samples under the different pH buffers were expressed relative to that of the control (100% activity).16 The pH stability of the β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was determined using the same buffer systems in the range of pH 6.5–9.0. After incubation of the enzyme solution at various pH values for 0, 40, 80, 160 and 200 min, the relative enzyme activity was measured using the highest enzyme activity as control (100%).The effect of temperature on the purified enzyme activity was determined by incubating the enriched β-mannanase fraction produced by HDYM-04 (0.21 mg mL−1 final concentration) in 0.1 mol L−1 Tris–HCl buffer (pH 8.0) at temperatures ranging from 30 to 80 °C for 30 min, and assayed for enzyme activity as described above. The enzyme activity of those incubated at 4 °C was considered as 100% and the activity of the other samples under the different temperatures were expressed relative to that of the control (100% activity). To estimate the thermal stability, β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was incubated at the temperatures range from 50 to 80 °C for 6, 12, 24, 48 and 72 h in 0.1 mol L−1 Tris–HCl buffer (pH 8.0), and the residual enzyme activity was measured. The enzyme activity of those incubated at 4 °C was considered as 100% and the activities of the samples under the different temperatures were expressed relative to that of the control (100% activity).
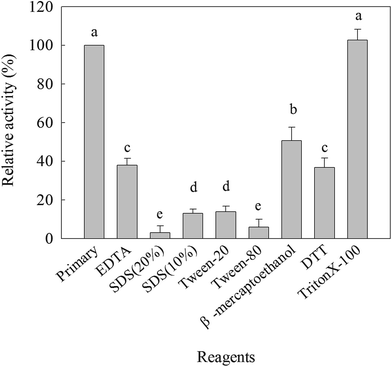
2.5 Effects of metal ions and reagents on the activity of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04
Metal ions (Ag+, Co2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Hg+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Mg2+, Cd2+, Ba2+, K+, 50 and 100 mmol L−1), inhibitors (β-mercaptoethanol, β-Me; dithiothreitol and DTT; 25 mmol L−1) and different organic solvents (25 mmol L−1 Triton X-100; 25 mmol L−1 EDTA; 20% Tween-20; 20% Tween-80; 20% SDS) were contributed to detect their effect on β-mannanase activity. 5 mL of metal ions solution/10 mL of inhibitors or organic solvents were mixed with β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 to give the final concentrations of 0.124 mg mL−1, holding on for 10 min under room temperature and then the enzyme activity was tested as described above. The enzyme activity of those in 0.1 mol L−1 Tris–HCl buffer (pH 8.0) at 4 °C was considered as 100% and the activity of the samples mixed with different metal ions or reagents were expressed relative to that of the control.2.6 Effect of salt and urea on the activity and stability of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04
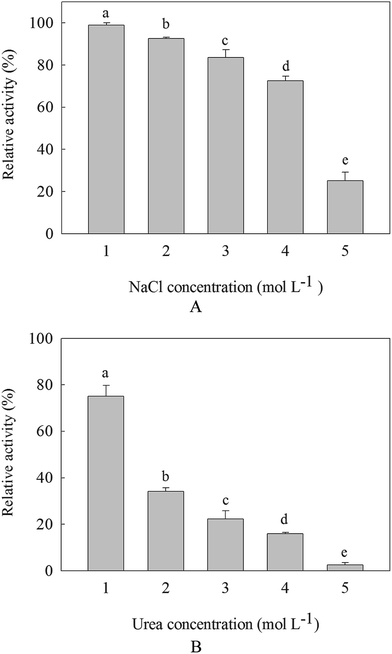
The purified β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 (1 mL) was diluted with an equal volume of NaCl solution or 10 mL of urea ranging from 1 to 5 mol L−1, and then incubated for 30 min at room temperature. The residual β-mannanase activity produced by HDYM-04 was assayed under standard conditions. The enzyme activity of those in 0.1 mol L−1 Tris–HCl buffer (pH 8.0) at 4 °C was considered as 100% and the activity of the samples mixed with different concentrations of NaCl or urea were expressed relative to that of the control (100% activity).2.7 Effects of chemical modification of amino acid residues on β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04
To determine the effect of chemical modification (NEM, N-AI and NBS) on the stability of enzyme, β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was incubated with various chemical modification solutions, and the residual activity was assayed under the different reaction system. 2 mL of purified β-mannanase from HDYM-04 (0.202 mg mL−1) was mixed with 0.1–0.5 mL of different chemical modification solution (4 mmol L−1) and then incubated in Tris–HCl buffer (0.2 mol L−1, pH 8.0) for 30 min, and then enzyme activities were detected. As cysteine can repair the damage caused by thiol (NEM in this paper), and hydroxylamine can deacetylate the acetyl on tyrosine which induced by N-AI, we added cysteine and hydroxylamine to the modified enzyme solution to used as control. 0.1–0.5 mL cysteine (Cys) and hydroxylamine were added to the enzyme modified systems and the final volume could be reached 2 mL with Tris–HCl buffer, respectively. The residual activity was measured using the standard assay method. A control assay of the β-mannanase activity produced by HDYM-04 was done without chemical modification and resulting in activity was taken as 100%.2.8 CD analysis for secondary structure of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04
CD spectra analysis of the purified β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was performed using JASCOJ-815 (JASCO, Japan) spectrometer following the instructions of instrument. The secondary structures of protein containing α-helix, β-sheet, random coil, and turn were estimated using the secondary structure analysis software supplied by JASCO. Spectra were recorded on a JASCOJ-815 Spectropolarimeter in the far UV region (190–260 nm) at room temperature and in the range of 20–70 °C using a 400 μL-sample holder and 0.1 cm path length cell. Each CD spectrum was scanned at 100 nm min−1, data points were recorded at 0.1 nm intervals and the response time was 0.5 s.17 The secondary structural components were determined by CONTINLL algorithm.18 The ellipticity values (θ) for every nanometer wavelength increase were obtained in ‘mdeg’ directly from the instrument and were recorded online with a computer.19The effects of environmental factors on the secondary structures of the β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 were also studied. When measuring the affection of different pH (ranged from 4 to 10) on CD spectra, the purified enzyme (0.314 mg mL−1) was dialyzed against different buffers at 4.0, 6.0, 8.0 and 10.0 for 30 min at room temperature, and CD spectra were detected. The enzyme (0.608 mg mL−1) was incubated at 20–70 °C in buffer (pH 8.0) using a circulating water bath to detect the affection of temperature on CD spectra.
2.9 Decolorization of dyes by the β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04
All the tested dyes were purchased from Sigma Company (Table 1). The active β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 (40![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 U mL−1) and commercial β-mannanase (40
000 U mL−1) and commercial β-mannanase (40![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 U mL−1) were used to decolorize ten kinds of dyes. The reaction mixture respectively contained 0.05 mg mL−1 dyes, Na2HPO4–citric acid buffer (0.2 M, pH 6.0) and β-mannanase from HDYM-04. During incubation at 37 °C, the time course of decolorization was determined by full spectrum scan among 200–1000 nm at 12 h. The decolorization of dyes, expressed as dye decolorization (%), was calculated by means of the formula: decolorization (%) = (1 − A/A0) × 100%, A0: initial absorbance of the dyes, A: absorbance of the dyes along the time. All experiments were performed in triplicate. The decolorization efficiency of each dye was shown as dye decolorization (%).
000 U mL−1) were used to decolorize ten kinds of dyes. The reaction mixture respectively contained 0.05 mg mL−1 dyes, Na2HPO4–citric acid buffer (0.2 M, pH 6.0) and β-mannanase from HDYM-04. During incubation at 37 °C, the time course of decolorization was determined by full spectrum scan among 200–1000 nm at 12 h. The decolorization of dyes, expressed as dye decolorization (%), was calculated by means of the formula: decolorization (%) = (1 − A/A0) × 100%, A0: initial absorbance of the dyes, A: absorbance of the dyes along the time. All experiments were performed in triplicate. The decolorization efficiency of each dye was shown as dye decolorization (%).
| Dyes | Type | λmax (nm) | Chemical formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Congo red | Azo | 484 | C32H22N6Na2O6S2 |
| Amido black | Azo | 620 | C22H14N6Na2O9S2 |
| Eriochrome black T | Azo | 624 | C20H12N3NaO7S |
| Titan yellow | Azo | 388 | C28H19N5Na2O6S4 |
| Water soluble aniline blue | Triaromatic methane | 610 | C34H32ClN3NaO6S2 |
| Malachite green | Triaromatic methane | 617 | C23H25ClN2 |
| Basic violet 3 | Triaromatic methane | 612 | C25H30ClN3 |
| Bromocresol green | Triaromatic methane | 632 | C21H14Br4O5S |
| Crystal violet | Triaromatic methane | 583 | C25H30N3Cl·9H2O |
| Phenol red | Triaromatic methane | 558/432 | C19H14O5S |
2.10 Statistical analysis
All tests were performed in three replications. The average standard errors of the data were expressed. SPSS version 10.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL., USA) was used for the statistical analysis; and Tukey test was performed for determining the significant differences at 95% confidence interval (p < 0.05).3 Result and discussion
3.1 Purification of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04
The crude extract of the β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was purified to homogeneity using a three-step purification procedure as summarized in Table 2. The specific activity of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was found to be increased to 5484.16 U mg−1 protein, resulting 19.32-fold purification. The purified enzyme showed a single band on SDS-PAGE with a mobility equivalent to the molecular mass of 42 kDa as visualized by Coomassie brilliant blue staining. 383 amino acids were detected, the ten amino acid of N-terminal was MKLSNVCLTL and the ten amino acid of C terminal was VTDHVAAIGSA. Peptides of the protein revealed 93.6% and 93% identity with the hypothetical endo-β-1,4-mannanases from B. licheniformis DOHU30 and B3F2Y5. These results showed the homospecificity of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 with those from B. licheniformis.| Purification step | Volume (mL) | Total activity (U) | Total protein (mg) | Yield (%) (per step) | Specific activity (U mg−1) | Fold purification (per step) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude culture | 2000 | 84![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 866 866 |
299.56 | 100% | 238.29 | 1 |
| Acetone precipitation | 10 | 79![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 016 016 |
48.76 | 93.11% | 1620.51 | 5.72 |
| DEAE-cellulose column | 10 | 63![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 212 212 |
14.71 | 80% | 4297.21 | 8.31 |
| Sephadex G-75 column | 10 | 51![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 606 606 |
9.41 | 60.08% | 5484.16 | 19.32 |
3.2 Effect of pH and temperature on the activity and stability of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04
β-Mannanase activities produced by HDYM-04 were exhibited low–high–low tendency with pH variation (from acidic to basic, 4.0, 5.0, 5.5, 6, 6.5, 7.0, 7.5, 8.0, 8.5, 9.0, 9.5, 10.0 and 11). The maximal value (527.66 U mL−1) appeared at pH 8.0 (p < 0.05), this phenomenon suggested that the optimal pH for β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was 8.0 (Fig. 1A). The relative enzyme activity showed different stabilities under different pH when keeping enzyme solution for 40, 80, 120, 160 and 200 min. The enzyme activity remained above 90% after 160 min at pH 8.0, and dropped to 56.35% at 200 min. While in other pH, the enzyme activities were dropped before 40 min, and then kept stable during 40 to 160 min, while only about 20% activity left. When keeping enzyme solution for 200 min, the enzyme activity dropped continuously and 11.65% (for pH 6.5), 15.18% (for pH 7.5), 56.34% (for pH 8.0), 24.58% (for pH 8.5) and 14.78% (for pH 9.0) activity left, respectively (Fig. 1B). HDYM-04 can produce the highest value of β-mannanase at pH 8.0 and also stable at pH 8.0.The purified β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 showed maximum activity (508 U mL−1) at 60 °C, and more than 60% of the activity could be detected at temperatures 50 °C and 70 °C (Fig. 2A). The enzyme had high-thermal stability. After incubation below 60 °C for 72 h, the enzyme activity remained 27.88% (147.15 U mL−1) of the maximum activity (440.36 U mL−1). When incubated below 55 °C for 72 h, less than 22% of the activity was remained. However, the enzyme activity sharply decreased when the temperature was above 60 °C and almost no activity was detected at 70 °C (Fig. 2B).
The optimal temperature for β-mannanase activity produced by HDYM-04 was 60 °C. It was similar to that from B. licheniformis and B. stearothermophilus.20,21 However, it was higher than that from Paenibacillus polymyxa (37 °C), and lower than that from B. subtilis WD23 (70 °C).22,23 The thermostability is comparable to those reported for several mannanases from the thermophilic fungus and significantly higher than those of other B. subtilis strains.24,25 A higher temperature optimum and thermostability of β-mannanase activity produced by HDYM-04 let it more suitable for possible application in biobleaching of pulp, which is carried out at high temperature.
3.3 Effect of metal ions and reagents on the activity of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04
The effects of various ions on the β-mannanase activity produced by HDYM-04 are shown in Table 3. The enzyme activity was reduced by Hg+, Ag+, Fe3+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Cd2+ and Fe2+ at the tested concentrations and strongly inhibited by 50 mmol L−1 Hg+ and 50 mmol L−1 Ag+ in a dose-dependent manner reaching as high as 95% inhibition in both cases. The enzyme activity was significantly increased by the presence of Mg2+ (25 mmol L−1, 114.51%), Co2+ (25 mmol L−1, 106.90%), K+ (25 mmol L−1, 104.88%), Ba2+ (25 mmol L−1, 102.06%) (p < 0.05), while they were slightly decreased when the concentration of these metal ions was raised to 50 mmol L−1. Different chemical reagents could inhibit the β-mannanase activity produced by HDYM-04 (Fig. 3). β-Mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was inhibited by copper chelators such as Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid (EDTA), the percentage of inhibition being 48.97% at a concentration of 25 mmol L−1 of EDTA, the result was the same with the β-mannanase from B. licheniformis WY34.26 Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), Tween-20 and Tween-80 are protein denaturants as well as surfactant, which could significantly inhibited enzyme activity of the β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 to 88% (10% of SDS, w/v), 98% (20% of SDS, w/v), 87.10% (Tween-20) and 5.43% (Tween-80). Furthermore, β-mercaptoethanol induced decrease of the enzyme activity to 50%, and DTT, which is a strong reducing agent on disulphide bonds, strongly inhibited the enzyme to 64%. The inhibition of different metal reagents showed significantly difference (p < 0.05).| Metal ions | Residual activity (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mmol L−1 | The degree of promotion or inhibition | 50 mmol L−1 | The degree of promotion or inhibition | |
| a The degrees of promotion or inhibition of enzyme activity by different metal ions were according to rules as follows: the enzyme activity less than 30% were thought to be strongly inhibited, expressed as −−−; 30–70% enzyme activity left were thought to be medium inhibition, expressed as −−; 70–99% enzyme activity left were thought to be inhibition, expressed as −; the enzyme activity more than 100% were thought to be promotion. Different letters indicated significant differences among samples incubated with different metal ions in the same column (p < 0.05). Same letter indicated no significant difference among samples incubated with different metal ions in the same column (p < 0.05). | ||||
| Non-ions | 100 | 100 | ||
| HgCl2 | 6.32f | −−− | 2.84f | −−− |
| AgCl | 9.78f | −−− | 3.01f | −−− |
| FeCl3 | 12.00f | −−− | 12.00e | −−− |
| CuCl2 | 35.99e | −− | 32.16d | −− |
| MnCl2 | 62.91d | −− | 59.62c | −− |
| CdCl2 | 69.23d | −− | 59.12c | −− |
| FeCl2 | 80.00c | − | 78.51b | − |
| BaCl2 | 102.06b | + | 99.85a | − |
| KCl | 104.88b | + | 102.13a | + |
| CoCl2 | 106.90b | + | 105.10a | + |
| MgCl2 | 114.51a | + | 104.66a | + |
Metal ions especially heavy metal ions are common environmental pollutants and can affect the production and stability of the enzymes. The enzyme activity was significantly enhanced by Co2+, Mg2+, K+, Ba2+ and Na+ and inhibited by Hg2+ and Fe3+. In agreement with our results, enhancement of enzyme activity had been reported in the presence of Ni2+, Co2+, Zn2+ and Mg2+ in case of Cellulosimicrobium sp. strain HY-13 (ref. 27) and Pantoea agglomerans28 and inhibition of mannanase activity by Cd2+, Mn2+, Hg2+ and Ag+ in case of Bacillus sp. N16-5.29 The enzyme activity was inhibited by β-mercaptoethanol, DTT, SDS, Tween and EDTA. It was similar to that the β-mannanase activity was inhibited strongly by SDS and EDTA.5,24 It suggested that disulphide linkages have a critical role in maintaining an appropriate conformation of the enzyme for its catalytic activity.
3.4 Effect of salt and urea on the activity of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04
Along with the increasement of NaCl and urea, the activities of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 were decreased. It was found that the salt tolerance of the enzyme was more than that of the urea tolerance. β-Mannanase activity produced by HDYM-04 was almost 100% at concentration of 1 mol L−1 NaCl when incubated for 30 min, showing that this enzyme was stable under such condition. The enzyme activity was reduced to 80% when urea concentration was 1 mol L−1. And the enzyme activities retained 25.12% and 3.23% at 5.0 mol L−1 NaCl and urea concentrations, respectively (Fig. 4). The inhibition of NaCl and urea showed significantly difference (p < 0.05).It is well known that the presence of high salt concentration destabilizes ion pairs and salt bridges and alters electrostatic interactions between charged amino acids, leading to enzyme denaturation. We found that the β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 did not lose its activity at a high NaCl concentration (5 mol L−1). Bacillus sp. Mg-33 also could tolerate 4 mol L−1 of NaCl.30 The stability of the enzyme in the presence of high salt concentrations revealed its moderately high halotolerant nature,31 which is a desirable characteristic because NaCl is used as a core component in granulation of the enzyme prior to its addition to detergents.32
3.5 Effects of chemical modification of amino acid residues on the activity of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04
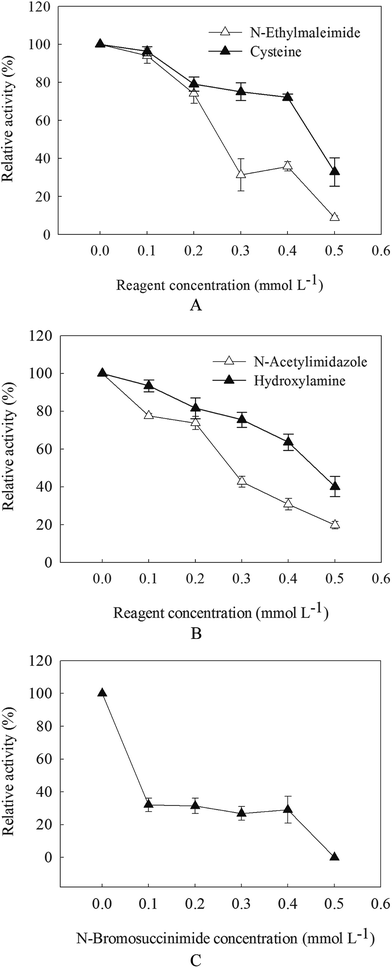
With the increasement of chemical modification concentration, the activity of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 continued to decrease. The residual activity of enzyme was reduced to 5.10%, 19.71% and 0% with 0.5 mmol L−1 of N-ethylmaleimide (NEM), N-acetylimidazole (N-AI) and N-bromosuccinimide (NBS), after 30 min incubation (Fig. 5). When adding cysteine to enzyme system modified by NEM, the enzyme activity increased, which showed that NEM can modify the thiol of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 and let the decreasement of enzyme activity, cysteine can repair such lesion and improve the enzyme activity.When adding hydroxylamine to enzyme system modified by N-AI, the enzyme activity increased, which suggested that the tyrosine in β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was destroyed and further to be repaired by hydroxylamine. NBS also can modify the indolyl of tryptophan, when adding NBS to enzyme system, the enzyme activities decreased with the increasement of NBS concentration. The maximum activity of the enzyme was found with 0 mmol L−1 of NBS, and β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 had an residual activity of 31.5%, 26.9% and 29.1% at NBS concentration of 0.1, 0.2, 0.3 mmol L−1, respectively (Fig. 5C).
The enzyme was subjected to chemical modification, and the activity of the modified enzyme was examined. These results indicated the existence of amino acid residues in the activity center of the β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04. Chemical modification (NEM, N-AI, and NBS) caused complete inactivation of the enzyme, which suggested that NEM and N-AI can modify the enzyme's thiol and tyrosine residues and resulting in the structural changes of the enzyme, thereby reduced the enzyme activity. Tyrosine, thiol and tryptophan are important for the maintenance of the stability of the enzyme. The effect of tryptophan modification on the activity of the enzyme was the biggest one. It can be inferred that tryptophan may be located in the center of the enzyme.
3.6 CD analysis for secondary structure of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04
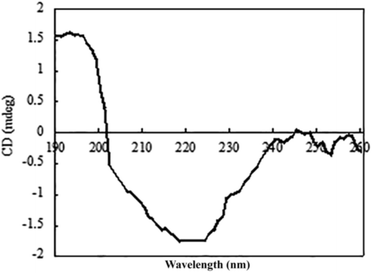
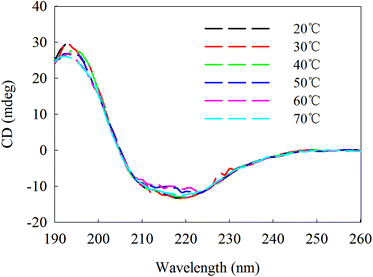
The circular dichroism (CD) spectrum of the purified protein showed two negative peaks at 208 and 222 nm and one positive peak at 192 nm (Fig. 6), which are typical peaks for a protein consisting mostly of α-helix. The β-sheet had a negative peak and a positive peak at 216 nm and 195–200 nm, separately. The spectral data of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 included 0% of α-helix, 27.9% of β-sheet, 24.4% of turn and 47.7% of random coil.β-Mannanase produced by HDYM-04 maintained its secondary structure at the initial 20 °C, as shown in Fig. 7. As temperature was increased from 20 to 60 °C, the secondary structure of the enzyme was slightly changed in the ellipticity values at 216, 195–200, and 206 nm, respectively, and the activity of enzyme was increased. Furthermore, these spectra revealed strong conformational changes, approximately 6.6% increased in random coil and 8.9% decreased in β-sheets conformation, and enzyme activity was 396.51 U mL−1 at 60 °C (Table 4). CD-based conformational evaluation of the enzyme after incubation at different pH values demonstrated that deviation in the β-sheet and random coil were directly correlated with the altered (increased/decreased) β-mannanase activity produced by HDYM-04 (Table 5). With the pH increasing from 4.0 to 10.0, the enzyme changed its secondary structure. Estimation of the β-sheet contents of the proteins based upon the spectra found in Fig. 8, which resulted in a range of values from 26.6% at pH 4.0 to 30.6% at pH 10.0. However, the turn and random coil were reduced from 24.7% and 48.7% to 22.0% and 47.4%, respectively.
| Secondary structure (%) | α-Helix | Beta | Turn | Random coil | Activity (U mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | 0 | 39.6 | 18.4 | 42.1 | 343.1 |
| 30 °C | 0 | 39 | 18.9 | 42.1 | 361.7 |
| 40 °C | 0 | 38.4 | 19 | 42.6 | 355.2 |
| 50 °C | 0 | 36.1 | 19 | 44.9 | 361.8 |
| 60 °C | 0 | 30.7 | 20.6 | 48.7 | 396.5 |
| 70 °C | 0 | 38.7 | 19.2 | 42.1 | 352.8 |
| Secondary structure (%) | α-Helix | Beta | Turn | Random coil | Activity (U mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0 | 26.6 | 24.7 | 48.7 | 314.4 |
| 6 | 0 | 26.9 | 24.5 | 48.6 | 318.5 |
| 8 | 0 | 27.9 | 24.4 | 47.6 | 385.4 |
| 10 | 0 | 30.6 | 22 | 47.4 | 341.2 |
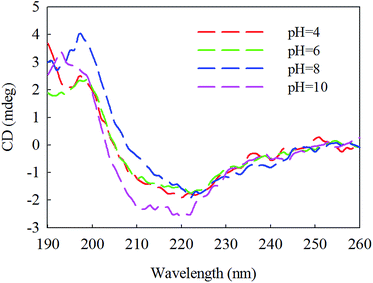 | ||
| Fig. 8 Second chromatographic analysis under different pH of β-mannase secondary structure. Different pH was illustrated as color (red, 4), (green, 6), (dark blue, 8), (pink, 10). | ||
An initial analysis of the CD spectrum in the ultraviolet range revealed that the enzyme is predominantly a β-pleated structure and a detailed structural composition showed 27.9% of β-sheets. These results were different with the secondary structure content of β-mannanase produced by Trichoderma reesei (PDB entry 1QNS, chain A) which has a (β/α) 8-barrel structure with a 34.9% of α-helix and a 16.6% of β-strand.33 The CD-based conformational evaluation of the enzyme after incubation at different temperature and pH values revealed that the change in the β-content directly corresponded to the altered enzyme activity. As temperature was increased, the activity of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was increased.
The secondary structure of β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 was relatively stable. The enzyme was slightly increased in β-sheet content when in optimum pH (8.0). There was a concomitant aggrandize in β-mannanase activity produced by HDYM-04 to 385.38 U mL−1. It was clear that with a reduction in turn and random coil, the enzyme activity was significantly increased. The extent of random coil at other pH values also corresponded with their residual enzyme activities. Different temperature and pH had effect on the amino acid dissociation of protein molecules and changed the activity of enzyme by the state of the side chain groups. The structure of β-sheet and random coil is more orderly, and can make the protein molecules have a higher degree of tightness.
3.7 Decolorization of dyes by β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04
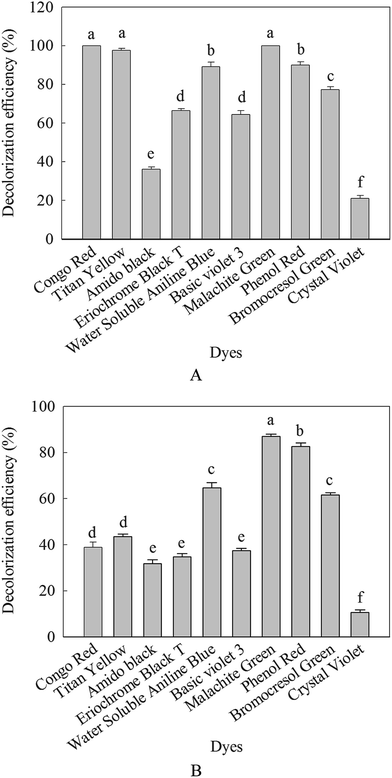
In this work, different dyes solution were decolorized with β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04 in order to evaluate the applicability of these processes to real situation. Fig. 9 showed the degradation of ten structurally different dyes including azo and triaromatic methane by the purified enzyme and commercial β-mannanase. Compared with the commercial β-mannanase, the purified enzyme displayed stronger ability of decolorization no matter what kind of dyes (p < 0.05). For the purified enzyme, the highest decolorization efficiency for 24 h of incubation was detected to be 100% for Congo red, 66.52% for eriochrome black T, 98.60% for titan yellow, 89.46% for water soluble aniline blue, 100% for malachite green, 64.80% for crystal violet, 19.29% for basic violet 3, 77.65% for bromocresol green, 37.45% for amido black and 91% for phenol red, significantly higher than the decolorization effect of the commercial β-mannanase (p < 0.05) (Fig. 9).The decolorization capability of this purified enzyme was compared with that of other enzyme reported previously. Previous researches have reported that the protease enzyme derived from B. cereus strain wwcp1 could decolorize 98% of malachite green for 24 h of incubation.34 Azo dye could be decolorized by the Bacillus sp. VUS, but the decolorization efficiency was relatively low. The decolorization efficiency for eriochrome black T only reached 57% within 12 h.35 However, no report was about decolorization of dyes by β-mannanase from B. licheniformis. Based on these superior points, the β-mannanase derived from HDYM-04 showed great potential and promising application in decolorizing industrial dyes.
4 Conclusions
This study reported the purification and characterization of a β-mannanase produced by HDYM-04. To sum up, the purified β-mannanase from HDYM-04 catalytic activity was very high, and it was resistant to metal ions and highly stable against the temperature and different pH. The enzyme obtained from this research possessed much higher stability in weak alkaline conditions, which was in accordance with the feature of the other β-mannanases that have been reported.36 The enzyme is subjected to chemical modification, and the activities of the modified enzyme is examined. Tyrosine, thiol and tryptophan in the enzyme are important for the maintenance of the stability of the enzyme. An initial analysis of the CD spectrum in the ultraviolet range revealed that the β-mannanase is predominantly a β-pleated structure and a detailed structural composition showed 27.9% β-sheets. The CD-based conformational evaluation of the β-mannanase after incubation at different temperature and pH values, revealed that the change in the β-content directly corresponded to the altered enzyme activity. Besides, we find that the β-mannanase enzyme we use show remarkably high activities and find to be capable of decolorize and degrade different structure of synthetic dyes. So the decolorization of dyes by β-mannanase is simple and cheap. The obtained results display that the use of the β-mannanase has an enormous potential to degrade textile dyes. So, this enzyme can be used for treating textile wastewaters, particularly for water recycling.Author contributions
J. P. Ge and R. P. Du: these two authors contributed equally to this work, including acquisition of funding, literature research, experimental studies, manuscript preparation. D. Zhao, G. Song and M. Jin: data collection and data analysis. W. X. Ping: the corresponding author, acquisition of funding, study concepts, study design, final version approval. All authors reviewed the manuscript.Acknowledgements
The research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31270534), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31470537), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31570492), and the Science and Technology Innovation Team Construction Project of Heilongjiang Province (2012td009).Notes and references
- H. Wang, H. Luo, J. Li, Y. Bai, H. Huang, P. Shi, Y. Fan and B. Yao, Bioresour. Technol., 2010, 101, 8376–8382 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- C. Songsiriritthigul, B. Buranabanyat, D. Haltrich and M. Yamabhai, Microb. Cell Fact., 2010, 9, 312–332 CrossRef PubMed
.
- W. H. Van Zyl, S. H. Rose, K. Trollope and J. F. Görgens, Process Biochem., 2010, 45, 1203–1213 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Dhawan and J. Kaur, Crit. Rev. Biotechnol., 2007, 27, 197–216 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. Q. Jiang, Y. Wei, D. Y. Li, C. Lite, P. P. Chai and I. Kusakabe, Carbohydr. Polym., 2006, 66, 88–96 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. J. Ham, H. J. Lee and H. Y. Cho, Bioresour. Technol., 2011, 102, 9185–9192 CrossRef PubMed
.
- J. P. Zhou, R. Zhang, Y. J. Gao, J. J. Li, X. H. Tang, Y. L. Mu, F. Wang, C. Li, Y. Y. Dong and Z. X. Huang, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 2012, 113, 568–574 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. A. Filichkin, H. D. Priest, S. A. Givan, R. K. Shen, D. W. Bryant, S. E. Fox, W. K. Wong and T. C. Mockler, Genome Res., 2010, 20, 45–58 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. Charrier and C. Rouland, J. Exp. Zool., 2001, 290, 125–135 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- P. S. Chauhan, N. George, S. Sondhi, N. Puri and N. Gupta, Int. J. Biol. Sci., 2014, 5, 176–192 CAS
.
- P. S. Chauhan, P. Sharma, N. Puri and N. Gupta, Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng., 2014, 37, 1459–1467 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- E. A. Erkurt, A. Ünyayar and H. Kumbur, Process Biochem., 2007, 42, 1429–1435 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Cing and O. Yesilada, J. Basic Microbiol., 2004, 44, 263–269 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- G. L. Miller, Anal. Chem., 1959, 31, 426–428 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. M. Bradford, Anal. Biochem., 1976, 72, 248–254 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Zeilinger, D. Kristufek, I. Arisan-Atac, R. Hodits and C. P. Kubicek, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1993, 59, 1347–1353 CAS
.
- S. W. Provencher and J. Glockner, Biochemistry, 1981, 20, 33–37 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. W. Provencher and J. Glockner, Biochemistry, 1981, 20, 33–37 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Bakhtiar, M. M. Andersson, A. Gessesse, B. Mattiasson and R. Hatti-Kaul, Enzyme Microb. Technol., 2002, 32, 525–531 CrossRef
.
- J. Zhang, Z. He and K. Hu, Biotechnol. Lett., 2000, 22, 1375–1378 CrossRef CAS
.
- G. Talbot and J. Sygusch, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1990, 56, 3505–3510 CAS
.
- U. A. Zahura, M. M. Rahman, A. Inoue, H. Tanaka and T. Ojima, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., Part B: Biochem. Mol. Biol., 2011, 159, 227–235 CrossRef PubMed
.
- H. Li, Z. Liu, C. Wang, S. C. Huang and M. Zhao, Eur. Food Res. Technol., 2015, 240, 671–677 CrossRef CAS
.
- K. M. Cho, S. Y. Hong, S. M. Lee, Y. H. Kim, G. G. Kahng, H. Kim and H. D. Yun, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2006, 73, 618–630 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- G. Singh, A. Bhalla and G. S. Hoondal, BioResources, 2010, 5, 1689–1701 Search PubMed
.
- P. Summpunn, S. Chaijan, D. Isarangkul, S. Wiyakrutta and V. Meevootisom, J. Microbiol, 2011, 49, 86–93 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. J. Ham, H. J. Lee, Y. J. Kim, D. H. Shin, Y. H. Rhee, K. H. Son and H. Y. Park, Enzyme Microb. Technol., 2011, 48, 365–370 CrossRef PubMed
.
- J. Wang, J. Z. Z. Shao, Y. Z. Hong, C. J. Li, X. Y. Fu and Z. D. Liu, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2010, 26, 1777–1784 CrossRef CAS
.
- P. L. Yang, Y. N. Li, Y. R. Wang, K. Meng, H. Y. Luo, T. Z. Yuan, Y. G. Bai, Z. C. Zhan and B. Yao, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 2009, 159, 85–94 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. Meenakshi and S. Gursharam, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 2012, 53, 345–361 Search PubMed
.
- S. K. Singh, V. R. Tripathi, R. K. Jain, S. Vikram and S. K. Garg, Microb. Cell Fact., 2010, 9, 1–7 CrossRef PubMed
.
- B. Jaouadi, S. Ellouz-Chaabouni, M. Rhimi and S. Bejar, Biochimie, 2008, 90, 1291–1305 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- T. Kaper, T. Kaper, H. H. van Heusden, B. van Loo, A. Vasella, J. van der Oost and W. M. de Vos, Biochemistry, 2002, 41, 4147–4155 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- W. C. Wanyonyi, J. M. Onyari, P. M. Shiundu and F. J. Mulaa, IOSR-JESTFT, 2014, 8, 58–64 CrossRef
.
- D. Deng, J. Guo, G. Zeng and G. Q. Sun, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2008, 62, 263–269 CrossRef CAS
.
- X. P. He, N. Liu, W. W. Li, Z. Y. Zhang, B. R. Ma and Y. H. Ma, Enzyme Microb. Technol., 2008, 43, 13–18 CrossRef CAS
.
Footnote |
| † These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |