Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Distribution of oxygen functional groups of graphene oxide obtained from low-temperature atomic layer deposition of titanium oxide†
Dong Seok Shin‡
a,
Hyun Gu Kim‡b,
Ho Seon Ahn‡c,
Hu Young Jeongd,
Youn-Jung Kime,
Dorj Odkhuua,
N. Tsogbadrakhf,
Han-Bo-Ram Lee*b and
Byung Hoon Kim *a
*a
aDepartment of Physics, Incheon National University, Incheon 22012, Republic of Korea. E-mail: kbh37@inu.ac.kr
bDepartment of Materials Science and Engineering, and Innovation Center for Chemical Engineering, Incheon National University, Incheon 22012, Republic of Korea. E-mail: hbrlee@inu.ac.kr
cDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, Incheon National University, Incheon 22012, Republic of Korea
dUNIST Central Research Facilities (UCRF), School of Materials Science and Engineering, UNIST, Ulsan 44919, Republic of Korea
eDepartment of Marine Science, Incheon National University, Incheon 22012, Republic of Korea
fDepartment of Physics, National University of Mongolia, Ulaanbaatar 14201, Mongolia
First published on 2nd March 2017
Abstract
The distribution of oxygen functional groups on the surface of graphene oxide (GO) has been investigated experimentally and theoretically. Atomic layer deposition of TiOx was used to clarify the location of oxygen functional groups. We found that the oxygen functional groups are distributed in the form of islands, which is confirmed using aberration corrected transmission electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The density functional studies further support these findings. The evolution of oxygen functional groups was also investigated with GO treated at 150, 200, 250, and 300 °C. In addition, the reduction of epoxide and hydroxyl groups on the GO surface at different temperatures has been discussed in connection with ab initio molecular dynamics simulations.
Introduction
Graphene oxide (GO) had been revisited due to the possibility of the mass production of graphene.1 GO has attracted lots of attention as a building block for novel applications towards not only enhancement of electrochemical performance,2–7 gas storage capacity,8–11 and efficiency of solar cells12 but also development of artificial muscle13 and shape-memory polymers,14 and so on. Even though the existence of functional groups and large surface area have been suggested as the dominant factors for these superior properties of GO in the various fields, the exact mechanisms are still veiled. Hence, the structure of GO must be verified to understand the reason for the outstanding properties and to improve the efficiency in energy storage, gas sensing properties, and other applications. Especially, the distribution of the oxygen functional groups is the most important to understand the mechanisms,15,16 for example, the pathway of Li ions and charge storage in a GO-based Li-ion battery and supercapacitor, respectively. The existence of functional groups such as epoxy, hydroxyl, and carboxyl surface groups17,18 was already known, and the quantity of the functional groups with respect to a graphitic region have been reported experimentally19,20 and theoretically.21 Moreover, the atomic structure of a highly-reduced GO (rGO) using chemical agents and high temperature over 550 °C (ref. 22–24) has been established. However, the structure of GO at low temperature is more important to understand the energy storage of GO8,25 and pillared GO.10 Nevertheless, the distribution of the oxygen functional groups in GO at low temperature has rarely been investigated26,27 because the functional groups in a wide region of GO surface cannot be identified clearly.Herein, we report the results of experimental and theoretical investigations on the distribution of oxygen functional groups over GO surface. The experiments were performed using a titanium nanostructure deposited on the oxygen groups of GO by atomic deposition layer (ALD) method. Since a thin film by ALD forms only through surface reactions of precursors with surface species, the nucleation of ALD film strongly depends on the surface species. Surface reaction mechanisms of TiO2 ALD has been many times reported through experimental and theoretical studies, and it has been known that Ti precursor chemisorbs on surface via reactions with oxygen species, such as 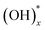 and Ox.28–30 The pristine graphene surface is chemically inert, so that the Ti precursor is hard to adsorb on the surface for initiating nucleation of TiO2. Therefore, once nuclei of ALD TiO2 are formed on graphene surface, it can be inferred that the graphene surface has reactive oxygen functional groups, which promote Ti precursor adsorptions, such as
and Ox.28–30 The pristine graphene surface is chemically inert, so that the Ti precursor is hard to adsorb on the surface for initiating nucleation of TiO2. Therefore, once nuclei of ALD TiO2 are formed on graphene surface, it can be inferred that the graphene surface has reactive oxygen functional groups, which promote Ti precursor adsorptions, such as 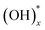 and Ox. In other words, the oxygen functional groups can be traced through analyze of ALD TiO2 formation on graphene. Titanium oxide was deposited at various temperatures (150, 200, 250, and 300 °C) using low temperature deposition method. The distribution was observed and compared with aberration corrected transmission electron microscopy (TEM), which shows that the oxygens are distributed with the form of island. This was further confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and density functional theory (DFT) studies. Moreover, the experimentally observed reduction process of epoxide and hydroxyl groups on GO surface at the elevated temperature has been discussed in connection with ab initio molecular dynamic (AIMD) simulations.
and Ox. In other words, the oxygen functional groups can be traced through analyze of ALD TiO2 formation on graphene. Titanium oxide was deposited at various temperatures (150, 200, 250, and 300 °C) using low temperature deposition method. The distribution was observed and compared with aberration corrected transmission electron microscopy (TEM), which shows that the oxygens are distributed with the form of island. This was further confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and density functional theory (DFT) studies. Moreover, the experimentally observed reduction process of epoxide and hydroxyl groups on GO surface at the elevated temperature has been discussed in connection with ab initio molecular dynamic (AIMD) simulations.
Experimental
We prepared the titanium oxide-deposited GO (TiGO) using ALD. The procedure is as follows. GO was synthesized by a modified Hummers method with graphite powder of 450 nm size. The graphite was oxidized with concentrated H2SO4, K2S2O8 and P2O5. After filtering, washing, and drying the product was re-suspended in concentrated H2SO4 and oxidized further with KMnO4 and H2O2; the result was a thick, brownish yellow GO suspension. The GO suspension was centrifuged and washed with 10% HCl and DI water, and then the suspension was dried at 50 °C for three days to obtain GO. The well dispersed GO in DI water was dropped on Mo TEM grid. Prior to ALD process, the Mo TEM grid was annealed at 150, 200, 250, and 300 °C for 20 minutes to reduce GO in the ALD chamber. Hence, ALD of titanium oxide was performed on rGO in a commercial ALD system (SN-100, SNTEK) using titanium(IV) isopropoxide 97% (TTIP) precursor (Sigma-Aldrich) and H2O reactant. The ALD system is a traveling wave type chamber and capable up to 4 inch wafer and further detail configuration of ALD chamber can be found in our previous paper.31 N2 was used for purging gas. Substrate temperature was controlled from 150 to 300 °C, and the bubbler was heated at 50 °C to obtain a proper vapour pressure. Both exposure times of TTIP precursor and H2O reactant were 2 s, and purging times after precursor exposure and reactant exposure were 15 s and 30 s, respectively. The thickness of the deposited titanium oxide thin film was fixed to 1.0 nm by changing the number of ALD cycle number. TEM study was performed by aberration corrected TEM (FEI Titan cube G2 60-300) operated at an accelerating voltage of 80 kV. XPS of the samples was measured with PHI 5000 Versa Probe II (ULVAC-PHI) using a monochromatic Al-Kα X-ray source at 23.1 W.Computation method
The DFT simulations were carried out within the framework of the projector augmented-wave formalism32 as implemented in the Vienna ab initio simulation package (VASP).33 The generalized gradient approximation formulated by Perdew, Burke, and Ernzerhof was employed for the exchange correlation potential.34 We used an energy cutoff of 400 eV and a k-point sampling of 3 × 3 × 1 for the 6 × 6 graphene cell with periodic boundary conditions along the xy-direction. The vertical vacuum size of the supercell along the z-axis was chosen no less than 15 Å to avoid a possible interaction between the repeated layers (an isolated graphene). We optimize the in-plane lattice for each sample while kept fixed the z-axis. The optimization of both lattice and atomic positions proceeds until the changes in energy were less than 10−5 eV per cell and the forces acting on atoms were less than 10−2 eV Å−1. Both the spin-polarized and spin-non-polarized calculations were taken into account (Table S1 in the ESI†), and results presented in the following paragraphs are those from the spin-polarized calculations. In the AIMD simulations, we use a time step of 2 fs and a Nose thermostat35 to model a canonical ensemble. A total simulation time was thus 2 ps and there is no difference between temperature profiles at 2 and 4 ps. All the AIMD calculations were performed at the constant volume and same evaluated simulation temperature, where a k-point sampling and energy cutoff were restricted to the Γ point and 300 eV, respectively.Results and discussion
The deposition of titanium oxide on graphene oxide was confirmed by XPS study. Fig. 1 shows the O 1s spectra of TiGO as a function of the deposition temperature. The O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–OH at 530.80 eV, C
C–OH at 530.80 eV, C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O at 531.75 eV, and C–OH at 532.99 eV were observed in the pristine GO. After ALD process, the peak corresponding to the titanium oxide at 529.15 eV was developed. This peak increased with the increase of the deposition temperature. Since the detachment of oxygen functional groups from GO layers becomes enhanced as the temperature increases, the quantity of titanium oxide (red arrow in Fig. 1) increases with respect to that of oxygen functional groups. Titanium oxide deposition onto GO surface was also proved by TEM.
O at 531.75 eV, and C–OH at 532.99 eV were observed in the pristine GO. After ALD process, the peak corresponding to the titanium oxide at 529.15 eV was developed. This peak increased with the increase of the deposition temperature. Since the detachment of oxygen functional groups from GO layers becomes enhanced as the temperature increases, the quantity of titanium oxide (red arrow in Fig. 1) increases with respect to that of oxygen functional groups. Titanium oxide deposition onto GO surface was also proved by TEM.
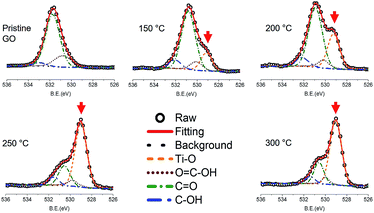 | ||
| Fig. 1 O 1s XPS spectra of TiGO as a function of the deposition temperature. The red arrow indicates the peak corresponding to titanium oxide. | ||
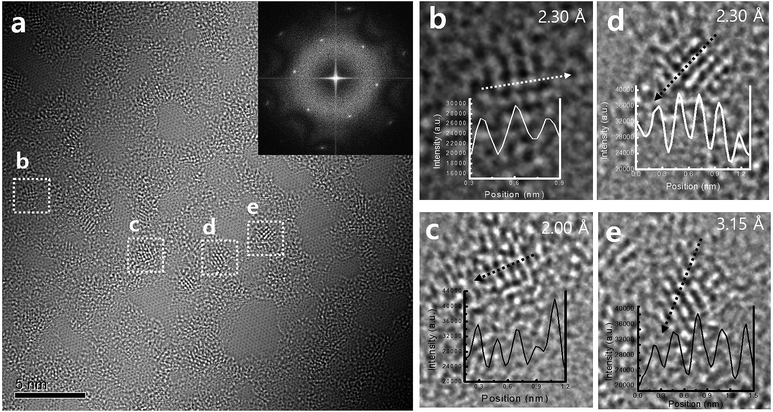
The single-layer GO was used to investigate the oxygen distribution (inset of Fig. 2a). Titanium oxide-deposited GO at 150 °C (TiGO150, the number 150 indicates the deposition temperature) is shown in Fig. 2. The three representative structures were observed; the clean hexagonal region, nanocrystalline structures, and bright amorphous structure. The clean hexagonal regions are graphitic carbons without any oxygen functional groups (sp2 carbon). Nanocrystalline structures with 1–2 nm of size were not distributed evenly. Although they were identified as TiO, TiO2, and Ti2O3, we found that the rutile TiO2 was the main nanostructure among them, which was proved by the profiles of the magnified TEM images (Fig. 2b–e). We observed the lattice spacings of d = 2.30, 2.00, and 3.15, which respectively correspond to the lattice spacings for (220), (210), and (110) planes of the rutile TiO2. In the case of the bright amorphous atoms, although we cannot define them at this stage, they are to be the noncrystalline titanium oxide.
It is well established that the oxygen functional groups are desorbed at high temperature and this behaviour is enhanced with the increase of temperature. This was also confirmed using the variation of C 1s peak in XPS study (Fig. 3). The C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond at 283.85 eV, C–OH bond at 284.58 eV, C–O–C bond at 285.99 eV, C
C bond at 283.85 eV, C–OH bond at 284.58 eV, C–O–C bond at 285.99 eV, C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond at 286.89 eV, and O
O bond at 286.89 eV, and O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–O bond at 287.39 eV were found in the pristine GO. The C
C–O bond at 287.39 eV were found in the pristine GO. The C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bonds increased from 40.470% for pristine GO to 80.012% for TiGO300. On the contrary, the oxygen functional groups, C–OH, C–O–C, C
C bonds increased from 40.470% for pristine GO to 80.012% for TiGO300. On the contrary, the oxygen functional groups, C–OH, C–O–C, C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O, and O
O, and O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–O, decreased as the deposition temperature increased. TEM study also shows this behaviour (Fig. 4). Although the clean hexagonal region (bright grey in Fig. 4), i.e., the area for sp2 carbons did not increase up to 80% of total region in TEM image of TiGO300, we found that it became larger as the deposition temperature increased (from 19.2% for TiGO150 to 29.9% for TiGO300). Note that the titanium oxide and amorphous bright regions are not evenly distributed. They are gathered in the form of the islands which are distributed irregularly.
C–O, decreased as the deposition temperature increased. TEM study also shows this behaviour (Fig. 4). Although the clean hexagonal region (bright grey in Fig. 4), i.e., the area for sp2 carbons did not increase up to 80% of total region in TEM image of TiGO300, we found that it became larger as the deposition temperature increased (from 19.2% for TiGO150 to 29.9% for TiGO300). Note that the titanium oxide and amorphous bright regions are not evenly distributed. They are gathered in the form of the islands which are distributed irregularly.
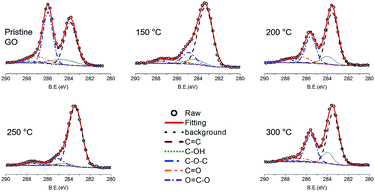 | ||
| Fig. 3 C 1s XPS spectra of TiGO as a function of the deposition temperature. The oxygen functional groups decreased as the temperature increased. | ||
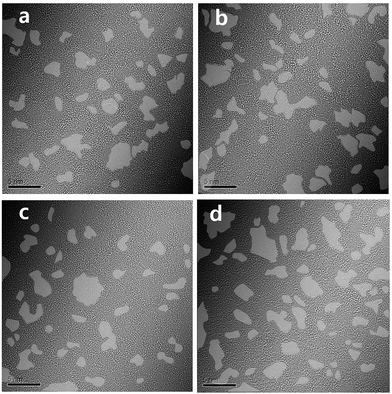 | ||
| Fig. 4 TEM image of TiGO treated at various deposition temperatures (a) 150 °C, (b) 200 °C, (c) 250 °C, (d) 300 °C. The grey colour indicates the clean hexagonal region. | ||
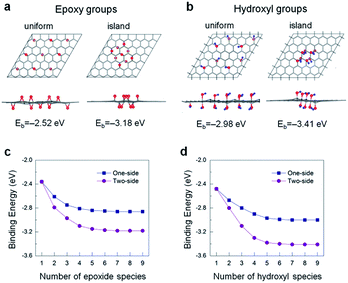
To better certify the aforementioned results, we conduct the first-principles DFT and AIMD calculations. We first explore the structural features and energetics of oxidation functional groups on a single-layer graphene. The modelled geometries consist of the 1–9 epoxide and 1–8 hydroxyl units adsorbed on a 6 × 6 lateral unit cell of graphene. As an example, we show the optimized atomic structures with the 9 epoxide and 8 hydroxyl groups in Fig. 5a and b, respectively, in which the functional groups are present on the both sides of graphene. This two-side adsorption is identified to be energetically favourable against the one-side configurations because of a cancellation of vertical structural distortion (Fig. S5†), as addressed in the previous studies.36,37 The three distinct principal adsorption sites of epoxide and hydroxyl groups on graphene have been taken into account; namely hollow-, bridge-, and top-site. As shown in Fig. S1 and S2,† the total energy calculations show that the most stable adsorption site of the epoxide group is the bridge-site, whereas it is the top-site with C–O bond for the hydroxyl group. Overall the optimized atomic structures of graphene with the epoxide and hydroxyl species are in agreement with those reported in the previous studies.36–38
The oxide functional coverage of graphene surface can possibly exist in various configurations of the distribution. Among the several geometries explored, the top and side views of two selected patterns, named as ‘uniform’ (left panel) and ‘island’ (right panel), are shown in Fig. 5a and b for the two-sided epoxide and hydroxyl groups, respectively. In the uniform configuration, the functional groups are distributed evenly with the similar distances from each other across the graphene surface. In the island configuration, the functional groups are aggregated rather in close proximity within the highly oxidized domain like distribution. In order to identify a ground-state phase of oxygen distribution, we formulate the binding energetics (Eb) as39
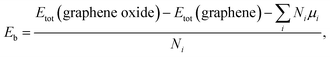 | (1) |
Next, the AIMD simulations are used to investigate the decomposition process of the functional groups from GO surface at an elevated temperature. As a precursor, only the two neighbouring epoxide-only and hydroxyl-only species, incorporating the energetically favourable building blocks,41 chemisorbed onto the one-side of graphene have been modelled in the present computation. The left panels shown in Fig. 6a and b are the top and side views of the optimized atomic structures for the epoxide and hydroxyl groups on graphene at absolute zero temperature, 0 K or −273.15 °C. It is seen that the presence of the functional groups can induce a tenuous local distortion in graphene lattice. This effect is indeed expected from the previous studies that the chemisorption of functional atoms (e.g., O, H, and F) onto graphene results in a phase transition from planar sp2 to distorted sp3 like hybridization.36–39,41 As temperature increases up to 300 °C, such a structural instability of graphene upon functionalization is even further deformed while the entire area of a flat graphene is significantly wrinkled, as seen in the middle and right panels in Fig. 6a and b. Furthermore, the C–O bond lengths of epoxide groups on graphene increase from about 1.44 Å at 0 K to 1.51 Å at 150 °C to 1.64 Å at 300 °C. This reveals a tendency of the functional group desorption from the graphene surface at high temperature although not complete.
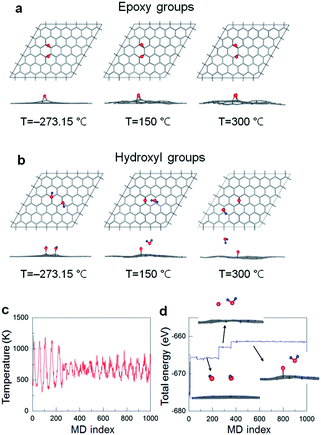 | ||
| Fig. 6 AIMD simulations for the decomposition process of (a) epoxy groups and (b) hydroxyl groups at various temperatures. Atomic symbols are the same as used in Fig. 5. (c) Temperature and (d) energy profiles during AIMD simulation with 1000 ionic steps. | ||
Notably, the hydroxyl groups decompose into single oxygen atoms as an epoxide on graphene and desorbed water molecules (H2O) even at 150 °C, where the GO surface would be served as a catalytic activity at finite temperature. We also show the temperature (both begin and end points at 150 °C) and total energy profiles during the AIMD simulation with 1000 ionic steps in Fig. 6c and d, respectively. The decomposition process from hydroxyl groups into H2O molecules is also illustrated in the inset in Fig. 6d. The hydroxyl groups are first detached from graphene, and then the isolated water and oxygen atoms form. Such an oxygen atom eventually adsorbs onto graphene, making epoxide with graphene shown in the middle panel in Fig. 6b. We finally would like to note that the direct comparison between experimental and theoretical results requires some cautions, and the further simulations with more realistic geometric patterns – considering a broad ranges of sample stoichiometry with the presence of graphene defects (e.g., edge and vacancy sites), different relative amounts and mixed phases of epoxide and hydroxyl groups, domains of various intermediate phases – should be carried out to provide more practical results and insights.
Conclusions
In summary, the oxygen functional groups on GOs treated at 150, 200, 250, and 300 °C was identified by the deposition of TiO2 on the GO surface using ALD. We found that the oxygen functional groups are not distributed evenly but in the form of island. This structural information was obtained from the aberration corrected TEM and XPS. To understand this distribution of oxygen functional groups, we conduct the DFT calculations, where the binding energetics reveals that the oxygen functional groups prefer the island formation rather than uniform distribution. Moreover, the reduction process of epoxide and hydroxyl groups on GO surface at different temperatures was investigated with the ab initio molecular dynamics simulations. This work provides not only the fundamental properties of GO but also offers the information on designing the GO-based energy materials.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Incheon National University Research Grant in 20141308. This work was also partially supported by the National University of Mongolia for the visiting fellowship research program (Grant No. P2016-1161).References
- S. Stankovich, D. A. Dikin, R. D. Piner, K. A. Kohlhaas, A. Klennhammes, Y. Jia, Y. Wu, S. T. Nguyen and R. S. Ruoff, Carbon, 2007, 45, 1558–1565 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Hu, C. Xu, Z. Sun, S. Wang, H.-M. Cheng, F. Li and W. Ren, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 1603–1609 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Song, Z. Yu, M. L. Gordin and D. Wang, Nano Lett., 2016, 16, 864–870 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Gong, S. Yang, Z. Liu, L. Ma, R. Vajtai and P. M. Ajayan, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25, 3979–3984 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. I. Shin, A. Go, I. Y. Kim, J. M. Lee, Y. Lee and S.-J. Hwang, Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, 6, 608–617 CAS.
- R.-Z. Li, R. Peng, D. D. Kihm, S. Bai, D. Bridges, U. Tumuluri, Z. Wu, T. Zhang, G. Compagnini, Z. Feng and A. Hu, Energy Environ. Sci., 2016, 9, 1458–1467 CAS.
- C. Zhang, X. Wang, Q. Liang, X. Liu, Q. Weng, J. Liu, Y. Yang, Z. Dai, K. Ding, Y. Bando, J. Tang and D. Golberg, Nano Lett., 2016, 16, 2054–2060 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. H. Kim, W. G. Hong, H. Y. Yu, Y.-K. Han, S. M. Lee, S. J. Chang, H. R. Moon, Y. Jun and H. J. Kim, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14, 1480–1484 RSC.
- W. G. Hong, B. H. Kim, S. M. Lee, H. Y. Yu, Y. J. Yun, Y. Jun, J. B. Lee and H. J. Kim, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37, 7594–7599 CrossRef CAS.
- B. H. Kim, W. G. Hong, H. R. Moon, S. M. Lee, J. M. Kim, S. Kang, Y. Jun and H. J. Kim, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37, 14217–14222 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Liu, L. Sun, F. Xu, J. Zhang, C. Jiao, F. Li, Z. Li, S. Wang, Z. Wang, X. Jiang, H. Zhou, L. Yang and C. Schick, Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, 6, 818–823 CAS.
- J. Liu, M. Durstock and L. Dai, Energy Environ. Sci., 2014, 7, 1297–1306 CAS.
- M. Kotal, J. Kim, K. J. Kim and I.-K. Oh, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 1610–1615 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Li, L. Qiu, B. Zhang, D. Li and C.-Y. Liu, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 1510–1516 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Chen, H. Feng and J. Li, Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 6027–6053 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Huang, C. Li and G. Shi, Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5, 8848–8868 CAS.
- D. A. Dikin, S. Stankovich, E. J. Zimney, R. D. Piner, G. H. B. Dommett, G. Evmenenko, S. T. Nguyen and R. S. Ruoff, Nature, 2007, 448, 457–460 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Gao, L. B. Alemany, L. Ci and P. M. Ajayan, Nat. Chem., 2009, 1, 403–408 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Y. S. Eng, C. K. Chua and M. Pumera, Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 20256–20266 RSC.
- A. Hunt, D. A. Kikin, E. Z. Kumaev, T. D. Boyko, P. Bazylewski, G. S. Chang and A. Moewes, Adv. Mater., 2012, 22, 3950–3957 CAS.
- L.-C. Lin and J. C. Grossman, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 8335 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Gómez-Navarro, J. C. Meyer, R. S. Sundaram, A. Chuvilin, S. Kurasch, M. Burghard, K. Kern and U. Kaiser, Nano Lett., 2010, 10, 1144–1148 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Erickson, R. Emi, Z. Lee, N. Alem, W. Gannett and A. Zettl, Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 4467–4472 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. B. Boothroyd, M. S. Moreno, M. Duchamp, A. Kovacs, G. M. Morales, C. A. Barbero and R. E. Bunin-Borkowski, Ultramicroscopy, 2014, 145, 66–73 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. M. Kim, W. G. Hong, S. M. Lee, S. J. Chang, Y. Jun, B. H. Kim and H. J. Kim, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39, 3799–3804 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Gao, J. Jang and S. Nagase, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 832–842 CAS.
- C.-M. Chen, Q. Zhang, M.-G. Yang, C.-H. Huang, Y.-G. Yang and M.-Z. Wang, Carbon, 2012, 50, 3572–3584 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Y. Lee, C. Jeon, S. H. Kim, Y. Kim, W. Jung, K. S. An and C. Y. Park, J. Appl. Phys., 2012, 51, 2–4 Search PubMed.
- D. M. King, X. Liang, Y. Zhou, C. S. Carney, L. F. Hakim, P. Li and A. W. Weimer, Powder Technol., 2008, 183, 356–363 CrossRef CAS.
- J. H. Yoon, S. C. Jung and J. S. Kim, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, 125, 342–346 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Lee, J. Yoon, H. G. Kim, S. Kang, W.-S. Oh, H. Algadi, S. Al-Sayari, B. Shong, S.-H. Kim, H. Kim, T. Lee and H.-B.-R. Lee, NPG Asia Mater., 2016, 8, e331 CrossRef CAS.
- P. E. Blochl, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1994, 50, 17953 CrossRef.
- G. Kresse and J. Hafner, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1993, 47, 558 CrossRef CAS.
- J. P. Perdew, K. Burke and M. Ernzerhof, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1996, 77, 3865 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. M. Bylander and L. Kleinman, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1992, 46, 13756 CrossRef.
- D. W. Boukhvalov and M. I. Katsnelson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 10697 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. A. Yan, L. Xian and M. Y. Chou, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2009, 103, 086802 CrossRef PubMed.
- J.-L. Li, K. N. Kudin, M. J. McAllister, R. K. Prudhomme, I. A. Aksay and R. Car, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2006, 96, 176101 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Odkhuu, D. Shin, R. S. Ruoff and N. Park, Scientific Reports, 2013, 3, 3276 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Odkhuu, Phys. Rev. B, 2016, 94, 060403 CrossRef.
- S. S. Han, H. Jung, D. H. Jung, S. H. Choi and N. Park, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 2012, 85, 155408 CrossRef.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c7ra00114b |
| ‡ These author contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 |