Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleC-Glycosylated cinnamoylfuran derivatives as novel anti-cancer agents†
Ananya Dutta
a,
Debashis Dhara‡a,
Pravat Kumar Paridaa,
Anshupriya Sia,
Ravichandran Yesuvadianb,
Kuladip Jana*a and
Anup Kumar Misra *a
*a
aBose Institute, Division of Molecular Medicine, P-1/12, C.I.T. Scheme VII-M, Kolkata-700054, India. E-mail: akmisra69@gmail.com; Fax: +91 33 2355 3886; Tel: +91 33 2569 3240
bDepartment of Biotechnology, School of Bioengineering, SRM University, Kattankulathur – 603203, Tamil Nadu, India
First published on 31st May 2017
Abstract
A series of C-glycosylated cinnamoylfuran derivatives were synthesized in excellent yield from free sugars. The C-glycosylated furan derivatives were prepared under aqueous reaction conditions. The anticancer potentials of the synthesized compounds were evaluated on the basis of their comparative cytotoxic effects on cancer cells (MCF-7 and HeLa) and normal cells (NKE). Among 28 compounds evaluated for their cytotoxic effects on cancer cells, three compounds (compounds 8, 24 and 28) were shown to have significant cytotoxic effects on MCF-7 and HeLa cell lines and comparatively less toxicity against normal NKE cell line. Based on its selectivity index, compound 24 was considered the most promising anticancer agent amongst the above three compounds. Further biochemical studies with compound 24 showed that both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis contribute to compound 24 mediated cytotoxicity.
Introduction
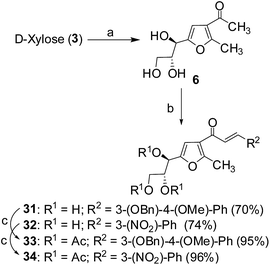
Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, representing a number of diseases due to uncontrolled cell division.1 Cervical cancer and breast cancer are the most frequent among several organ-specific cancers found in women throughout the world and their management strategies are quite expensive.2,3 Although several anticancer therapeutics are available in clinics, they suffer from poor prognosis due to their nonspecific action and cytotoxic effects towards normal cells.4–6 The use of many commonly used chemotherapeutic agents is limited because of drug resistance.7 Therefore, the development of novel therapeutics with better efficacy and lower toxicity is a thrusting area in medicinal chemistry. Over the years, several chemotherapeutic agents have been developed against a number of organ-specific cancers, taking their lead from natural products or synthetic intermediates.8,9 In the recent past, C-glycosylated heterocycles, such as C-glycosylfuran derivatives and related compounds, have been reported for their therapeutic potential.10–15 In addition, a variety of cinnamoylated C-glycoside derivatives have been synthesized with a similar sugar moiety but different aryl groups and evaluated for their potential as anti-mycobacterial agents,16,17 anti-cancer agents,18 lectin inhibitors,19,20 enzyme inhibitors,21 and anti-filarial agents.22 Inspired by these earlier reports, it was decided to synthesize a series of C-glycosylated cinnamoylfuran derivatives to evaluate their potential against cancer cell lines to develop novel anticancer agents. It was envisioned that the presence of a C-glycosylated furan moiety as well as an aryl cinnamoyl functionality in the molecules could improve their efficacy to act as effective cytotoxic agents against cancer cells. The C-glycosylated furan derivatives containing an α-methylcarbonyl functionality were prepared from commercially available reducing sugars under aqueous reaction conditions, following an earlier report.23,24 The furan derivatives were treated with a number of aryl aldehydes in the presence of a base to furnish the desired compounds. Some selected C-cinnamoylated products were acetylated to check whether the O-acetyl group has any influence on the biological activities. The synthesized compounds (7–34) were evaluated for their cytotoxicity potential against two cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and HeLa) as well as a normal cell line (NKE). The synthesis of a series of novel C-glycosyl cinnamoylfuran derivatives and their potential as anticancer agents are reported herein.Results and discussion
Chemistry
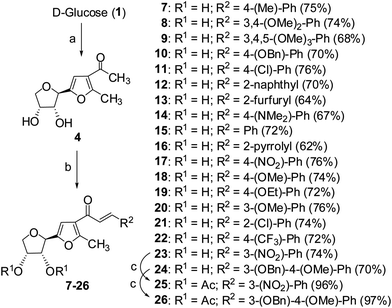 | ||
| Scheme 1 Reagents and conditions: (a) pentane-2,4-dione, CeCl3·7H2O, H2O, 90 °C, 6 h, 90%; (b) ArCHO, CH3ONa, CH3OH, rt, 12 h; (c) acetic anhydride, pyridine, rt, 3 h. | ||
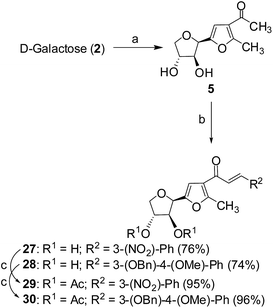 | ||
| Scheme 2 Reagents and conditions: (a) pentane-2,4-dione, CeCl3·7H2O, H2O, 90 °C, 6 h, 90%; (b) ArCHO, CH3ONa, CH3OH, rt, 12 h; (c) acetic anhydride, pyridine, rt, 3 h. | ||
Biology
| Compd | MCF-7 | HeLa | NKE |
|---|---|---|---|
| a IC50 = concentration at which 50% inhibition in motility was achieved. | |||
| 7 | ≥60 | ≥60 | — |
| 8 | 17.77 ± 1.46 | 15.98 ± 1.85 | 46.03 ± 10.56 |
| 9 | ≥60 | 10.93 ± 5.36 | 109 ± 7.85 |
| 10 | 64.54 ± 13.16 | ≥60 | 75.07 ± 27.83 |
| 11 | ≥60 | ≥60 | — |
| 12 | ≥60 | ≥60 | — |
| 13 | ≥60 | ≥60 | — |
| 14 | 68.75 ± 12.84 | 81.48 ± 76.22 | ≥60 |
| 15 | 90.77 ± 105.53 | 35.93 ± 10.13 | 59.05 ± 59.05 |
| 16 | 54.07 ± 6.49 | ≥60 | ≥60 |
| 17 | ≥60 | ≥60 | — |
| 18 | ≥60 | ≥60 | — |
| 19 | 43.49 ± 7.39 | 47.58 ± 10.37 | ≥60 |
| 20 | ≥60 | ≥60 | — |
| 21 | 45.37 ± 14.31 | ≥60 | 99.92 ± 27.89 |
| 22 | 33.0 ± 1.5 | ≥60 | 24.38 ± 11.38 |
| 23 | ≥60 | ≥60 | — |
| 24 | 9.588 ± 5.25 | 14.22 ± 3.94 | 54.14 ± 1.56 |
| 25 | ≥60 | ≥60 | — |
| 26 | ≥60 | ≥60 | — |
| 27 | 32.35 ± 3.6 | ≥60 | ≥60 |
| 28 | 22.98 ± 4.19 | 22.29 ± 4.03 | 40.29 ± 11.87 |
| 29 | 34.79 ± 6.86 | ≥60 | ≥60 |
| 30 | ≥60 | ≥60 | — |
| 31 | 43.84 ± 7.66 | 30.25 ± 6.76 | 30.23 ± 23 |
| 32 | ≥60 | ≥60 | — |
| 33 | 91.27 ± 53.63 | ≥60 | 23.84 ± 17.45 |
| 34 | ≥60 | ≥60 | — |
| Etoposide | 24.77 ± 3.4 | 29.12 ± 8.56 | — |
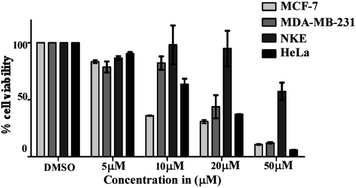
Out of 28 tested compounds, compound 8 (IC50: 17.77 ± 1.46 μM), compound 24 (IC50: 9.588 ± 5.25 μM) and compound 28 (IC50: 22.98 ± 4.19 μM) showed higher efficacy than etoposide (IC50: 24.77 ± 3.4 μM) in MCF-7 cells. In another set of HeLa cells, compound 8 (IC50: 15.98 ± 1.85 μM), compound 24 (IC50: 14.22 ± 3.94 μM), compound 28 (IC50: 22.29 ± 4.03 μM) and also compound 9 (IC50: 10.93 ± 5.36 μM) exerted lower IC50 as compared to etoposide (IC50: 29.12 ± 8.56 μM). From these results, it was found that compound 24 was more potent in both MCF-7 and HeLa cells as compared to compound 8 and compound 28, whereas compound 9 was only effective in HeLa cells. Consequently, an evaluation of the cytotoxic effect of compounds 8, 24 and 28 against NKE cells showed significantly higher IC50 values than their IC50 values against MCF-7 and HeLa cells [compound 24 (IC50: 54.14 ± 1.56 μM), compound 8 (IC50: 46.03 ± 10.56 μM) and compound 28 (IC50: 40.29 ± 11.87 μM)]. Subsequently, when the selectivity indexes (SI) were calculated based on the IC50 value ratio of compounds in NKE vs. MCF-7, it was found that compound 24 (SI = 7.93 ± 4.18) possessed higher SI in comparison to compound 8 (SI = 2.56 ± 0.38) and compound 28 (SI = 4.05 ± 0.06). In the case of HeLa cells, compound 24 also showed a better SI value than the other two compounds [compound 24 (SI = 3.42 ± 0.30), 8 (SI = 3.33 ± 0.34) and 28 (SI = 1.71 ± 0.20)].
The activity of compound 24 was further tested against MDA-MB-231 cells. Interestingly, it was also observed that compound 24 was very effective in inhibiting the proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells and the calculated IC50 value was 19.16 ± 5.97 μM (Fig. 1). Based on the preliminary MTT experimental data and selectivity index, compound 24 has been selected as a promising anti-cancer agent and considered for further evaluation.
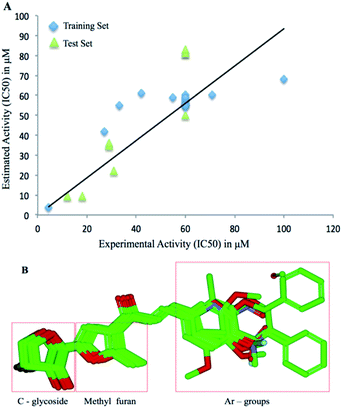
| Training set | Test set |
|---|---|
| a N1 and N2: number of molecules in the training and test set, respectively; RMSD: root-mean square deviation. | |
| N1 = 18 | N2 = 9 |
| Corr. coefficient = 0.9407 | Corr. coefficient = 0.8694 |
| RMSD = 0.1995 | RMSD = 0.2631 |
| Max. fit value = 7.9529 | Max. fit value = 3.9561 |
| Weight = 1.1257 | Weight = 1.1276 |
Conclusions
In summary, a series of C-glycosyl cinnamoylfuran derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for their in vitro cytotoxic activity against cancer cells (MCF-7 and HeLa) and normal cells (NKE). Three compounds (8, 24 and 28) showed significant cytotoxic effects on MCF-7 and HeLa cell lines. Based on the selectivity index, compound 24 was considered the most promising anticancer agent. Further biochemical studies showed that compound 24 mediated cytotoxicity appeared to be due to both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis. QSAR studies have also been carried out to establish the structure–activity relationships of the active compounds.Experimental
General methods
All reactions were monitored by thin layer chromatography over silica gel coated TLC plates. The spots on TLC were visualized by warming ceric sulphate (2% Ce(SO4)2 in 2 N H2SO4) sprayed plates on a hot plate. Silica gel 230–400 mesh was used for column chromatography. 1H and 13C NMR, 2D COSY, HSQC spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance 500 MHz spectrometer using CDCl3 as solvent and TMS as the internal reference unless stated otherwise. Chemical shift values are expressed in δ ppm. ESI-MS were recorded on a Micromass mass spectrometer. Elementary analysis was carried out on a Carlo Erba analyzer. Optical rotations were measured at 25 °C on a Jasco P-2000 polarimeter. Biological experiments were carried out in a Shimadzu UV-2401PC spectrophotometer. Commercially available grades of organic solvents of adequate purity were used in many reactions. The cell culture media along with ingredients were purchased from HiMedia (India). FBS was procured from Gibco (USA). DMSO was purchased from SRL (India). An annexin V-FITC apoptosis assay kit was bought from BD Bioscience (India). A Caspase 3 Assay Kit (ab39401) and Human Apoptosis Array Kit were purchased from AbCam (UK) and R&D Systems (USA), respectively. MCF-7, MDA-MB-231 (human breast cancer) cells, HeLa (human cervical cancer) cells were obtained from the central cell repository of National Center for Cell Science (NCCS), Pune, India. Normal Kidney Epithelial cell (NKE) was a kind gift from Dr K. Biswas, Bose Institute, Kolkata. The cell lines were cultured in RPMI-1640 or DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 2 mM L-glutamine, non-essential amino acids, 100 units per ml penicillin, 50 μg ml−1 streptomycin and 50 μg ml−1 gentamicin sulfate at 37 °C in a humidified incubator containing 5% CO2 atmosphere.General experimental condition for the preparation of compound 7–34
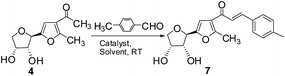
To a solution of compound 4 or 5 or 6 (1 mmol) in CH3OH (10 ml) were added aromatic aldehyde (1.05 mmol) and NaOCH3 (100 mg) and the reaction mixture was allowed to stir at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction mixture was diluted with water and acidified with 1 N HCl. The white solid precipitated out from the solution, which was filtered and crystallized from EtOH to give pure products 7–34 in appropriate yield, as mentioned in the schemes.Analytical data of the compounds 7–34
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2); mp 120–122 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −51 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.71 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.50 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.21 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.14 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.72 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.68 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.42–4.38 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.29–4.26 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.92 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.5 Hz, H-2′), 2.65 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.41 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C
2); mp 120–122 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −51 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.71 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.50 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.21 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.14 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.72 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.68 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.42–4.38 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.29–4.26 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.92 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.5 Hz, H-2′), 2.65 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.41 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 159.7 (C-4), 150.9 (C-1), 143.5 (COCH = CH), 140.8, 132.2, 129.6, 128.4 (Ar-C), 122.6 (COCH = CH), 122.3 (C-2), 109.0 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.1 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 21.5, 14.6 (2C, CH3); ESI-MS: 351.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C19H20O5 (328.36): C, 69.50; H, 6.14%; found: C, 69.45; H, 6.34%.
O), 159.7 (C-4), 150.9 (C-1), 143.5 (COCH = CH), 140.8, 132.2, 129.6, 128.4 (Ar-C), 122.6 (COCH = CH), 122.3 (C-2), 109.0 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.1 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 21.5, 14.6 (2C, CH3); ESI-MS: 351.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C19H20O5 (328.36): C, 69.50; H, 6.14%; found: C, 69.45; H, 6.34%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2); mp 128–130 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −34 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.58 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.10 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.03 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 6.96 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.79 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.65 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.61 (d, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.32–4.29 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.19–4.17 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.86–3.82 (m, 7H, H-2′, 2 OCH3), 2.55 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C
2); mp 128–130 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −34 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.58 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.10 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.03 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 6.96 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.79 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.65 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.61 (d, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.32–4.29 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.19–4.17 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.86–3.82 (m, 7H, H-2′, 2 OCH3), 2.55 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 159.7 (C-4), 151.5 (C-1), 150.0, 149.2 (Ar-C), 143.8 (COCH = CH), 127.6 (Ar-C), 122.2 (COCH = CH), 122.3 (C-2), 121.5 (Ar-C), 110.1, 110.2 (Ar-C), 109.1 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.1 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 55.7 (2C, 2 OCH3), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 397.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C20H22O7 (374.38): C, 64.16; H, 5.92%; found: C, 64.42; H, 6.01%.
O), 159.7 (C-4), 151.5 (C-1), 150.0, 149.2 (Ar-C), 143.8 (COCH = CH), 127.6 (Ar-C), 122.2 (COCH = CH), 122.3 (C-2), 121.5 (Ar-C), 110.1, 110.2 (Ar-C), 109.1 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.1 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 55.7 (2C, 2 OCH3), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 397.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C20H22O7 (374.38): C, 64.16; H, 5.92%; found: C, 64.42; H, 6.01%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2); mp 141–142 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −41 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.63 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.05 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.81 (s, 2H, Ar-H), 6.73 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.69 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.43–4.38 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.30 (dd, 1H, J = 5.0, 10.0 Hz, H-3′), 3.92–3.84 (m, 10H, H-2′, 3 OCH3), 2.66 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.4 (C
2); mp 141–142 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −41 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.63 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.05 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.81 (s, 2H, Ar-H), 6.73 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.69 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.43–4.38 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.30 (dd, 1H, J = 5.0, 10.0 Hz, H-3′), 3.92–3.84 (m, 10H, H-2′, 3 OCH3), 2.66 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.4 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 159.8 (C-4), 153.4 (Ar-C), 149.9 (C-1), 143.6 (COCH = CH), 137.7 (Ar-C), 130.2 (C-2), 126.2 (Ar-C), 123.0 (COCH = CH), 109.0 (C-3), 105.7 (2C, Ar-C), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 60.9, 56.1 (3C, 3OCH3), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 427.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C21H24O8 (404.41): C, 62.37; H, 5.98%; found: C, 62.47; H, 6.11%.
O), 159.8 (C-4), 153.4 (Ar-C), 149.9 (C-1), 143.6 (COCH = CH), 137.7 (Ar-C), 130.2 (C-2), 126.2 (Ar-C), 123.0 (COCH = CH), 109.0 (C-3), 105.7 (2C, Ar-C), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 60.9, 56.1 (3C, 3OCH3), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 427.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C21H24O8 (404.41): C, 62.37; H, 5.98%; found: C, 62.47; H, 6.11%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2); mp 99–101 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −21 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.72 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.56 (d, 2H, J = 9.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.44–7.34 (m, 5H, Ar-H), 7.07 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.00 (d, 2H, J = 9.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.72 (s, 1H, H-4), 5.12 (brs, 2H, PhCH2), 4.69 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.43–4.38 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.30–4.27 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.93 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.5 Hz, H-2′), 2.65 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C
2); mp 99–101 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −21 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.72 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.56 (d, 2H, J = 9.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.44–7.34 (m, 5H, Ar-H), 7.07 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.00 (d, 2H, J = 9.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.72 (s, 1H, H-4), 5.12 (brs, 2H, PhCH2), 4.69 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.43–4.38 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.30–4.27 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.93 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.5 Hz, H-2′), 2.65 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 160.7 (C-4), 150.2 (C-1), 143.2 (COCH = CH), 136.3, 130.1, 128.6 (Ar-C), 128.1 (COCH = CH), 127.7, 127.4 (Ar-C), 121.5 (C-2), 115.2 (Ar-C), 109.0 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 70.0 (PhCH2), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 443.11 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C25H24O6 (420.45): C, 71.41; H, 5.75%; found: C, 71.30; H, 5.87%.
O), 160.7 (C-4), 150.2 (C-1), 143.2 (COCH = CH), 136.3, 130.1, 128.6 (Ar-C), 128.1 (COCH = CH), 127.7, 127.4 (Ar-C), 121.5 (C-2), 115.2 (Ar-C), 109.0 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 70.0 (PhCH2), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 443.11 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C25H24O6 (420.45): C, 71.41; H, 5.75%; found: C, 71.30; H, 5.87%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2); mp 124–125 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −15 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.56 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.43 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.28 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.04 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.62 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.58 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.31–4.27 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.18–4.15 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.81 (dd, 1H, J = 2.5, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.54 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 186.3 (C
2); mp 124–125 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −15 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.56 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.43 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.28 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.04 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.62 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.58 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.31–4.27 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.18–4.15 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.81 (dd, 1H, J = 2.5, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.54 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 186.3 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 161.1 (C-4), 150.0 (C-1), 141.9 (COCH = CH), 136.2, 133.2, 129.5, 128.4, 129.2 (Ar-C), 124.0 (COCH = CH), 122.2 (C-2), 108.9 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.1 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 371.0 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C18H17ClO5 (348.78): C, 61.99; H, 4.91%; found: C, 61.84; H, 5.02%.
O), 161.1 (C-4), 150.0 (C-1), 141.9 (COCH = CH), 136.2, 133.2, 129.5, 128.4, 129.2 (Ar-C), 124.0 (COCH = CH), 122.2 (C-2), 108.9 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.1 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 371.0 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C18H17ClO5 (348.78): C, 61.99; H, 4.91%; found: C, 61.84; H, 5.02%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3); mp 122–123 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −10 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.54 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 8.21 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.86–7.76 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.55–7.42 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.21 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.71 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.67 (d, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.35–4.34 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.22–4.19 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.87–3.85 (m, 1H, H-2′), 2.63 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.2 (C
3); mp 122–123 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −10 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.54 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 8.21 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.86–7.76 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.55–7.42 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.21 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.71 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.67 (d, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.35–4.34 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.22–4.19 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.87–3.85 (m, 1H, H-2′), 2.63 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.2 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 160.0 (C-4), 150.3 (C-1), 140.2 (COCH = CH), 133.7, 132.1, 131.8, 130.7, 128.7, 127.5, 126.4, 125.3, 125.1, (Ar-C), 123.5 (COCH = CH), 122.3 (C-2), 108.9 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 387.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C22H20O5 (364.39): C, 72.51; H, 5.53%; found: C, 72.42; H, 5.65%.
O), 160.0 (C-4), 150.3 (C-1), 140.2 (COCH = CH), 133.7, 132.1, 131.8, 130.7, 128.7, 127.5, 126.4, 125.3, 125.1, (Ar-C), 123.5 (COCH = CH), 122.3 (C-2), 108.9 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 387.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C22H20O5 (364.39): C, 72.51; H, 5.53%; found: C, 72.42; H, 5.65%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); mp 103–104 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −26 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.60 (d, 1H, J = 9.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.58 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.18 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.81–6.79 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 6.60 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.77 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.52–4.46 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.38–4.35 (m, 1H, H-3′), 4.01–3.98 (m, 1H, H-2′), 2.75 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.2 (C
1); mp 103–104 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −26 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.60 (d, 1H, J = 9.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.58 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.18 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.81–6.79 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 6.60 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.77 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.52–4.46 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.38–4.35 (m, 1H, H-3′), 4.01–3.98 (m, 1H, H-2′), 2.75 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.2 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 160.0 (C-4), 150.3 (C-1), 144.7 (COCH = CH), 129.3 (C-2), 121.2 (COCH = CH), 116.0, 112.6 (Ar-C), 109.0 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.1 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 327.0 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C16H16O6 (304.29): C, 63.15; H, 5.30%; found: C, 63.10; H, 5.42%.
O), 160.0 (C-4), 150.3 (C-1), 144.7 (COCH = CH), 129.3 (C-2), 121.2 (COCH = CH), 116.0, 112.6 (Ar-C), 109.0 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.1 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 327.0 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C16H16O6 (304.29): C, 63.15; H, 5.30%; found: C, 63.10; H, 5.42%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3); mp 93–95 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −37 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.76 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.58 (d, 2H, J = 9.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.05 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.78–6.75 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 6.66 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.73 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.50–4.44 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.37–4.32 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.99 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 3.15 (s, 6H, N (CH3)2), 2.46 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C
3); mp 93–95 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −37 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.76 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.58 (d, 2H, J = 9.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.05 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.78–6.75 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 6.66 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.73 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.50–4.44 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.37–4.32 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.99 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 3.15 (s, 6H, N (CH3)2), 2.46 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 159.7 (C-4), 149.7 (C-1), 148.6 (Ar-C), 144.7 (COCH = CH), 130.4 (2C, Ar-C), 122.6 (COCH = CH), 121.9 (Ar-C), 118.5 (C-2), 111.9 (2C, Ar-C), 109.0 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.1 (C-2′), 40.1 (2C, N (CH3)2), 14.6 (2C, CH3); ESI-MS: 380.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C20H23NO5 (357.40): C, 67.21; H, 6.49%; found: C, 67.14; H, 6.60%.
O), 159.7 (C-4), 149.7 (C-1), 148.6 (Ar-C), 144.7 (COCH = CH), 130.4 (2C, Ar-C), 122.6 (COCH = CH), 121.9 (Ar-C), 118.5 (C-2), 111.9 (2C, Ar-C), 109.0 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.1 (C-2′), 40.1 (2C, N (CH3)2), 14.6 (2C, CH3); ESI-MS: 380.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C20H23NO5 (357.40): C, 67.21; H, 6.49%; found: C, 67.14; H, 6.60%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2); mp 102–104 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −20 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.80 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.69–7.68 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.50–7.48 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.27 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.81 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.78 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.51–4.47 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.38–4.35 (m, 1H, H-3′), 4.01 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.73 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.5 (C
2); mp 102–104 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −20 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.80 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.69–7.68 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.50–7.48 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.27 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.81 (s, 1H, H-4), 4.78 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.51–4.47 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.38–4.35 (m, 1H, H-3′), 4.01 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.73 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.5 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 159.9 (C-4), 150.0 (C-1), 143.5 (COCH = CH), 134.7, 130.4, 128.9, 128.4 (Ar-C), 123.6 (COCH = CH), 122.3 (C-2), 109.0 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 337.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C18H18O5 (314.33): C, 68.78; H, 5.77%; found: C, 68.65; H, 5.90%.
O), 159.9 (C-4), 150.0 (C-1), 143.5 (COCH = CH), 134.7, 130.4, 128.9, 128.4 (Ar-C), 123.6 (COCH = CH), 122.3 (C-2), 109.0 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 337.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C18H18O5 (314.33): C, 68.78; H, 5.77%; found: C, 68.65; H, 5.90%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3); mp 108–110 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −21 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 13.2 (s, 1H, NH), 6.76 (d, 1H, J = 14.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.75 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.67 (s, 1H, H-4), 6.53–6.49 (m, 3H, COCH = CH, Ar-H), 4.77 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.48–4.46 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.37–4.34 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.98 (dd, 1H, J = 2.5, 10.5 Hz, H-2′), 2.65 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.2 (C
3); mp 108–110 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −21 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 13.2 (s, 1H, NH), 6.76 (d, 1H, J = 14.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.75 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.67 (s, 1H, H-4), 6.53–6.49 (m, 3H, COCH = CH, Ar-H), 4.77 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.48–4.46 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.37–4.34 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.98 (dd, 1H, J = 2.5, 10.5 Hz, H-2′), 2.65 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.2 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 157.1 (C-4), 149.0 (C-1), 138.9 (C-2), 128.5 (COCH = CH), 123.9 (Ar-C), 118.9 (COCH = CH), 111.4 (Ar-C), 109.9 (C-3), 107.7, 103.2 (Ar-C), 77.3 (C-1′), 74.6 (C-3′), 73.0 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.0 (CH3); ESI-MS: 326.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C16H17NO5 (303.31): C, 63.36; H, 5.65%; found: C, 63.20; H, 5.48%.
O), 157.1 (C-4), 149.0 (C-1), 138.9 (C-2), 128.5 (COCH = CH), 123.9 (Ar-C), 118.9 (COCH = CH), 111.4 (Ar-C), 109.9 (C-3), 107.7, 103.2 (Ar-C), 77.3 (C-1′), 74.6 (C-3′), 73.0 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.0 (CH3); ESI-MS: 326.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C16H17NO5 (303.31): C, 63.36; H, 5.65%; found: C, 63.20; H, 5.48%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5); mp 145–147 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −32 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.26 (d, 2H, J = 6.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.75 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.73 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.29 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.76 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.71 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.46–4.41 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.32–4.22 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.94 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.65 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C
5); mp 145–147 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −32 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.26 (d, 2H, J = 6.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.75 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.73 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.29 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.76 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.71 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.46–4.41 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.32–4.22 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.94 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.65 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 159.7 (C-4), 142.1 (C-1), 140.1 (COCH = CH), 132.2, 129.6, 128.4 (Ar-C), 127.4 (COCH = CH), 124.2 (Ar-C), 123.1 (C-2), 108.8 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.3 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 382.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C18H17NO7 (359.33): C, 60.17; H, 4.77%; found: C, 60.00; H, 4.95%.
O), 159.7 (C-4), 142.1 (C-1), 140.1 (COCH = CH), 132.2, 129.6, 128.4 (Ar-C), 127.4 (COCH = CH), 124.2 (Ar-C), 123.1 (C-2), 108.8 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.3 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 382.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C18H17NO7 (359.33): C, 60.17; H, 4.77%; found: C, 60.00; H, 4.95%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2); mp 133–135 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −35 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.59 (d, 1H, J = 16.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.45 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.95 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.82 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.61 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.59 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.32–4.28 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.19 (dd, 1H, J = 4.5, 10.0 Hz, H-3′), 3.82 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 3.75 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.53 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.2 (C
2); mp 133–135 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −35 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.59 (d, 1H, J = 16.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.45 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.95 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.82 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.61 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.59 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.32–4.28 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.19 (dd, 1H, J = 4.5, 10.0 Hz, H-3′), 3.82 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 3.75 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.53 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.2 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 161.2 (Ar-C), 159.0(C-4), 151.1 (C-1), 143.3 (COCH = CH), 130.1, 127.4 (Ar-C), 123.5 (C-2), 121.4 (COCH = CH), 114.4 (Ar-C), 109.1 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 55.3 (OCH3), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 367.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C19H20O6 (344.36): C, 66.27; H, 5.85%; found: C, 66.07; H, 6.00%.
O), 161.2 (Ar-C), 159.0(C-4), 151.1 (C-1), 143.3 (COCH = CH), 130.1, 127.4 (Ar-C), 123.5 (C-2), 121.4 (COCH = CH), 114.4 (Ar-C), 109.1 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 55.3 (OCH3), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 367.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C19H20O6 (344.36): C, 66.27; H, 5.85%; found: C, 66.07; H, 6.00%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3); mp 138–140 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −31 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.57 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.43 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.93 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.70 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.60 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.58 (d, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.32–4.27 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.17–4.15 (dd, 1H, J = 4.5, 10.0 Hz, H-3′), 3.99 (q, 2H, J = 7.0 Hz each, OCH2CH3), 3.81 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.52 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.36 (t, 3H, J = 7.0 Hz, OCH2CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C
3); mp 138–140 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −31 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.57 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.43 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.93 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.70 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.60 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.58 (d, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.32–4.27 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.17–4.15 (dd, 1H, J = 4.5, 10.0 Hz, H-3′), 3.99 (q, 2H, J = 7.0 Hz each, OCH2CH3), 3.81 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.52 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.36 (t, 3H, J = 7.0 Hz, OCH2CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 161.0 (Ar-C), 159.6 (C-4), 149.8 (C-1), 143.5 (COCH = CH), 130.2, 127.2 (Ar-C), 122.4 (C-2), 121.2 (COCH = CH), 114.8 (Ar-C), 109.1 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.1 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 63.5 (OCH2CH3), 14.7 (CH3), 14.6 (OCH2CH3); ESI-MS: 381.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C20H22O6 (358.39): C, 67.03; H, 6.19%; found: C, 66.90; H, 6.27%.
O), 161.0 (Ar-C), 159.6 (C-4), 149.8 (C-1), 143.5 (COCH = CH), 130.2, 127.2 (Ar-C), 122.4 (C-2), 121.2 (COCH = CH), 114.8 (Ar-C), 109.1 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.1 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 63.5 (OCH2CH3), 14.7 (CH3), 14.6 (OCH2CH3); ESI-MS: 381.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C20H22O6 (358.39): C, 67.03; H, 6.19%; found: C, 66.90; H, 6.27%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2); mp 125–127 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −40 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.56 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.21–7.15 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.07–6.98 (m, 3H, COCH = CH, Ar-H), 6.83 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.62 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.58 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.28–4.26 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.16–4.12 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.80–3.73 (m, 4H, OCH3, H-2′), 2.50 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C
2); mp 125–127 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −40 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.56 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.21–7.15 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.07–6.98 (m, 3H, COCH = CH, Ar-H), 6.83 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.62 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.58 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.28–4.26 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.16–4.12 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.80–3.73 (m, 4H, OCH3, H-2′), 2.50 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 159.9 (Ar-C), 159.9 (C-4), 150.0 (C-1), 143.5 (COCH = CH), 136.0, 129.9, 123.9 (Ar-C), 122.2 (C-2), 121.0 (COCH = CH), 116.2, 113.4 (Ar-C), 109.1 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.1 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 55.2 (OCH3), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 367.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C19H20O6 (344.36): C, 66.27; H, 5.85%; found: C, 66.10; H, 5.99%.
O), 159.9 (Ar-C), 159.9 (C-4), 150.0 (C-1), 143.5 (COCH = CH), 136.0, 129.9, 123.9 (Ar-C), 122.2 (C-2), 121.0 (COCH = CH), 116.2, 113.4 (Ar-C), 109.1 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.1 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 55.2 (OCH3), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 367.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C19H20O6 (344.36): C, 66.27; H, 5.85%; found: C, 66.10; H, 5.99%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2); mp 155–157 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −16 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.12 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.69 (dd, 1H, J = 2.0, 7.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.44 (dd, 1H, J = 1.0, 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.34–7.24 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.16 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.74 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.71 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.45–4.39 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.30–4.27 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.92 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.65 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 186.2 (C
2); mp 155–157 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −16 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.12 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.69 (dd, 1H, J = 2.0, 7.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.44 (dd, 1H, J = 1.0, 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.34–7.24 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.16 (d, 1H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.74 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.71 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.45–4.39 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.30–4.27 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.92 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.65 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 186.2 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 160.3 (C-4), 149.9 (C-1), 139.3 (COCH = CH), 135.5, 133.1, 131.1, 130.3, 127.7, 127.0 (Ar-C), 126.4 (COCH = CH), 122.1 (C-2), 109.1 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.3 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 371.0 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C18H17ClO5 (348.78): C, 61.99; H, 4.91%; found: C, 61.82; H, 5.05%.
O), 160.3 (C-4), 149.9 (C-1), 139.3 (COCH = CH), 135.5, 133.1, 131.1, 130.3, 127.7, 127.0 (Ar-C), 126.4 (COCH = CH), 122.1 (C-2), 109.1 (C-3), 77.2 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.3 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 371.0 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C18H17ClO5 (348.78): C, 61.99; H, 4.91%; found: C, 61.82; H, 5.05%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2); mp 121–123 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −18 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.61–7.39 (m, 5H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH, Ar-H), 7.13 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.64 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.59 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.31–4.27 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.18–4.15 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.81 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 9.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.54 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.0 (C
2); mp 121–123 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −18 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.61–7.39 (m, 5H, J = 16.0 Hz, COCH = CH, Ar-H), 7.13 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.64 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.59 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.31–4.27 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.18–4.15 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.81 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 9.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.54 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.0 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 160.3 (C-4), 150.2 (C-1), 141.4 (COCH = CH), 138.1, 128.4, 126.9, 125.8 (Ar-C), 125.8 (COCH = CH), 122.2 (C-2), 108.9 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 405.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C19H17F3O5 (382.33): C, 59.69; H, 4.48%; found: C, 59.58; H, 4.60%.
O), 160.3 (C-4), 150.2 (C-1), 141.4 (COCH = CH), 138.1, 128.4, 126.9, 125.8 (Ar-C), 125.8 (COCH = CH), 122.2 (C-2), 108.9 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 405.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C19H17F3O5 (382.33): C, 59.69; H, 4.48%; found: C, 59.58; H, 4.60%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2); mp 167–169 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −29 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.35 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.12 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.76 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.61 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.50 (t, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz each, Ar-H), 7.19 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.67 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.60 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.31–4.28 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.18–4.15 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.82 (dd, 1H, J = 2.5, 10.5 Hz, H-2′), 2.54 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 184.6 (C
2); mp 167–169 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −29 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.35 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.12 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.76 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.61 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.50 (t, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz each, Ar-H), 7.19 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.67 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.60 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.31–4.28 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.18–4.15 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.82 (dd, 1H, J = 2.5, 10.5 Hz, H-2′), 2.54 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 184.6 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 160.6 (C-4), 150.3 (C-1), 148.7 (Ar-C), 140.2 (COCH = CH), 136.5, 134.3, 129.9, 126.2, 124.5 (Ar-C), 122.2 (COCH = CH), 122.0 (C-2), 108.8 (C-3), 77.0 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 382.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C18H17NO7 (359.33): C, 60.17; H, 4.77%; found: C, 60.05; H, 4.95%.
O), 160.6 (C-4), 150.3 (C-1), 148.7 (Ar-C), 140.2 (COCH = CH), 136.5, 134.3, 129.9, 126.2, 124.5 (Ar-C), 122.2 (COCH = CH), 122.0 (C-2), 108.8 (C-3), 77.0 (C-1′), 74.8 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.0 (C-2′), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 382.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C18H17NO7 (359.33): C, 60.17; H, 4.77%; found: C, 60.05; H, 4.95%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2); mp 98–100 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −21 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.59 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.46–7.12 (m, 5H, Ar-H), 7.15–7.12 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 6.91 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.86 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.66 (s, 1H, H-4), 5.16 (br s, 2H, PhCH2), 4.67 (d, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.37–4.35 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.25–4.23 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.90–3.88 (m, 4H, H-2′, OCH3), 2.58 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C
2); mp 98–100 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −21 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.59 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.46–7.12 (m, 5H, Ar-H), 7.15–7.12 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 6.91 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.86 (d, 2H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.66 (s, 1H, H-4), 5.16 (br s, 2H, PhCH2), 4.67 (d, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.37–4.35 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.25–4.23 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.90–3.88 (m, 4H, H-2′, OCH3), 2.58 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 159.6 (C-4), 152.1 (C-1), 150.0, 148.3 (Ar-C), 143.2 (COCH = CH), 136.7, 128.6, 128.0, 127.5, 127.3, (Ar-C), 123.3 (COCH = CH), 122.4 (Ar-C), 121.5 (C-2), 113.1, 111.5 (Ar-C), 109.1 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.2 (PhCH2), 71.0 (C-2′), 55.9 (OCH3), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 473.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C26H26O7 (450.48): C, 69.32; H, 5.82%; found: C, 69.18; H, 6.00%.
O), 159.6 (C-4), 152.1 (C-1), 150.0, 148.3 (Ar-C), 143.2 (COCH = CH), 136.7, 128.6, 128.0, 127.5, 127.3, (Ar-C), 123.3 (COCH = CH), 122.4 (Ar-C), 121.5 (C-2), 113.1, 111.5 (Ar-C), 109.1 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′), 74.7 (C-3′), 73.2 (C-4′), 71.2 (PhCH2), 71.0 (C-2′), 55.9 (OCH3), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 473.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C26H26O7 (450.48): C, 69.32; H, 5.82%; found: C, 69.18; H, 6.00%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); mp 113–115 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −68 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.57 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.36 (dd, 1H, J = 1.5, 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.99 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.86 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.73 (t, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz each, Ar-H), 7.39 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.88 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.64–5.58 (m, 2H, H-3′, H-2′), 5.03 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.51 (dd, 1H, J = 5.0, 10.5 Hz, H-4′a), 4.09 (dd, 1H, J = 3.5, 10.5 Hz, H-4′b), 2.79 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.24, 2.22 (2 s, 6H, CH3CO); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 184.3 (C
1); mp 113–115 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D −68 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.57 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.36 (dd, 1H, J = 1.5, 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.99 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.86 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.73 (t, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz each, Ar-H), 7.39 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.88 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.64–5.58 (m, 2H, H-3′, H-2′), 5.03 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.51 (dd, 1H, J = 5.0, 10.5 Hz, H-4′a), 4.09 (dd, 1H, J = 3.5, 10.5 Hz, H-4′b), 2.79 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.24, 2.22 (2 s, 6H, CH3CO); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 184.3 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 169.7, 169.5 (CH3CO), 160.9 (C-4), 148.8 (C-1), 148.7 (Ar-C), 140.2 (COCH = CH), 136.6, 134.1, 129.9, 126.2, 124.5 (Ar-C), 122.2 (COCH = CH), 122.0 (C-2), 109.2 (C-3), 74.9 (C-1′), 73.7 (C-3′), 71.2 (C-2′), 70.7 (C-4′), 20.6, 20.5 (CH3CO), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 466.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C22H21NO9 (443.40): C, 59.59; H, 4.77%; found: C, 59.47; H, 4.88%.
O), 169.7, 169.5 (CH3CO), 160.9 (C-4), 148.8 (C-1), 148.7 (Ar-C), 140.2 (COCH = CH), 136.6, 134.1, 129.9, 126.2, 124.5 (Ar-C), 122.2 (COCH = CH), 122.0 (C-2), 109.2 (C-3), 74.9 (C-1′), 73.7 (C-3′), 71.2 (C-2′), 70.7 (C-4′), 20.6, 20.5 (CH3CO), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 466.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C22H21NO9 (443.40): C, 59.59; H, 4.77%; found: C, 59.47; H, 4.88%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); [α]25D −20 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.73 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.58 (d, 2H, J = 7.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.51 (t, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz each, Ar-H), 7.44 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.30 (dd, 1H, J = 1.5, 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.24 (d, 1H, J = 1.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.04 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.01 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.81 (s, 1H, H-4), 5.63–5.58 (m, 2H, H-2′, H-3′), 5.30 (brs, 2H, PhCH2), 5.02 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.50 (dd, 1H, J = 5.0, 10.0 Hz, H-4′), 4.08 (dd, 1H, J = 3.5, 10.0 Hz, H-4′), 4.04 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.74 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.24, 2.19 (2 s, 6H, CH3CO); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.4 (C
1); [α]25D −20 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.73 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.58 (d, 2H, J = 7.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.51 (t, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz each, Ar-H), 7.44 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.30 (dd, 1H, J = 1.5, 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.24 (d, 1H, J = 1.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.04 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.01 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.81 (s, 1H, H-4), 5.63–5.58 (m, 2H, H-2′, H-3′), 5.30 (brs, 2H, PhCH2), 5.02 (d, 1H, J = 6.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.50 (dd, 1H, J = 5.0, 10.0 Hz, H-4′), 4.08 (dd, 1H, J = 3.5, 10.0 Hz, H-4′), 4.04 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.74 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.24, 2.19 (2 s, 6H, CH3CO); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.4 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 169.7, 169.5 (2C, CH3CO), 159.8 (C-4), 152.2 (C-1), 148.3 (Ar-C), 143.2 (COCH = CH), 136.7, 128.6, 128.0, 127.6, 127.3, (Ar-C), 123.4 (COCH = CH), 122.5 (C-2), 121.6, 113.1, 111.5 (Ar-C), 109.5 (C-3), 74.9 (C-1′), 73.7 (C-2′), 71.3 (C-3′), 71.1 (C-4′), 70.7 (PhCH2), 55.9 (OCH3), 20.6, 20.5 (2C, CH3CO), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 557.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C30H30O9 (534.55): C, 67.41; H, 5.66%; found: C, 67.30; H, 5.80%.
O), 169.7, 169.5 (2C, CH3CO), 159.8 (C-4), 152.2 (C-1), 148.3 (Ar-C), 143.2 (COCH = CH), 136.7, 128.6, 128.0, 127.6, 127.3, (Ar-C), 123.4 (COCH = CH), 122.5 (C-2), 121.6, 113.1, 111.5 (Ar-C), 109.5 (C-3), 74.9 (C-1′), 73.7 (C-2′), 71.3 (C-3′), 71.1 (C-4′), 70.7 (PhCH2), 55.9 (OCH3), 20.6, 20.5 (2C, CH3CO), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 557.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C30H30O9 (534.55): C, 67.41; H, 5.66%; found: C, 67.30; H, 5.80%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3); mp 123–125 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D +17 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.46 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.25 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.89 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.76 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.62 (t, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz each, Ar-H), 7.32 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.87 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.15 (d, 1H, J = 3.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.50 (brs, 1H, H-2′), 4.42–4.38 (m, 1H, H-4′a), 4.26 (brs, 1H, H-4′b), 3.87 (d, 1H, J = 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.67 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 184.7 (C
3); mp 123–125 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D +17 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.46 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.25 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.89 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.76 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.62 (t, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz each, Ar-H), 7.32 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.87 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.15 (d, 1H, J = 3.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.50 (brs, 1H, H-2′), 4.42–4.38 (m, 1H, H-4′a), 4.26 (brs, 1H, H-4′b), 3.87 (d, 1H, J = 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 2.67 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 184.7 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 160.5 (C-4), 148.7 (C-1), 148.4 (Ar-C), 140.3 (COCH = CH), 136.5, 134.2, 123.0, 126.3, 124.6 (Ar-C), 122.3 (COCH = CH), 122.1 (C-2), 109.2 (C-3), 78.0 (C-1′), 77.2 (C-2′), 76.8 (C-3′), 73.9 (C-4′), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 382.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C18H17NO7 (359.33): C, 60.17; H, 4.77%; found: C, 60.05; H, 4.95%.
O), 160.5 (C-4), 148.7 (C-1), 148.4 (Ar-C), 140.3 (COCH = CH), 136.5, 134.2, 123.0, 126.3, 124.6 (Ar-C), 122.3 (COCH = CH), 122.1 (C-2), 109.2 (C-3), 78.0 (C-1′), 77.2 (C-2′), 76.8 (C-3′), 73.9 (C-4′), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 382.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C18H17NO7 (359.33): C, 60.17; H, 4.77%; found: C, 60.05; H, 4.95%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); mp 131–133 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D +12 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.70 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.59–7.41 (m, 5H, Ar-H), 7.27 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.23 (d, 1H, J = 1.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.05 (d, 1H, J = 15.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.98 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.78 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.28 (brs, 2H, PhCH2), 4.78 (d, 1H, J = 4.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.50–4.46 (m, 2H, H-3′, H-2′), 4.23 (dd, 1H, J = 4.5, 10.0 Hz, H-4′b), 4.10 (dd, 1H, J = 2.5, 10.0 Hz, H-4′a), 4.02 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.71 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.6 (C
1); mp 131–133 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D +12 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.70 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.59–7.41 (m, 5H, Ar-H), 7.27 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.23 (d, 1H, J = 1.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.05 (d, 1H, J = 15.0 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.98 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.78 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.28 (brs, 2H, PhCH2), 4.78 (d, 1H, J = 4.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.50–4.46 (m, 2H, H-3′, H-2′), 4.23 (dd, 1H, J = 4.5, 10.0 Hz, H-4′b), 4.10 (dd, 1H, J = 2.5, 10.0 Hz, H-4′a), 4.02 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.71 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.6 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 159.4 (C-4), 152.1 (C-1), 148.3 (Ar-C), 143.6 (COCH = CH), 136.7, 128.6, 128.0, 127.3 (Ar-C), 123.6 (COCH = CH), 122.5 (C-2), 121.5, 113.1, 113.0, 111.5, 109.5 (Ar-C), 108.5 (C-3), 81.2 (C-1′), 80.1 (C-2′), 78.2 (C-3′), 73.5 (C-4′), 71.2 (PhCH2), 55.9 (OCH3), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 473.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C26H26O7 (450.48): C, 69.32; H, 5.82%; found: C, 69.20; H, 5.95%.
O), 159.4 (C-4), 152.1 (C-1), 148.3 (Ar-C), 143.6 (COCH = CH), 136.7, 128.6, 128.0, 127.3 (Ar-C), 123.6 (COCH = CH), 122.5 (C-2), 121.5, 113.1, 113.0, 111.5, 109.5 (Ar-C), 108.5 (C-3), 81.2 (C-1′), 80.1 (C-2′), 78.2 (C-3′), 73.5 (C-4′), 71.2 (PhCH2), 55.9 (OCH3), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 473.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C26H26O7 (450.48): C, 69.32; H, 5.82%; found: C, 69.20; H, 5.95%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); [α]25D +26 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.58 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.57 (dd, 1H, J = 1.0, 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.99 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.87 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.73 (t, 1H, J = 7.5, 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.40 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.90 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.57 (d, 1H, J = 3.0 Hz, H-2′), 5.36–5.34 (m, 1H, H-3′), 4.91 (d, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.33 (dd, 1H, J = 5.0, 10.5 Hz, H-4′a), 4.20 (dd, 1H, J = 2.0, 11.5 Hz, H-4′b), 2.77 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.24, 2.23 (2 s, 6H, CH3CO); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 184.7 (C
1); [α]25D +26 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.58 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.57 (dd, 1H, J = 1.0, 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.99 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.87 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.73 (t, 1H, J = 7.5, 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.40 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.90 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.57 (d, 1H, J = 3.0 Hz, H-2′), 5.36–5.34 (m, 1H, H-3′), 4.91 (d, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.33 (dd, 1H, J = 5.0, 10.5 Hz, H-4′a), 4.20 (dd, 1H, J = 2.0, 11.5 Hz, H-4′b), 2.77 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.24, 2.23 (2 s, 6H, CH3CO); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 184.7 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 158.7 (C-4), 149.8 (C-1), 140.2 (COCH = CH), 136.8, 134.2, 129.9, 126.3, 124.5 (Ar-C), 122.2 (COCH = CH), 122.0 (C-2), 109.2 (C-3), 108.7 (Ar-C), 79.7 (C-1′), 78.4 (C-2′), 77.9 (C-3′), 72.0 (C-4′), 20.8, 20.5 (2C, CH3CO), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 466.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C22H21NO9 (443.40): C, 59.59; H, 4.77%; found: C, 59.45; H, 4.90%.
O), 158.7 (C-4), 149.8 (C-1), 140.2 (COCH = CH), 136.8, 134.2, 129.9, 126.3, 124.5 (Ar-C), 122.2 (COCH = CH), 122.0 (C-2), 109.2 (C-3), 108.7 (Ar-C), 79.7 (C-1′), 78.4 (C-2′), 77.9 (C-3′), 72.0 (C-4′), 20.8, 20.5 (2C, CH3CO), 14.7 (CH3); ESI-MS: 466.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C22H21NO9 (443.40): C, 59.59; H, 4.77%; found: C, 59.45; H, 4.90%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3); [α]25D +29 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.73 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.58–7.23 (m, 7H, Ar-H), 7.05 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.01 (d, 1H, J = 2.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.99 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.58 (d, 1H, J = 3.0 Hz, H-2′), 5.34 (dd, 1H, J = 2.5, 4.5 Hz, H-3′), 5.29 (brs, 2H, PhCH2), 4.91 (d, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.32 (dd, 1H, J = 5.0, 10.5 Hz, H-4′a), 4.18 (dd, 1H, J = 2.0, 12.5 Hz, H-4′b), 4.05 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.72 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.23, 2.20 (2 s, 6H, CH3CO); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.2 (C
3); [α]25D +29 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.73 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.58–7.23 (m, 7H, Ar-H), 7.05 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.01 (d, 1H, J = 2.0 Hz, Ar-H), 6.99 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.58 (d, 1H, J = 3.0 Hz, H-2′), 5.34 (dd, 1H, J = 2.5, 4.5 Hz, H-3′), 5.29 (brs, 2H, PhCH2), 4.91 (d, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.32 (dd, 1H, J = 5.0, 10.5 Hz, H-4′a), 4.18 (dd, 1H, J = 2.0, 12.5 Hz, H-4′b), 4.05 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.72 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.23, 2.20 (2 s, 6H, CH3CO); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.2 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 170.0, 169.5 (CH3CO), 159.5 (C-4), 152.0 (C-1), 148.3, 147.1 (Ar-C), 143.3 (COCH = CH), 136.8, 128.6, 128.0, 127.6, 127.3 (Ar-C), 123.4 (COCH = CH), 122.5 (C-2), 121.6, 113.2, 111.5 (Ar-C), 109.0 (C-3), 79.7 (C-1′), 78.3 (C-2′), 77.9 (C-3′), 72.0 (C-4′), 71.2 (PhCH2), 55.9 (OCH3), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 557.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C30H30O9 (534.55): C, 67.41; H, 5.66%; found: C, 67.31; H, 5.70%.
O), 170.0, 169.5 (CH3CO), 159.5 (C-4), 152.0 (C-1), 148.3, 147.1 (Ar-C), 143.3 (COCH = CH), 136.8, 128.6, 128.0, 127.6, 127.3 (Ar-C), 123.4 (COCH = CH), 122.5 (C-2), 121.6, 113.2, 111.5 (Ar-C), 109.0 (C-3), 79.7 (C-1′), 78.3 (C-2′), 77.9 (C-3′), 72.0 (C-4′), 71.2 (PhCH2), 55.9 (OCH3), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 557.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C30H30O9 (534.55): C, 67.41; H, 5.66%; found: C, 67.31; H, 5.70%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3); mp 99–101 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D +13 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.70 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.56 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.49 (t, 2H, J = 8.0, 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.41 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.27 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.22 (d, 1H, J = 2.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.03 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.97 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.80 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.27 (brs, 2H, PhCH2), 4.83 (d, 1H, J = 5.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.12 (m, 1H, H-2′), 4.02 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.88 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 12.5 Hz, H-3′a), 3.76 (dd, 1H, J = 5.5, 12.5 Hz, H-3′b), 2.69 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C
3); mp 99–101 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D +13 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.70 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.56 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.49 (t, 2H, J = 8.0, 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.41 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.27 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.22 (d, 1H, J = 2.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.03 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.97 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.80 (s, 1H, H-3), 5.27 (brs, 2H, PhCH2), 4.83 (d, 1H, J = 5.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.12 (m, 1H, H-2′), 4.02 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.88 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 12.5 Hz, H-3′a), 3.76 (dd, 1H, J = 5.5, 12.5 Hz, H-3′b), 2.69 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.7 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 158.9 (C-4), 152.1 (C-1), 151.3, 148.3 (Ar-C), 143.5 (COCH = CH), 136.7, 128.6, 128.0, 127.5, 127.3 (Ar-C), 123.5 (COCH = CH), 122.0 (C-2), 121.5, 113.1, 111.5 (Ar-C), 108.1 (C-3), 72.9 (C-1′), 71.2 (PhCH2), 68.3 (C-2′), 63.5 (C-3′), 55.9 (OCH3), 14.5 (CH3); ESI-MS: 461.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C25H26O7 (438.47): C, 68.48; H, 5.98%; found: C, 68.30; H, 6.13%.
O), 158.9 (C-4), 152.1 (C-1), 151.3, 148.3 (Ar-C), 143.5 (COCH = CH), 136.7, 128.6, 128.0, 127.5, 127.3 (Ar-C), 123.5 (COCH = CH), 122.0 (C-2), 121.5, 113.1, 111.5 (Ar-C), 108.1 (C-3), 72.9 (C-1′), 71.2 (PhCH2), 68.3 (C-2′), 63.5 (C-3′), 55.9 (OCH3), 14.5 (CH3); ESI-MS: 461.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C25H26O7 (438.47): C, 68.48; H, 5.98%; found: C, 68.30; H, 6.13%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3); mp 94–96 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D +7 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.44 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.22 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.85 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.73 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.58 (t, 1H, J = 8.0, 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.26 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.74 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.72 (d, 1H, J = 5.0 Hz, H-1′), 3.99–3.79 (m, 1H, H-2′), 3.88 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 12.5 Hz, H-3′a), 3.76 (dd, 1H, J = 5.5, 12.5 Hz, H-3′b), 2.68 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.6 (C
3); mp 94–96 °C [EtOH]; [α]25D +7 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.44 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.22 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.85 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.73 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.58 (t, 1H, J = 8.0, 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.26 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.74 (s, 1H, H-3), 4.72 (d, 1H, J = 5.0 Hz, H-1′), 3.99–3.79 (m, 1H, H-2′), 3.88 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 12.5 Hz, H-3′a), 3.76 (dd, 1H, J = 5.5, 12.5 Hz, H-3′b), 2.68 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 185.6 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 158.7 (C-4), 149.8 (C-1), 139.9 (COCH = CH), 135.5, 133.6, 129.6, 126.3, 124.2 (Ar-C), 123.5 (COCH = CH), 122.1 (C-2), 107.5 (C-3), 72.8 (C-1′), 68.4 (C-2′), 63.3 (C-3′), 14.4 (CH3); ESI-MS: 370.26 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C17H17NO7 (347.32): C, 58.79; H, 4.93%; found: C, 58.62; H, 5.10%.
O), 158.7 (C-4), 149.8 (C-1), 139.9 (COCH = CH), 135.5, 133.6, 129.6, 126.3, 124.2 (Ar-C), 123.5 (COCH = CH), 122.1 (C-2), 107.5 (C-3), 72.8 (C-1′), 68.4 (C-2′), 63.3 (C-3′), 14.4 (CH3); ESI-MS: 370.26 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C17H17NO7 (347.32): C, 58.79; H, 4.93%; found: C, 58.62; H, 5.10%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); [α]25D +12 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.73 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.59 (d, 2H, J = 7.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.52 (t, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz each, Ar-H), 7.45 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.30 (dd, 1H, J = 1.5, 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.25 (d, 1H, J = 2.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.02 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.01 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.87 (s, 1H, H-3), 6.15 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, H-1′), 5.70–5.68 (m, 1H, H-2′), 5.31 (brs, 2H, PhCH2), 4.48 (dd, 1H, J = 8.5, 12.5 Hz, H-3′a), 4.05–4.02 (m, 4H, OCH3, H-3′b), 2.74 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.2, 2.18 (2 s, 6H, CH3CO); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 184.9 (C
1); [α]25D +12 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.73 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.59 (d, 2H, J = 7.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.52 (t, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz each, Ar-H), 7.45 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.30 (dd, 1H, J = 1.5, 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.25 (d, 1H, J = 2.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.02 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.01 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz, Ar-H), 6.87 (s, 1H, H-3), 6.15 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, H-1′), 5.70–5.68 (m, 1H, H-2′), 5.31 (brs, 2H, PhCH2), 4.48 (dd, 1H, J = 8.5, 12.5 Hz, H-3′a), 4.05–4.02 (m, 4H, OCH3, H-3′b), 2.74 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.2, 2.18 (2 s, 6H, CH3CO); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 184.9 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 170.1, 169.7, 169.4 (3C, CH3CO), 159.9 (C-4), 152.1 (C-1), 148.4, 146.3 (Ar-C), 143.5 (COCH = CH), 136.8, 128.6, 128.0, 127.3 (Ar-C), 123.5 (COCH = CH), 122.5 (C-2), 121.4, 113.0, 111.5 (Ar-C), 110.6 (C-3), 71.2 (PhCH2), 70.2 (C-1′), 66.4 (C-2′), 62.0 (C-3′), 55.9 (OCH3), 20.8, 20.7, 20.6 (3C, CH3CO), 14.5 (CH3); ESI-MS: 587.2 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C31H32O10 (564.58): C, 65.95; H, 5.71%; found: C, 65.86; H, 5.89%.
O), 170.1, 169.7, 169.4 (3C, CH3CO), 159.9 (C-4), 152.1 (C-1), 148.4, 146.3 (Ar-C), 143.5 (COCH = CH), 136.8, 128.6, 128.0, 127.3 (Ar-C), 123.5 (COCH = CH), 122.5 (C-2), 121.4, 113.0, 111.5 (Ar-C), 110.6 (C-3), 71.2 (PhCH2), 70.2 (C-1′), 66.4 (C-2′), 62.0 (C-3′), 55.9 (OCH3), 20.8, 20.7, 20.6 (3C, CH3CO), 14.5 (CH3); ESI-MS: 587.2 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C31H32O10 (564.58): C, 65.95; H, 5.71%; found: C, 65.86; H, 5.89%.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); [α]25D +11 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.48 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.26 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.89 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.75 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.62 (t, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz each, Ar-H), 7.28 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.85 (s, 1H, H-3), 6.02 (d, 1H, J = 3.5 Hz, H-1′), 5.53–5.50 (m, 1H, H-2′), 4.43 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 12.5 Hz, H-3′a), 3.94 (dd, 1H, J = 5.5, 12.0 Hz, H-3′b), 2.68 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.12, 2.11, 2.09 (3 s, 9H, CH3CO); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 183.8 (C
1); [α]25D +11 (c 1.0, CHCl3); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.48 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.26 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.89 (d, 1H, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.75 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 7.62 (t, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz each, Ar-H), 7.28 (d, 1H, J = 15.5 Hz, COCH = CH), 6.85 (s, 1H, H-3), 6.02 (d, 1H, J = 3.5 Hz, H-1′), 5.53–5.50 (m, 1H, H-2′), 4.43 (dd, 1H, J = 3.0, 12.5 Hz, H-3′a), 3.94 (dd, 1H, J = 5.5, 12.0 Hz, H-3′b), 2.68 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.12, 2.11, 2.09 (3 s, 9H, CH3CO); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ 183.8 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 170.0, 169.8, 169.1 (3C, CH3CO), 160.6 (C-4), 148.7 (C-1), 140.3 (COCH = CH), 136.4, 133.9, 129.7, 127.9, 126.0, 125.5 (Ar-C), 122.2 (COCH = CH), 122.8 (C-2), 110.5 (C-3), 70.1 (C-1′), 66.1 (C-2′), 61.6 (C-3′), 20.7, 20.6, 20.5 (3C, CH3CO), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 496.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C23H23NO10 (473.43): C, 58.35; H, 4.90%; found: C, 58.47; H, 5.10%.
O), 170.0, 169.8, 169.1 (3C, CH3CO), 160.6 (C-4), 148.7 (C-1), 140.3 (COCH = CH), 136.4, 133.9, 129.7, 127.9, 126.0, 125.5 (Ar-C), 122.2 (COCH = CH), 122.8 (C-2), 110.5 (C-3), 70.1 (C-1′), 66.1 (C-2′), 61.6 (C-3′), 20.7, 20.6, 20.5 (3C, CH3CO), 14.6 (CH3); ESI-MS: 496.1 [M + Na]+; anal. calcd for C23H23NO10 (473.43): C, 58.35; H, 4.90%; found: C, 58.47; H, 5.10%.MTT cell proliferation assay
The anti-proliferative effects of the C-glycosyl-3-cinnamoylfuran derivatives (7–34) were assessed by a MTT proliferation assay.26 For this experiment, cells were seeded in triplicate in 96 well plates and incubated overnight. Post incubation cells were treated with compounds at various concentrations (5 μM, 10 μM, 20 μM and 50 μM) for 48 h. After the treatment, 200 μl of MTT solution (0.5 mg ml−1) were added to each well and incubated at 37 °C for 3 h. Subsequently, the MTT media was discarded and purple colored formazan crystals were dissolved using DMSO. The absorbance was measured at 570 nm in a 96 well micro-plate reader (Thermo, Multiskan Go).Clonogenic survival assay
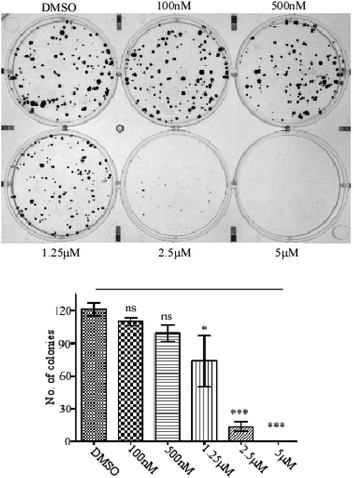
In 6 well plates around 200 MCF-cells were seeded in each of the wells and cells were allowed to attach to the plates for 2 h. Then the cells were treated with different concentrations of compound 24 (0 nM, 100 nM, 500 nM, 1.25 μM, 2.5 μM and 5 μM) for the next 15 days with continuous change of media on every 3rd day with or without compounds. After 15 days the cells were washed with 1X PBS and incubated with 3 ml of a mixture of 3.7% formaldehyde in 1X PBS and 0.5% crystal violet for 30 minutes. The formaldehyde crystal violet mixture was carefully removed by rinsing with tap water and plates were allowed to dry at room temperature. Finally, the image was captured using Gel Doc XR + (Bio-Rad) and colony numbers were counted.Cell cycle arrest assay by propidium iodide staining
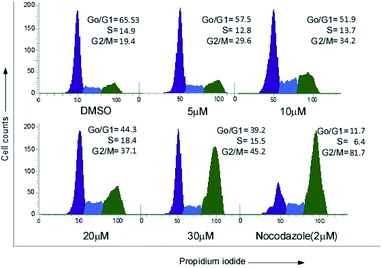
MCF-7 cells were treated with increasing concentrations (0, 5 μM, 10 μM, 20 μM, 30 μM) of compound 24 for 24 h and 2 μM of nocodazole was used as a positive control for G2 arrest. Post treatment cells were converted into single cell suspension and fixed with 75% ethanol overnight at −20 °C. Cells were centrifuged and resuspended in 1X PBS for 2 h followed by RNase A (20 μm) treatment for 2 h at 37 °C. Finally, propidium iodide was added and incubated for 20 minutes at room temperature. Flow cytometric analysis was immediately performed using a FACS Verse instrument (BD).Analysis of apoptosis by annexin V-FITC/PI
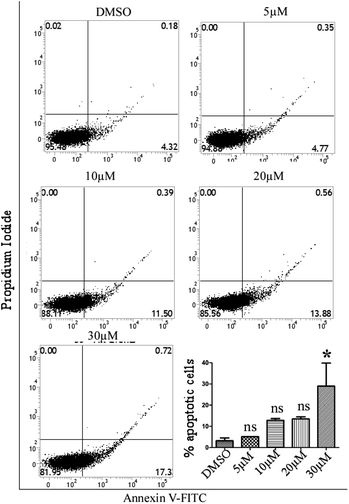
To determine the apoptosis-inducing ability of compound 24 on MCF-7 cells, a double staining method with annexin V-FITC and PI was performed using an assay kit (BD bioscience kit). MCF-7 cells were seeded in a 6 well plate and incubated overnight followed by treatment with various concentrations of compound 24 (5 μM, 10 μM, 20 μM and 30 μM) for 48 h. After treatment, the cells were washed with 1X PBS and resuspended in 100 μl of binding buffer. Finally, cells were incubated with 5 μl of annexin V-FITC and 5 μl of PI for 15 min at room temperature in the dark and flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD Verse FACS machine.Proteome Profiler array
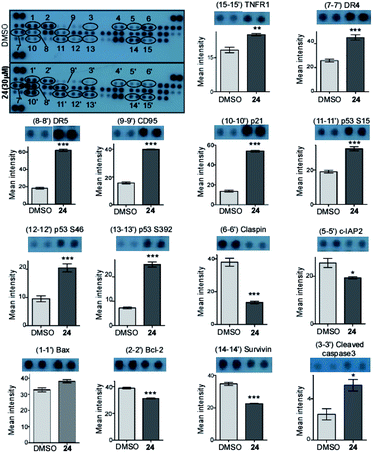
A Human Apoptosis Array Kit from R&D Systems (USA) was used for determining the apoptosis-related proteins following the manufacturer's protocol. Briefly, the cells were treated with compound 24 at 30 μM concentration for 48 h and a DMSO control was kept. 250 μg protein from each sample was incubated overnight with the array. Finally, the data was measured by developing the membrane and then the pixel density was calculated using Image J software. Data are representative of two independent experiments and the bar graph shows mean ± SEM (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns = not significant).Caspase 3 activity assay
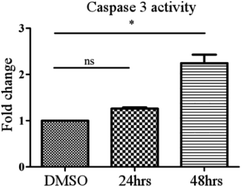
A colorimetric assay following the manufacturer's protocol (Caspase 3 Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (ab39401)) was used to measure the caspase activity. MCF-7 cells were treated with compound 24 at a concentration of 30 μM for 24 h and 48 h. The RIPA buffer method was used to prepare the cell lysates. Each cell lysate was incubated with 50 μl of 2× reaction buffer (containing 10 mM DTT) and 5 μl of the 4 mM DEVD-p-NA substrate (200 μM) and kept at 37 °C for 2 h. The OD was measured at 400 nm in a micro-plate reader and then the graph was plotted.Quantitative structure activity relationship (QSAR) analysis
Based on the experimental results, the molecular structures were compared with the IC50 value to elucidate a quantitative structure-activity relationship. The 3D-QSAR module of the Schrödinger program was used to derive the atom-based analysis. All molecular structures were prepared and minimized using Maestro GUI. The models were processed by categorizing all 28 molecules into a training set and a test set. The model divides the space of grids into uniform-sized cubes that reflect the biological relationship using structural features, corresponding through positive (blue) and negative (red) contours. Characterization of molecules is performed using independent variables for structural components to reflect statistically significant results. Model building was performed using partial least-squares regression (PLS). Detailed methodology and principles are similar to the reports published earlier.39Acknowledgements
D. D., P. P. and A. S. thank Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India for providing Senior Research Fellowships. This work is supported by CSIR, India [Grant No. 02(0237)/15/EMR-II (AKM)] and Bose Institute. Dr Anirban Bhunia, Bose Institute is thankfully acknowledged for valuable discussions regarding QSAR analysis.Notes and references
- T. Vij, Y. Prashar and D. Jain, Int. J. Pharmacol. Res., 2014, 4, 91–102 Search PubMed.
- G. A. Mishra, S. A. Pimple and S. S. Shastri, Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol., 2011, 32, 125–132 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Unger-Saldaña, World J. Clin. Oncol., 2014, 5, 465–477 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. L. Markman, A. Rekechenetskiy, E. Holler and J. Y. Ljubimova, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2013, 65, 1866–1879 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. H. Lee and A. Nan, J. Drug Delivery, 2012, 2012, 915375 Search PubMed.
- N. S. Gavande, P. S. VanderVere-Carozza, H. D. Hinshaw, S. I. Jalal, C. R. Sears, K. S. Pawelczak and J. J. Turchi, Pharmacol. Ther., 2016, 160, 65–83 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Housman, S. Byler, S. Heerboth, K. Lapinska, M. Longacre, N. Snyder and S. Sarkar, Cancers, 2014, 6, 1769–1792 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. L. Demain and P. Vaishnav, Microb. Biotechnol., 2011, 4, 687–699 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Kakizoe, Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol., 2003, 33, 421–442 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. A. El-Sayed, M. M. M. Ramiz and A. A.-H. Abdel-Rahman, Monatsh. Chem., 2008, 139, 1499–1505 CrossRef CAS.
- W. A. El-Sayed, I. F. Nassar and A. A.-H. Abdel-Rahman, Monatsh. Chem., 2009, 140, 365–370 CrossRef CAS.
- M. M. El-Sadek, S. Y. Hassan, N. S. Abdel-Dayem and G. A. Yacout, Molecules, 2012, 17, 7010–7027 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Yan, G.-F. Dai, J.-L. Yang, F.-W. Liu and H.-M. Liu, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2007, 17, 3454–3457 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Bokor, S. Kun, D. Goyard, M. Toth, J.-P. Praly, S. Vidal and L. Somsak, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 1687–1764 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Lalitha, K. Muthusamy, Y. S. Prasad, P. K. Vemula and S. Nagarajan, Carbohydr. Res., 2015, 402, 158–171 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Mugunthan, K. Ramakrishna, D. Sriram, P. Yogeeswari and K. P. R. Kartha, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2011, 21, 3947–3950 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. V. Buchieri, L. E. Riafrecha, O. M. Rodriguez, D. Vullo, H. R. Morbidoni, C. T. Supuran and P. A. Colinas, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2013, 23, 740–743 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. E. Riafrecha, O. M. Rodriguez, D. Vullo, C. T. Supuran and P. A. Colinas, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2014, 22, 5308–5314 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Giguere, S. Andre, M.-A. Bonin, M. A. Bellefleur, A. Provencal, P. Cloutier, B. Pucci, R. Roy and H.-J. Gabius, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2011, 19, 3280–3287 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Giguere, M.-A. Bonin, P. Cloutier, R. Patnam, C. St-Pierre, S. Sato and R. Roy, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2008, 16, 7811–7823 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. S. Bisht, S. Fatima, A. K. Tamrakar, N. Rahuja, N. Jaiswal, A. K. Srivastava and R. P. Tripathi, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2009, 19, 2699–2703 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Roy, D. Dhara, P. K. Parida, R. K. Kar, A. Bhunia, K. Jana, S. P. Sinha Babu and A. K. Misra, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2016, 114, 308–317 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. K. Misra and G. Agnihotri, Carbohydr. Res., 2004, 339, 1381–1387 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. S. Yadav, B. V. S. reddy, M. Sreenivas and G. Sathees, Synthesis, 2007, 1712–1716 CrossRef CAS.
- A. V. Lee, S. Oesterreich and N. E. Davidson, J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 2015, 107, DOI:/10.1093/jnci/djv073.
- J. R. Masters, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2002, 2, 315–319 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Barry, J. E. Reynolds and A. Eastman, Cancer Res., 1993, 53(10), 2349–2357 CAS.
- P. R. Twentyman and M. Luscombe, Br. J. Cancer, 1987, 56, 279–285 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. A. Franken, H. M. Rodermond, J. Haveman and C. van Bree, Nat. Protoc., 2006, 1, 2315–2319 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. J. Vasquez, B. Howell, A. M. Yvon, P. Wadsworth and L. Cassimeris, Mol. Biol. Cell, 1997, 8, 973–985 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Miller, Methods Mol. Med., 2004, 88, 191–202 CAS.
- R. S. Tibbetts, K. M. Brumbaugh, J. M. Williams, J. N. Sarkaria, W. A. Cliby, S. Y. Shieh, Y. Taya, C. Prives and R. T. Abraham, Genes Dev., 1999, 13, 152–157 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Loughery, M. Cox, L. M. Smith and D. W. Meek, Nucleic Acids Res., 2014, 42, 7666–7680 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Feng, M. Hollstein and Y. Xu, Cell Cycle, 2006, 5, 2812–2819 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Oda, H. Arakawa, T. Tanaka, K. Matsuda, C. Tanikawa, T. Mori, H. Nishimori, K. Tamai, T. Tokino, Y. Nakamura and Y. Taya, Cell, 2000, 102, 849–862 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. J. Ullrich, K. Sakaguchi, S. P. Lees-Miller, M. Fiscella, W. E. Mercer, C. W. Anderson and E. Appella, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1993, 90, 5954–5958 CrossRef CAS.
- B. B. Wolf, M. Schuler, F. Echeverri and D. R. Green, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, 274, 30651–30656 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. L. Dixon, A. M. Smondyrev, E. H. Knoll, S. N. Rao, D. E. Shaw and R. A. Friesner, J. Comput.–Aided Mol. Des., 2006, 20, 647–671 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. K. Kar, P. Suryadevara, B. R. Sahoo, G. C. Sahoo, M. R. Dikhit and P. Das, SAR QSAR Environ. Res., 2013, 24, 215–234 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Copies of 1D and 2D NMR spectra of compounds 7–34. See DOI: 10.1039/c7ra04207h |
| ‡ Contributed equally. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 |