Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: Enzyme-triggered compound release using functionalized antimicrobial peptide derivatives
Shin
Mizukami
*a,
Masayoshi
Kashibe
b,
Kengo
Matsumoto
b,
Yuichiro
Hori
bc and
Kazuya
Kikuchi
*bc
aInstitute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University, 2-1-1C Katahira, Aoba-ku, Sendai, Miyagi 980-8577, Japan. E-mail: s-mizu@tagen.tohoku.ac.jp
bDivision of Advanced Science and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University, 2-1 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan. E-mail: kkikuchi@mls.eng.osaka-u.ac.jp
cImmunology Frontier Research Center, Osaka University, 2-1 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan
First published on 13th March 2017
Abstract
Correction for ‘Enzyme-triggered compound release using functionalized antimicrobial peptide derivatives’ by Shin Mizukami et al., Chem. Sci., 2017, DOI: 10.1039/c6sc04435b.
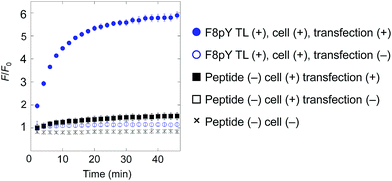
Owing to an oversight the third line of the legend of Fig. 4 “■ Peptide (−), cell (+), transfection (−)” should be corrected as “■ Peptide (−), cell (+), transfection (+)” and the figure with corrected legend is shown below. This error does not change the conclusion of the paper.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 |